Latest Energy Storage Articles
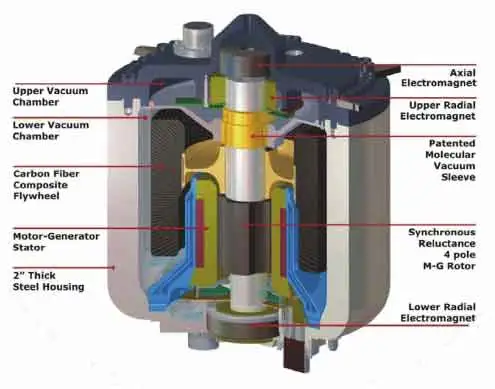
Flywheel Energy Storage vs. Other Technologies
Flywheel energy storage systems store kinetic energy in rotating mass to deliver rapid response, improve grid stability, and support renewable integration with high efficiency, reliability, long cycle life, low environmental impact, and sustainable performance.
What is Flywheel Energy Storage?
Flywheel energy storage (FES) is a mechanical system that stores energy in a rotating mass to deliver electricity quickly and efficiently.
✅ Provides rapid response for grid stability and renewable integration
✅ Offers long cycle life with minimal maintenance needs
✅ Enhances energy efficiency and reduces environmental impact
Flywheel energy storage is a promising technology for energy storage with several advantages over other energy storage technologies. Flywheels are efficient, have a longer lifespan, and can provide fast response times to changes in power demand. In addition, Flywheel systems have numerous applications, including grid stabilization, backup power, and UPS systems. While FES is still in the development and commercialization stage, ongoing research and development are expected to lead to further technological improvements, making it a more competitive option in the global energy mix.
Energy Storage Systems Training
How Does Flywheel Energy Storage Work?
FES works by converting electrical energy into kinetic energy stored in a high-speed rotor. A typical system includes a flywheel rotor made of steel or advanced composites, housed in a vacuum enclosure to minimize air drag. Bearings—mechanical, magnetic, or superconducting—support the rotor and reduce friction. Power electronics connect the flywheel to the grid or local load.
When electricity is supplied, the motor accelerates the rotor, storing energy as rotational kinetic energy. When electricity is required, the generator decelerates the rotor, converting the kinetic energy back into electrical energy. Magnetic and superconducting bearings, along with vacuum containment, help minimize losses and extend operational life.
Energy storage capacity is often measured in watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg), while response speed and round-trip efficiency (typically 70–90%) make flywheels competitive for short-duration, high-power applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the primary advantages of flywheels is their ability to respond almost instantly to fluctuations in power demand. Their long cycle life—often exceeding two decades—makes them sustainable compared to chemical batteries. Flywheels also exhibit minimal degradation over thousands of charge-discharge cycles and support ancillary services like frequency regulation.
However, challenges remain. Frictional and standby losses can reduce stored energy over time, even in vacuum-sealed systems. High rotational speeds demand strong, lightweight rotor materials such as carbon fiber composites, which increase manufacturing costs. Safety containment is crucial for handling potential rotor failure under extreme stress, which adds complexity and cost.
Flywheel Energy Storage Applications
Flywheel systems have been deployed across multiple sectors:
-
Grid Stabilization: Flywheels provide frequency regulation and voltage support, responding to demand spikes in milliseconds. Beacon Power has operated flywheel plants in the U.S. for grid ancillary services.
-
Backup Power and UPS Systems: In data centers, hospitals, and industrial facilities, flywheels serve as reliable, fast-response UPS solutions, reducing reliance on chemical batteries.
-
Transportation and Aerospace: Compact flywheel systems have been tested for buses, trains, and aircraft to recover braking energy and reduce fuel use.
-
Microgrids and Renewables Integration: Flywheels smooth variability from wind and solar power, stabilizing hybrid systems in remote or island grids.
Benchmarking Flywheel vs Other Energy Storage Technologies
| Technology | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life | Response Time | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flywheel | 20–80 | >20 years, >100k | Milliseconds | Grid stability, UPS, short bursts |
| Lithium-ion Battery | 100–250 | 5–15 years | Seconds | EVs, portable electronics, grid storage |
| Supercapacitor | 5–10 | >1M cycles | Milliseconds | Power quality, regenerative braking |
| Pumped Hydro | 0.5–1 | 30–60 years | Minutes | Bulk, long-duration energy storage |
| Compressed Air | 2–6 | 20–40 years | Minutes | Grid-scale long-term storage |
This comparison highlights where flywheels excel: ultra-fast response, long cycle life, and high power density, but lower energy density than batteries or hydro.
Efficiency and Performance
Flywheel systems typically achieve round-trip efficiencies of 70–90%. Losses occur from friction, magnetic drag, and electrical conversion. Unlike chemical batteries, flywheels self-discharge more quickly, making them better suited for short-term storage rather than long-duration energy shifting.
Still, their high power density, fast ramp rate, and low lifecycle cost per cycle make them ideal for applications needing immediate power injection.
Market Outlook and Adoption
The global FES market is expanding, projected to grow from USD 351.94 million in 2025 to USD 564.91 million by 2032, at a CAGR of nearly 7% (Fortune Business Insights).
Leading companies such as Beacon Power, Amber Kinetics, and Temporal Power have demonstrated commercial-scale flywheel projects for grid regulation and UPS. While adoption lags behind batteries, niche markets like microgrids, critical facilities, and renewable integration are driving growth.
Challenges include high upfront costs, rotor safety concerns, and competition from falling battery prices. However, ongoing research is improving rotor materials, reducing friction losses, and lowering costs.
