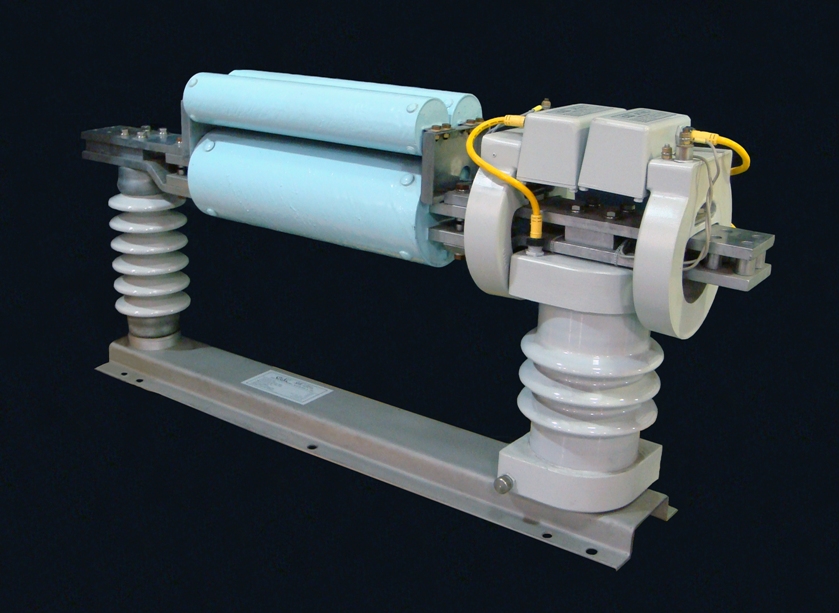
Vacuum Fault Interrupter Explained

Protective Relay Training - Basic
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
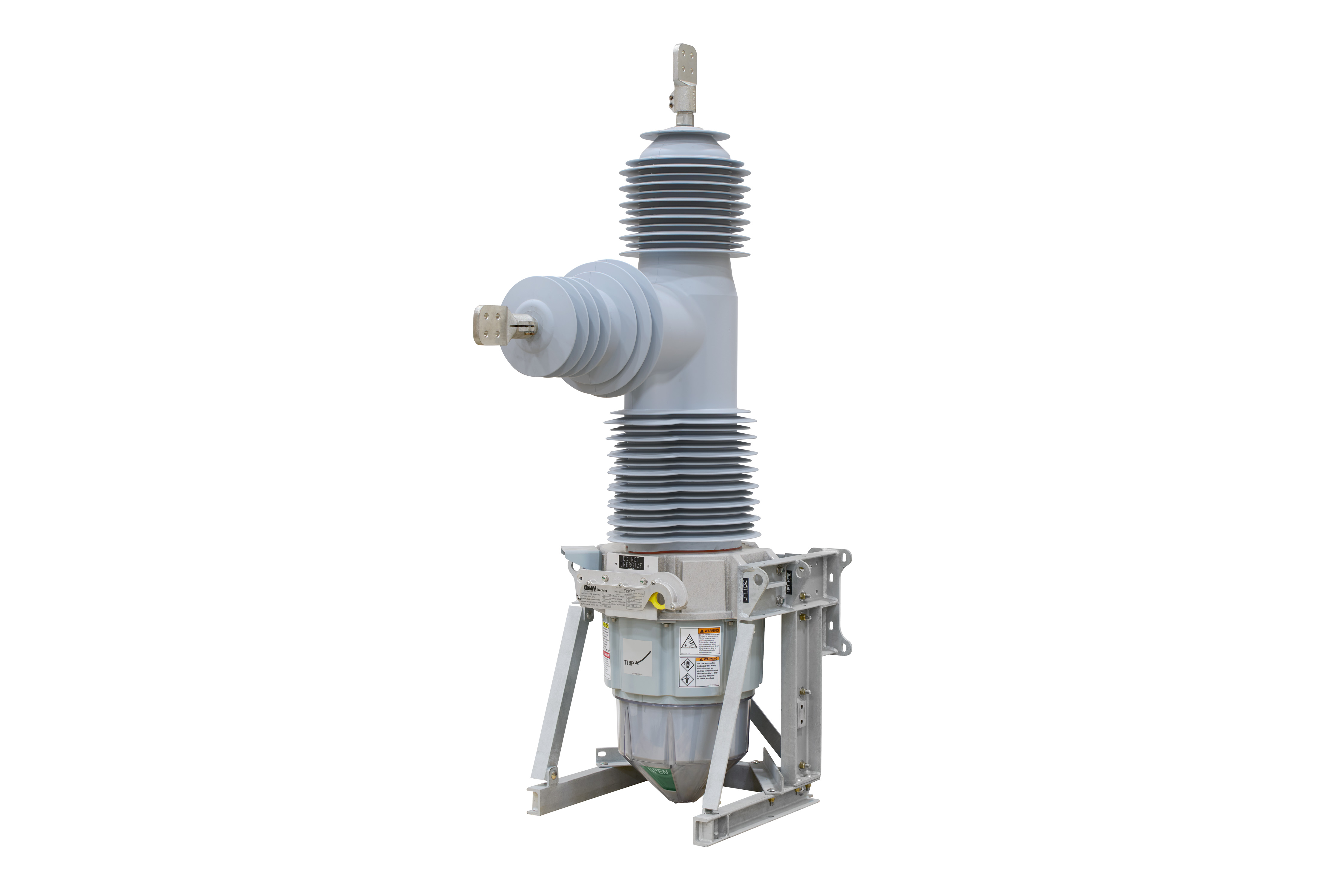
Vacuum fault interrupter delivers medium-voltage circuit protection using vacuum arc quenching, safeguarding distribution networks from faults, overcurrent, and short circuits; integrates with switchgear, protection relays, and SCADA systems for grid reliability and safety.
What Is a Vacuum Fault Interrupter?
A vacuum fault interrupter is an MV device that interrupts fault current with vacuum arc quenching to protect systems.
✅ High interrupting rating for MV distribution networks
✅ Solid-dielectric insulation; minimal maintenance requirements
✅ Integrates with relays, SCADA, and smart grid automation
A Vacuum Fault Interrupter plays a critical role in modern electrical engineering and maintenance by providing a reliable method for protecting power distribution systems from electrical faults. These devices offer superior arc quenching capabilities, ensuring faster response times and reducing the risk of equipment damage and service interruptions. For electrical engineers and maintenance professionals, understanding how vacuum fault interrupters function is essential for optimizing system reliability, enhancing worker safety, and minimizing costly downtime. As power grids evolve to incorporate more renewable energy sources and smart grid technology, the demand for efficient fault interruption solutions continues to grow. For a comprehensive overview of different circuit breakers, including vacuum circuit breakers, read Circuit Breaker Types Explained. For a primer on fundamentals, see what a circuit breaker is and how it underpins protective schemes.
Substation Relay Protection Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
What is a Vacuum Fault Interrupter?
A vacuum fault interrupter (VFI) is a specialized electrical switch designed to interrupt fault currents in medium-voltage power distribution systems rapidly. It utilizes a chamber to extinguish the electric arc generated during the interruption process.
Technology and Innovation
At the heart of the VFI lies the sophisticated technology that makes it so effective in managing power distribution systems. Unlike traditional fault protection devices, this kind uses a sealed chamber to extinguish electrical arcs. This chamber ensures that when contacts open, the absence of air and other gases allows the arc to be quickly and efficiently extinguished. The use of modern materials, such as advanced contact materials with