Power Line Carrier Communication Explained
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
Power line carrier communication enables data transmission over electrical power lines for grid automation, SCADA telemetry, and protective relaying, using coupling capacitors, line traps, and narrowband modulation to support substation monitoring and smart grid control.
What Is Power Line Carrier Communication?
A narrowband method sending control, protection, and telemetry data over power lines using coupling and line-trap equipment.
✅ Uses coupling capacitors and line traps to inject and isolate signals
✅ Supports SCADA, teleprotection, and substation automation traffic
✅ Typically narrowband FSK/PSK; robust against high-voltage noise
Power line carrier communication (PLCC) is a vital technology for electrical professionals to understand in today's evolving energy landscape. By utilizing existing power lines for data transmission, PLCC offers a cost-effective and reliable communication solution for a wide range of applications within industrial, commercial, and institutional power systems. In transmission engineering contexts, PLCC must account for impedance characteristics of overhead transmission lines to maintain carrier signal integrity across long spans.
Let's explore the evolution of PLCC, its crucial role in smart grids, its advantages compared to alternative communication technologies, the cybersecurity challenges it faces, and its integration with SCADA systems. By understanding these key concepts, we can harness the power of PLCC to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and security of modern power systems. These concepts align closely with the principles outlined in smart grid architectures that emphasize interoperability and resilience.
Power line carrier communication has emerged as a versatile and essential technology in modern industrial, commercial, and institutional power systems. By leveraging existing electrical infrastructure for data transmission, it offers a cost-effective and reliable solution for a wide range of applications. Within utility operations, PLCC complements core power distribution practices by enabling telemetry and control without new cabling.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Overhead T&D Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Overhead T&D Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Evolution of PLCC in Power Distribution
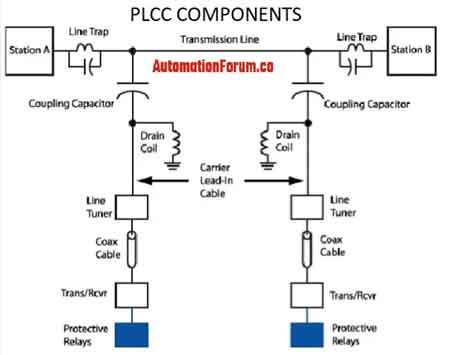
Power line carrier communication has come a long way from its early days of simple signaling and control functions. Initially, it relied on narrowband carrier frequencies transmitted over high voltage power lines. To achieve this, systems employed coupling capacitors, which provide high impedance to power frequency while allowing the passage of higher carrier frequencies. This ensures that the carrier signals do not interfere with the power flow. Furthermore, wave traps, also known as line traps, were installed to prevent the carrier signals from propagating beyond the desired sections of the power line, effectively creating a trap line for the communication signals. These early systems, often employing band pass filtering to further isolate carrier signals, were primarily used for basic communication between substations and protective relaying. However, with the rise of smart grids and advanced automation needs, PLCC has evolved to encompass broadband technologies, enabling higher data rates and supporting a wider range of applications. This evolution has been driven by advancements in signal processing, modulation techniques, and the development of sophisticated PLC terminal equipment. Design considerations also differ from direct current technology where coupling, filtering, and insulation coordination require different approaches.
Applications in Smart Grids
Power line carrier communication plays a crucial role in enabling the functionalities of modern smart grids. By providing a communication backbone for various grid devices, PLCC facilitates real-time monitoring and control of the power system. This includes applications like demand response, where it enables dynamic pricing and load control to optimize energy consumption. Moreover, it supports voltage control by allowing for real-time adjustments to maintain grid stability. It also aids in fault location by providing precise information about the location of disturbances, enabling faster restoration of power supply. PLCC can also coordinate distributed energy resources such as rooftop solar and battery inverters for local balancing and protection schemes.
PLCC vs. Alternative Communication Technologies
While it offers numerous advantages, it's essential to compare it with other communication technologies used in power distribution. Wireless communication, for instance, offers flexibility and ease of deployment but can be susceptible to interference and may have limited range, potentially impacting signal to noise ratio. Fiber optic communication provides high bandwidth and security but can be expensive to install, especially in challenging terrains. Coaxial cable, while offering a balance between cost and performance, may not be as readily available as existing electrical infrastructure. However, coaxial cables play a critical role within systems themselves, as they are often used to connect the equipment to the coupling capacitors, efficiently carrying the high-frequency carrier signals with minimal loss. PLCC, with its cost-effective utilization of existing power lines, often proves to be a compelling choice, particularly for applications requiring wide coverage and reliable communication in industrial settings. At the feeder level, advancements in overhead switchgear complement PLCC by enabling faster sectionalizing and restoration decisions.
Cybersecurity Challenges and Solutions
As power line carrier communication systems become more integrated into critical power infrastructure, ensuring their cybersecurity is paramount. PLCC is vulnerable to cyberattacks that can disrupt operations, compromise data integrity, and even cause widespread power outages. To mitigate these risks, robust security measures are essential. Encryption techniques protect sensitive data transmitted over PLCC channels, while authentication mechanisms prevent unauthorized access to the system. Intrusion detection systems continuously monitor the network for suspicious activity, enabling prompt response to potential threats. By implementing these security solutions, power systems can enhance the resilience of their infrastructure against cyberattacks. As utilities deploy more critical energy storage systems, securing PLCC channels that supervise these assets becomes increasingly important.
Test Your Knowledge About Overhead T&D!
Think you know Overhead T&D? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Integration with SCADA Systems
Power line carrier communication seamlessly integrates with SCADA systems, enhancing their functionality and providing real-time data for grid monitoring and control. SCADA systems rely on communication networks to gather data from remote terminal units (RTUs) and intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) located throughout the power system. It acts as a reliable and efficient communication channel for transmitting this data to the central control center. This real-time information enables operators to monitor grid conditions, detect anomalies, and take corrective actions promptly. The integration with SCADA systems improves situational awareness, facilitates faster response times, and enhances the overall efficiency of power distribution operations. Furthermore, by utilizing PLCC for communication, SCADA systems can leverage the inherent protection offered by devices like protective relays and wave traps, enhancing the overall system reliability.
Leading Questions:
What are the core advantages?
Power line carrier communication leverages existing electrical infrastructure, making it cost-effective. It offers wide coverage, especially in remote areas, and the inherent robustness of power lines ensures reliable communication even in harsh environments.
How does it contribute to smart grids?
PLCC enables essential smart grid features like demand response, voltage control, and fault location, contributing to optimized energy consumption, grid stability, and efficient power restoration.
What are the main challenges?
Signal attenuation and noise over long distances, electromagnetic compatibility issues, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and ensuring interoperability between different PLCC equipment are some of the challenges.
How do narrowband and broadband technologies differ?
Narrowband PLCC typically uses lower carrier frequencies and is suitable for longer distances and applications like SCADA and protection relaying. Broadband PLCC, with its higher data rates, caters to modern applications like smart metering and grid automation.
What are the future trends?
Advanced signal processing techniques, integration with IoT devices, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and applications in electric vehicle charging infrastructure are some of the future trends shaping the evolution of PLCC.