How to Read Nominal Voltage: Electrical System Engineering
Arc Flash Analysis/Study
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.
- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
Learn how to read nominal voltage by checking the standard voltage listed on the equipment's nameplate or datasheet. This value helps ensure electrical compatibility, proper performance, and safety when matching devices to power systems.
How to read nominal voltage?
Reading nominal voltage means identifying the standard voltage for which a device or system is designed to operate.
✅ Check the nameplate or datasheet for voltage ratings
✅ Identify single-phase or three-phase specifications
✅ Match system voltage to prevent overloading or failure
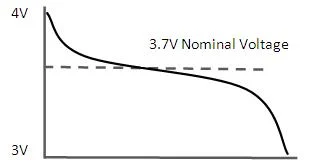
Nominal voltage refers to the designated electrical level at which a system or device is designed to operate. This concept is crucial for ensuring that equipment operates correctly and safely within its expected parameters. Whether in residential or industrial setups, reading nominal voltage correctly helps maintain system efficiency and prevent damage. It is a crucial reference for anyone involved in electrical design, maintenance, or troubleshooting.
What Does Nominal Voltage Mean, and How Is It Different from Actual Levels?
Nominal voltage is the standardized level assigned to an electrical system. It serves as a benchmark for the expected operating level, though actual levels may fluctuate slightly. For instance, in most homes, the nominal value is 120V, but the real-time measurement may be slightly higher or lower due to system load.
The actual level can be measured using a voltmeter, but it may not always match the nominal value exactly. As long as the variation stays within a safe range, equipment can operate efficiently. Major deviations, however, may indicate systemic problems that require attention.
How Do I Determine the Nominal Voltage of an Electrical System?
To find the nominal value, check the labels on devices, transformers, or electrical panels. Manufacturers typically indicate this information near input terminals. For larger systems, it may be documented in design schematics or guidelines outlined by national electrical codes, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC). The nominal value is critical for selecting compatible equipment and maintaining system safety.
Test Your Knowledge About Electrical Engineering!
Think you know Electrical Engineering? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Why Is Nominal Voltage Important in Electrical Design?
Nominal voltage plays a key role in selecting the right components for a system. If a device rated for a lower level is installed in a higher capacity system, it may overheat or fail, posing serious risks. By adhering to the nominal rating, engineers ensure that all components in the system work within a safe range.
Operating at a significantly higher or lower level than the system’s nominal value can result in malfunction or underperformance. Ensuring the correct value minimizes hazards, reduces the likelihood of equipment failure, and maintains overall system stability.
What Is the Difference Between Nominal and Rated Voltage?
While nominal voltage is the expected standard level, rated voltage refers to the maximum that a device or system can handle. For example, a device might have a nominal rating of 240V but could be rated to withstand surges up to 265V. Understanding this difference is crucial when selecting equipment, as it ensures that systems can withstand temporary spikes without damage.
Can Nominal Voltage Vary Over Time or Under Different Conditions?
Yes, nominal values can shift based on various factors, such as load demand or environmental conditions. For example, during times of high demand, actual levels may drop slightly. Conversely, during low demand, they may increase. While minor changes are normal, significant shifts may suggest issues with system components.
Different countries also have varying nominal values. In the United States, most homes use 120V, while other regions, such as Europe, commonly use 230V.
Understanding nominal voltage is fundamental to the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. It acts as a guideline for selecting compatible equipment and helps ensure that systems operate within safe parameters. By correctly reading and interpreting nominal values, you can protect both the equipment and individuals working with electrical systems.