high conductivity and wear resistance, further enhances performance. Recent innovations have introduced nano-engineered materials and optimized arc quenching mechanisms, significantly reducing contact erosion and increasing operational lifespan. These technological advancements establish VFIs as the gold standard for medium voltage protection. When prospective fault levels are high, integrating a fault current limiter can further protect equipment and coordinate interruption duties.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Reliability and Durability
Reliability is paramount in power distribution systems, and VFIs excel in this regard. Their robust design and high-quality materials enable them to withstand the rigors of daily operation. Unlike older technologies, which degrade more rapidly due to arc-induced wear, the circuit design ensures minimal contact erosion. The environment eliminates exposure to oxygen and other reactive gases, thereby reducing the rate of material degradation. Rigorous testing and advanced manufacturing processes ensure that each unit meets stringent performance standards. These factors contribute to the extended lifespan of vacuum interrupters, often requiring minimal maintenance over years of continuous use. This level of reliability makes them indispensable in critical power applications such as hospitals, data centres, and industrial manufacturing facilities. In distribution switchgear, pairing a VFI with a load break switch supports safe manual isolation and flexible operating sequences.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Safety is a key priority in electrical systems, and VFIs offer several safety benefits. Their ability to rapidly contain and extinguish electrical arcs significantly reduces the risk of fire and equipment damage. Since the interrupter’s contacts open within a chamber, arc flash exposure is drastically minimized, ensuring enhanced operator safety. This feature is especially critical in medium voltage applications, where arc flash incidents can have severe consequences. Additionally, vacuum interrupters are environmentally friendly. Unlike devices that use sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), a potent greenhouse gas, vacuum interrupters do not release harmful gases into the atmosphere. By opting for this kind of technology, power operators contribute to sustainability and align with global environmental goals. It is also important to distinguish a arc-fault interrupter used to detect parallel and series arcing in low voltage circuits from VFIs used for medium voltage fault clearing.
