ATPV - Arc Thermal Performance Value
NFPA 70e Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3873 Fact Sheet – Minimum Approach Distance and Training Requirements

- Calculate MAD using voltage and overvoltage values
- Ensure proper communication between host and contract employers
- Meet OSHA training requirements for qualified electrical workers
ATPV, or Arc Thermal Performance Value, measures the arc flash protection of flame-resistant clothing. It indicates the incident energy level with a 50% chance of causing second-degree burns, guiding PPE selection, worker safety, and compliance.
What is ATPV?
ATPV is a rating that indicates the protection level of flame-resistant clothing against arc flash heat exposure.
✅ Defines the energy level at which protective fabric prevents burns
✅ Helps select proper PPE for electrical safety compliance
✅ Guides workplace standards for arc flash hazard protection
Request a Free Training Quotation
How ATPV Determines Arc Rating (cal/cm²)
The arc thermal performance value is a key measurement used to determine arc ratings, expressed in calories per square centimeter (cal/cm²). Arc ratings indicate the level of protection provided by FR clothing. The test method for determining this value is ASTM F1959, and labeling requirements are governed by ASTM F1506. Both NFPA 70E in the U.S. and CSA Z462 in Canada require workers to wear PPE that matches or exceeds the arc incident energy identified in an arc flash risk assessment. Workers should match values to the required arc flash PPE category, ensuring their protective clothing meets or exceeds the calculated incident energy.
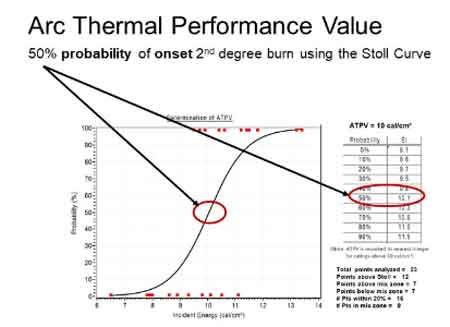
It is based on the Stoll Curve, which considers the onset of second-degree burns. This provides a 50% probability that the wearer will avoid burns in the event of an arc flash. Some materials are more insulative than strong, while others are stronger than insulative—this difference influences how ATPV and EBT values are assigned. Understanding arc flash hazards is essential, since ratings directly measure how flame-resistant clothing protects workers from the heat energy produced during these dangerous electrical events. Compliance with NFPA 70E arc flash requirements links directly to ratings, making them a central factor in both safety programs and regulatory adherence.
Test Your Knowledge About Arc Flash!
Think you know Arc Flash? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
ATPV is determined using a standard test method for assessing the arc rating of materials for clothing, where fabric samples are exposed to electrical arc energy until sufficient heat transfer occurs to cause injury. The value is based solely on the onset of second-degree burns, which is defined as the point at which there is a 50% chance of injury. If fabric breakopen occurs first, this is noted as arc rating EBT instead. Whichever threshold is first reached is reported as the arc rating on the clothing, ensuring workers understand the protective limit of their flame-resistant garments.
Arc Rating & Hazard Categories
Arc rating must align with hazard risk categories (HRC), also called categories (CAT). These are minimum arc rating thresholds for PPE:
-
CAT 1: ≥ 4 cal/cm²
-
CAT 2: ≥ 8 cal/cm²
-
CAT 3: ≥ 25 cal/cm²
-
CAT 4: ≥ 40 cal/cm²
Matching ATPV to the hazard category ensures that workers wear clothing with sufficient arc flash protection for the level of incident energy present. A proper arc flash risk assessment identifies the potential energy exposure, guiding the selection of FR clothing with the correct rating.
.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is ATPV Measured, and What Does the Rating Indicate?
ATPV is measured by exposing FR fabric to varying levels of incident energy in a controlled test environment. The moment when heat transfer reaches the point of second-degree burns is recorded as the arc rating. This value is displayed on clothing labels so workers understand the exact amount of arc flash energy their gear can withstand.
Key Takeaway: Always match PPE arc rating to the incident energy level identified in an arc flash risk assessment.
Comparing ATPV vs EBT in Arc Flash Protection
The key difference between ATPV and EBT (Energy Breakopen Threshold) lies in how they measure fabric performance. ATPV measures the heat transfer through fabric, while EBT measures the point at which the fabric physically breaks open.
Some fabrics break open before transmitting enough heat to burn skin, while others resist breakopen but allow heat transfer sooner. The lower of the two values, ATPV or EBT, is always used as the arc rating.
Important Clarification: ATPV and EBT are fundamentally equivalent—only the first threshold reached is reported as the arc rating, and neither offers superior protection.
| Metric | Definition | What If It’s Lower? |
|---|---|---|
| ATPV | Energy causing 50% chance of a 2nd-degree burn | Becomes Arc Rating if lower |
| EBT | Energy causing 50% chance of fabric breakopen | Becomes Arc Rating if lower |
Selecting the Right ATPV-Rated Clothing
When selecting arc-rated clothing, consider the results of your workplace's hazard risk assessment. The higher the arc incident energy, the higher the requirement.
Factors influencing clothing selection include:
-
Job duties: Different electrical tasks require different protection levels.
-
Exposure time: Longer exposure increases burn risk.
-
Environmental conditions: Weather and climate can significantly impact the performance of FR clothing.
Employers often use an arc flash calculator to determine incident energy levels, which directly dictate the minimum rating required for protective garments.
Factors Affecting ATPV Over Time
The ratings are not permanent. Clothing can degrade, reducing protection:
-
Wear and tear: Abrasion, cuts, or chemical exposure weaken fabric.
-
Cleaning and maintenance: Harsh detergents or improper storage can damage fibres.
-
Light and heat exposure: Sunlight and heat reduce long-term effectiveness.
Key Takeaway: Inspect and replace arc-rated clothing on a regular basis. Degradation reduces protective performance and increases risk.
It is crucial for determining the level of arc flash protection offered by flame-resistant clothing. By understanding the differences between ATPV and EBT, matching clothing to hazard categories, and adhering to standards such as ASTM F1959, ASTM F1506, NFPA 70E, and CSA Z462, workers can ensure they are properly protected.
Understanding how arc ratings work and maintaining PPE over time helps workers stay safe in environments where arc flash hazards are present. NFPA 70E standards require that NFPA 70E arc flash training include instruction on how to interpret ATPV and arc ratings when choosing appropriate PPE.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue








