Cyprus Electricity Interconnectors link the island to the EU grid via EuroAsia and EuroAfrica projects, enabling renewable energy trade, subsea transmission, market liberalization, and stronger energy security and diplomacy across the region.
Key Points
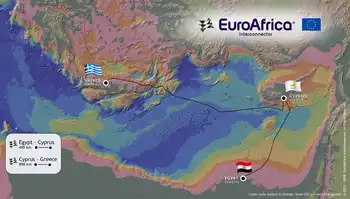
Subsea links connecting Cyprus to Greece, Israel and Egypt for EU grid integration, renewable trade and energy security.
✅ Connects EU, Israel, Egypt via EuroAsia and EuroAfrica
✅ Enables renewables integration and market liberalization
✅ Strengthens energy security, investment, and diplomacy
Electricity interconnectors bridging Cyprus with the broader geographical region, mirroring projects like the Ireland-France grid link already underway in Europe, are crucial for its diplomacy while improving its game to become a clean energy hub.
In an interview with Phileleftheros daily, Andreas Poullikkas, chairman of the Cyprus Energy Regulatory Authority (CERA), said electricity cables such as the EuroAsia Interconnector and the EuroAfrica Interconnector, could turn the island into an energy hub, creating investment opportunities.
“Cyprus, with proper planning, can make the most of its energy potential, turning Cyprus into an electricity producer-state and hub by establishing electrical interconnections, such as the EuroAsia Interconnector and the EuroAfrica Interconnector,” said Poullikkas.
He said these electricity interconnectors, “will enable the island to become a hub for electricity transmission between the European Union, Israel and Egypt, with developments such as the Israel Electric Corporation settlement highlighting regional dynamics, while increasing our energy security”.
Poullikkas argued it will have beneficial consequences in shaping healthy conditions for liberalising the country’s electricity market and economy, facilitating the production of electricity with Renewable Energy Sources and supporting broader efforts like the UK grid transformation toward net zero.
“Electricity interconnections are an excellent opportunity for greater business flexibility in Cyprus, ushering new investment opportunities, as seen with the Lake Erie Connector investment across North America, either in electricity generation or other sectors. Especially at a time when any investment or financial opportunity is welcomed.”
He said Cyprus’ energy resources are a combination of hydrocarbon deposits and renewable energy sources, such as solar.
This combination offers the country a comparative advantage in the energy sector.
Cyprus can take advantage of the development of alternative supply routes of the EU, as more links such as new UK interconnectors come online.
Poullikkas argued that as energy networks are developing rapidly throughout the bloc, serving the ever-increasing needs for electricity, and aligning with the global energy interconnection vision highlighted in recent assessments, the need to connect Cyprus with its wider geographical area is a matter of urgency.
He argues the development of important energy infrastructure, especially electricity interconnections, is an important catalyst in the implementation of Cyprus goals, while recognising how rule changes like Australia's big battery market shift can affect storage strategies.
“It should also be a national political priority, as this will help strengthen diplomatic relations,” added Poullikkas.
Implementing the electricity interconnectors between Israel, Cyprus and Greece through Crete and Attica (EuroAsia Interconnector) has been delayed by two years.
He said the delay was brought about after Greece decided to separate the Crete-Attica section of the interconnection and treat as a national project.
Poullikkas stressed the Greek authorities are committed to ensuring the connection of Cyprus with the electricity market of the EU.
“All the required permits have been obtained from the competent authorities in Cyprus and upon the completion of the procedures with the preferred manufacturers, construction of the Cyprus-Crete electrical interconnection will begin before the end of this year. Based on current data, the entire interconnection is expected to be implemented in 2023”.
“The EuroAfrica Interconnector is in the pre-works stage, all project implementation studies have already been completed and submitted to the competent authorities, including cost and benefit studies”.
EuroAsia Interconnector is a leading EU project of common interest (PCI), also labelled as an “electricity highway” by the European Commission.
It connects the national grids of Israel, Cyprus and Greece, creating a reliable energy bridge between the continents of Asia and Europe allowing bi-directional transmission of electricity.
The cost of the entire subsea cable system, at 1,208km, the longest in the world and the deepest at 3,000m below sea level, is estimated at €2.5 bln.
Construction costs for the first phase of the Egypt-Cyprus interconnection (EuroAfrica) with a Stage 1 transmission capacity of 1,000MW is estimated at €1bln.
The Cyprus-Greece (Crete) interconnection, as well as the Egypt-Cyprus electricity interconnector, will both be commissioned by December 2023.
Related News