Applications and Industries
The versatility of VFIs makes them essential in a wide range of applications. Their presence is crucial in power distribution systems, where they protect substations and feeder circuits from short circuits. Industrial automation relies on them to safeguard critical equipment, while renewable energy systems like wind turbines and solar farms utilize them to ensure smooth power generation. Data centres, which demand uninterrupted power, benefit from the reliability and fast fault-clearing capability of interrupters. Their widespread adoption in diverse industries highlights their adaptability and underscores their role as a critical asset in modern electrical infrastructure.Learn more about how overcurrent protection works and its importance in electrical systems by reading What Is Overcurrent Protection Explained. For building distribution, understanding arc fault circuit interrupter protection helps differentiate residential safety practices from utility and industrial applications.
On overhead feeders, coordination with a fuse cutout can localize faults and speed restoration while limiting outage scope.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
While VFIs are designed for longevity, proper maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance. Regular inspections and diagnostic tests are crucial for identifying early signs of wear or failure. One key maintenance aspect is monitoring the condition of the interrupter’s internal chamber, as any loss of integrity can compromise arc extinguishing performance. Technicians must also inspect the state of the contacts, ensuring they are not pitted or eroded. Common troubleshooting steps include checking for abnormal heating, misalignment of moving parts, and degradation of insulation materials. Early detection and intervention can prevent costly downtime and ensure the uninterrupted operation of power distribution systems. Proper coordination with a substation or feeder auto recloser ensures interruption and reclosing sequences do not overstress vacuum bottles.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Electrical Protection Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Electrical Protection Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
In conclusion, the VFI represents a significant advancement in the field of electrical protection. Through technological innovation, robust reliability, enhanced safety, and environmental consciousness, this device has become indispensable in power distribution and industrial systems. Its applications span industries ranging from renewable energy to critical infrastructure, reinforcing its status as a cornerstone of modern electrical protection. Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and extending service life. As electrical grids continue to evolve, the role of vacuum fault interrupters will only grow, ensuring a future of safer, more reliable, and more sustainable energy systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a Vacuum Interrupter Work?
When a fault occurs, the VFI's contacts open, creating an electric arc. The environment within the chamber rapidly cools and quenches the arc, preventing it from reigniting. This rapid interruption helps to protect electrical equipment and minimize damage.
What is the difference between a vacuum interrupter and a vacuum circuit breaker?
While both VFI and vacuum circuit breakers utilize technology to extinguish electrical arcs, their functions differ. A VFI is a component within a larger protection device, such as a vacuum fault interrupter. It focuses on the act of arc suppression when contacts open. In contrast, a vacuum circuit breaker is a standalone device that provides both interruption and switching capabilities. Circuit breakers can be manually or automatically opened and closed under normal operating conditions, whereas vacuum interrupters are typically engaged only during fault conditions. Delve into the concept of fault currents and their impact on electrical systems in What Is Fault Current - Electricity Explained.
Can a vacuum interrupter be used for isolation?
No, it is not typically used for isolation purposes. Its primary function is to interrupt electrical faults by opening contacts within a chamber. Isolation devices, such as disconnect switches, are specifically designed to create a visible, physical break in the circuit, ensuring that maintenance personnel can safely work on de-energized equipment. While they open contacts during fault conditions, they do not provide the visible separation required for isolation. Discover how auto reclosers function and their role in electrical protection in What Does An Auto Recloser Do? HV Electric Switch Explained.