What Determines the Severity of Injury in Arc Flash
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
NFPA 70e Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4475 Fact Sheet – Being Aware of Arc Flash Hazards

- Identify root causes of arc flash incidents and contributing conditions
- Apply prevention strategies including LOTO, PPE, and testing protocols
- Understand OSHA requirements for training and equipment maintenance
What determines the severity of injury in arc flash? Incident energy depends on fault current, arc duration (clearing time), working distance, voltage, electrode configuration, enclosure effects, and PPE per NFPA 70E and IEEE 1584.
What Determines the Severity of Injury in Arc Flash?
Severity is set by incident energy from fault current, clearing time, distance, voltage, and setup.
✅ Higher fault current increases incident energy and burn severity.
✅ Longer clearing time extends arc duration and heat exposure.
✅ Shorter working distance magnifies energy at the worker.
Determining the Severity of Injury in Arc Flash
The severity of injury in an arc flash depends on incident energy, working distance, and protective device performance. Higher energy exposure and closer proximity increase the risk of burns, trauma, and fatal injuries. For foundational definitions of hazard categories and energy thresholds, the Arc Flash Hazard overview provides context for interpreting severity assessments.
Another crucial factor is the working distance, which is the distance between the worker and the source of the electrical arc. The closer a person is to the arc, the higher the energy exposure, leading to more severe injuries. Properly performing an arc flash analysis can help determine the potential incident energy and establish safe working distances. To understand initiating mechanisms that elevate risk at close range, the causes of arc flash resource explains fault types, equipment conditions, and human factors.
Intensity of an Arc Flash
Several factors, including the electrical system parameters, such as voltage and fault current, influence an arc flash's intensity. The presence of protective devices, like circuit breakers and fuses, also plays a significant role in controlling the intensity by interrupting the fault quickly. For situational examples that tie parameters to real-world events, see when an arc flash is likely to occur for context on operating states and tasks.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Moreover, the condition and maintenance of electrical equipment are critical. Well-maintained equipment is less likely to experience faults that can lead to severe arc flash incidents. An arc flash risk assessment, as outlined in NFPA 70E, helps identify and mitigate potential hazards within an electrical system. For a structured approach to evaluating those conditions, the arc flash risk assessment guide details data collection, modeling, and control selection.
Biggest Factor Contributing to Severity
The incident energy level is the biggest factor contributing to the severity of an arc flash. Higher levels of incident energy result in more intense arcs, leading to severe burns and other injuries. Effective electrical safety programs, including regular maintenance and proper use of protective devices, can help manage and reduce incident energy levels. Practical mitigation tactics in the arc flash protection guide cover engineering controls, labeling strategies, and PPE integration.
Factors in Arc Flash Risk Assessment
An arc flash risk assessment involves evaluating three main factors:
-
Incident Energy: Calculating the potential energy release to determine appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements and safe work practices.
-
Working Distance: Establishing safe boundaries to minimize exposure to high-energy arcs. The arc flash boundary is a critical parameter in defining safe working zones.
-
Protective Devices: Ensuring that circuit breakers, fuses, and other protective devices are properly rated and maintained to interrupt faults and reduce the duration of an arc quickly.
Importance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential in protecting workers from the hazards of an electrical arc. The appropriate arc flash PPE category must be selected based on the incident energy levels identified during the risk assessment. Proper PPE, including flame-resistant clothing, face shields, and gloves, can significantly reduce the severity of injuries.
EF Partner Media
 Bushing Monitoring: What's the Difference Between Sum of Currents and Voltage Reference
Article
Bushing Monitoring: What's the Difference Between Sum of Currents and Voltage Reference
Article
 Power Transformer Market Research Report 2019 Predicts Global Power Transformer Market of $34 Billion by 2023
Catalog
Power Transformer Market Research Report 2019 Predicts Global Power Transformer Market of $34 Billion by 2023
Catalog
 Python® Cable Accessories Extruded Dielectric Cable 69kV-500kV Rating
Product
Python® Cable Accessories Extruded Dielectric Cable 69kV-500kV Rating
Product
 AreaMax LED Street & Area Light
AreaMax LED Street & Area Light
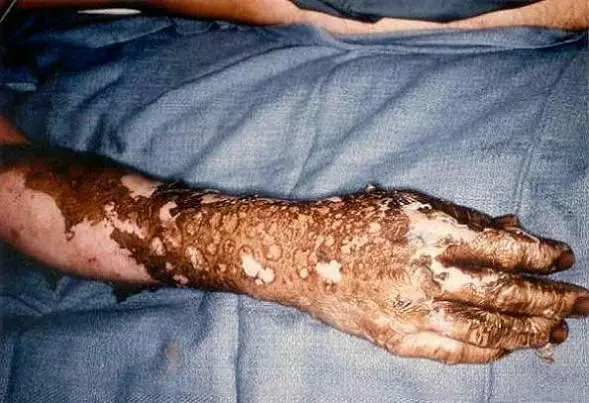
For evidence on injury patterns and treatment considerations, the arc flash injuries reference summarizes burn types, trauma mechanisms, and recovery implications.
Several key factors, including incident energy, working distance, and the condition of electrical equipment, determine the severity of injuries in an arc flash incident. Performing a thorough arc flash analysis and risk assessment guided by NFPA 70E is essential in identifying and mitigating these risks. Understanding the factors that influence the intensity and severity of an arc flash and implementing proper electrical safety measures and PPE can significantly reduce the risks associated with arc flash incidents.
This article has highlighted the critical elements determining the severity of injuries in an arc flash and the importance of comprehensive risk assessments and appropriate safety measures. By focusing on these areas, we can enhance the safety of electrical systems and protect workers from the severe consequences of arc flash incidents. Real-world perspectives from the arc flash victim profiles can reinforce training and hazard awareness across teams.
Related Resources




