Compliance Voltage
Emergency Generators & Standby Power Systems
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
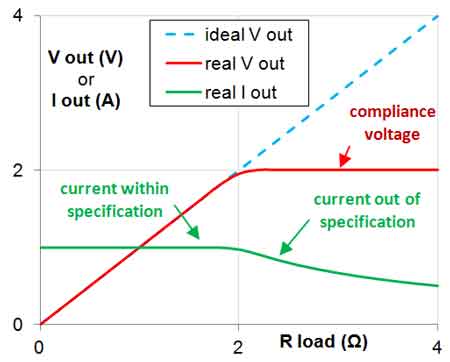
Compliance voltage defines the headroom a current source, op-amp, or transimpedance amplifier has across a load before saturation, ensuring regulated bias for photodiodes, LED drivers, DAC outputs, and sensor interfaces within power supply limits.
What Is Compliance Voltage?
Compliance voltage is the max load voltage a current source can provide while holding the set current without saturation.
✅ Defines max V across load to maintain set current.
✅ Limited by supply rails and driver headroom.
✅ Exceeding it causes saturation and loss of regulation.
Compliance voltage refers to the maximum allowable voltage that a power supply can output to maintain constant current within a circuit. This is especially important in systems that rely on constant current power supplies, where the V varies depending on the load. The circuit breaker in such systems helps to protect the components by cutting off power if the voltage exceeds the set compliance limit, ensuring that neither the power supply nor the load is damaged. Properly setting this voltage ensures that the system operates within safe parameters, enhancing its reliability. In specifying these limits, consulting the maximum continuous rating guidelines helps define safe headroom across varying loads.
Compliance voltage is the maximum voltage that can be applied between the counter electrode and the working electrode in an electrical system. It defines the limit for the output voltage to ensure that the system operates safely without exceeding the capacity of the components involved. By controlling the applied voltage between these electrodes, the system can maintain proper functioning and avoid overloading or damaging the sensitive parts of the circuit. In systems fed by a DC generator, the source characteristics influence the achievable compliance voltage range.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Generators/UPS Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Generators/UPS Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
How does compliance voltage affect the performance of a constant current power supply?
It plays a vital role in the performance of constant current power supplies by ensuring that the system can deliver the desired current regardless of variations in load resistance. If the voltage is set too low, the power supply may not provide enough V to maintain the desired current, resulting in underperformance. On the other hand, if it is set too high, the system might output excessive V, leading to overloading and potential damage. The voltage tester is an essential tool for verifying that the system operates within the correct voltage range. When paired with an uninterruptible power supply, proper compliance voltage preserves current regulation during switchover events.
Determining the Right Compliance Voltage
When selecting a power supply, it's essential to consider the following factors to determine the appropriate compliance voltage: For backup-integrated designs, aligning with UPS ratings ensures the supply and protection gear share compatible voltage envelopes.
Load Requirements: The voltage and current requirements of the devices to be powered will dictate the necessary voltage.
Power Supply Efficiency: A higher voltage may lead to lower efficiency, as the power supply needs to dissipate more power in the form of heat.
System Cost: Higher V power supplies often require more complex circuitry and components, which can increase the overall cost. Selecting high efficiency UPS systems can reduce waste heat and broaden acceptable compliance margins.
What happens if the compliance voltage is too low or too high for the system?
If the compliance voltage is set too low, the system may fail to deliver the necessary current, leading to reduced performance or failure to operate correctly. Conversely, setting the V too high can result in overloading, excessive heat generation, and potential damage to the system. The circuit breaker protects against these risks by shutting down the circuit if the voltage exceeds safe limits. Regular testing with a V tester ensures that the system remains within the appropriate voltage range. These conditions can also exacerbate UPS risks by stressing batteries and transfer components.
How is compliance voltage measured and adjusted in electronic systems?
It is measured using a voltage tester, which helps verify that the system is operating within its designated range. Adjusting the compliance voltage involves selecting the correct settings on your power supply or device, as demonstrated in the Reference 3000 potentiostat example. The system offers different V settings, allowing the user to switch between ±32 V and ±15 V based on the current required. Proper adjustment ensures the power supply provides adequate current without exceeding the maximum voltage limits. During commissioning, many UPS systems specify calibration steps to verify compliance range under load.
Compliance voltage is a critical parameter in maintaining the safety and efficiency of constant current power supplies. By understanding how to measure, set, and adjust this value, you can ensure your electrical systems operate effectively without risk of damage. Utilizing tools like V testers and circuit breakers allows for the proper regulation of voltage, enhancing both the performance and longevity of your electronic devices.