Future Trends and Research Directions
Flywheel development continues to advance with several key innovations:
-
Advanced Bearings: Active magnetic and superconducting bearings reduce friction and extend operational life.
-
Composite Rotors: High-strength carbon fiber improves energy density while reducing rotor mass.
-
Hybrid Systems: Integration with batteries or supercapacitors creates systems that combine high energy and high power.
-
Scalability and Modularization: Modular flywheels for microgrids and distributed energy resources are under active development.
-
Sustainability: Unlike chemical batteries, flywheels contain no toxic materials and are fully recyclable, making them attractive for green infrastructure.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, flywheels face challenges in adoption. High-speed rotation requires costly materials and precision engineering. Safety containment must be robust to prevent catastrophic failure. Standby losses limit long-duration storage applications. Regulatory standards and market structures also influence their competitiveness compared to established technologies, such as lithium-ion.
Addressing these barriers is crucial for the broader adoption of energy storage in global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can a flywheel store energy?
Typically from seconds to several hours, depending on rotor design, size, and bearing technology. They are most efficient for short-duration, high-power applications.
What limits flywheel energy storage?
The strength of the rotor material, frictional losses, and the cost of high-speed composite rotors are the primary limiting factors.
Is flywheel storage better than batteries?
For short-term, high-power needs and frequent cycling, yes. For long-duration storage, batteries are typically more practical.
What is the efficiency of flywheels?
Round-trip efficiency ranges between 70–90%, with losses from bearings, vacuum drag, and electrical conversion.
Where are flywheels used today?
They are deployed in grid stabilization plants, UPS systems for data centers and hospitals, microgrids, and experimental transport systems.
Related Articles
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Energy Storage Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Energy Storage Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
How big is the energy storage market?
How Big Is Energy Storage Market? Global battery storage (BESS) capacity and revenues surge across utility-scale, C&I, and residential segments, driven by lithium-ion, inverters, EMS, renewables integration, and ancillary services, with strong double-digit CAGR.
How Big Is Energy Storage Market?
The energy storage market is increasing as more and more countries, and companies recognize the importance of energy storage for the transition to a clean energy future; according to a recent report by BloombergNEF, the global energy storage market is expected to reach 741 gigawatt-hours (GWh) by 2030, up from just 17 GWh in 2015. Analysts tracking growth in utility-scale energy storage note that deployment pipelines are accelerating worldwide, reflecting the same trend.
The energy storage market is also becoming increasingly diversified, with various technologies and applications being developed and deployed. While lithium-ion batteries are currently the most common form of energy storage, other technologies such as flow batteries, compressed air energy storage, and pumped hydro storage are also being developed and deployed. Emerging chemistries and thermal approaches are also being explored to meet the unique requirements of long-term energy storage across seasonal balancing needs.
For readers new to the topic, what is energy storage is a concise primer on the fundamental concepts and use cases.
In the United States, the energy storage market is also growing rapidly. According to the US Energy Storage Monitor report, the US energy storage market grew by 240% in 2020, with a total of 2,156 megawatt-hours (MWh) of storage capacity installed. As of 2021, the US has an estimated 1,650 MW of storage capacity installed, with states such as California, Texas, and Hawaii leading the way in deployment. For project examples and policy context, see how energy storage systems in the USA span residential, commercial, and utility markets.
The growth of the energy storage market is driven by various factors, including the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, the need to improve grid stability and reliability, and the desire to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. As more and more countries set ambitious targets for reducing their greenhouse gas emissions, the demand for energy storage is only expected to grow. These drivers underscore why we need energy storage to integrate variable renewables and enhance resilience.
In addition, the declining cost of energy storage technologies is making them increasingly cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuel-powered plants. As the cost of lithium-ion batteries and other forms of energy storage continues to decline, they are expected to become an increasingly attractive option for meeting peak power demand and improving grid stability. Beyond economics, energy storage and the grid interact to provide frequency response, peak shaving, and capacity value.
Overall, the energy storage market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by a combination of market forces and government policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote the adoption of renewable energy sources. This trajectory reinforces why energy storage is important for delivering reliability and decarbonization at scale.
Related Articles

Can energy storage technology work with all fuel sources?
Energy storage fuel sources span batteries, hydrogen, supercapacitors, flywheels, and pumped hydro, enabling renewable integration, grid stability, load shifting, and high power density for electrical systems, peak shaving, microgrids, and ancillary services.
Energy Storage Fuel Sources Overview and Best Practices
Can energy storage technology work with all fuel sources?
For readers new to the topic, the basics of what energy storage is provide helpful context for evaluating how it pairs with different fuels.
Energy storage technology can work with many different fuel sources, both renewable and non-renewable. Understanding why we need energy storage clarifies its role across both renewable and conventional systems.
For renewable sources such as wind and solar, energy storage is essential, as these energy sources are subject to natural fluctuations in supply. By storing energy generated during periods of high supply and releasing it during periods of high demand, energy storage systems can help to improve the reliability and stability of the electrical power grid. These benefits are central to how storage supports the grid during variable renewable output.
Long-duration approaches such as seasonal storage are discussed in resources on long-term energy storage for balancing multi-day or multi-week mismatches.
Energy storage can also work with non-renewable sources such as natural gas and coal. In these cases, energy storage can provide backup power or smooth out fluctuations in demand, helping to reduce the need for peaker plants, which are typically used to meet peak demand. In fossil-based applications, adopting a hybrid energy storage system can combine rapid response with longer-duration reserves to reduce starts and ramping stress.
Different types of energy storage systems are better suited to other fuel sources. For example, lithium-ion batteries are a popular choice for energy storage in combination with renewable energy sources such as wind and solar. Flow batteries are another option well-suited to the storage of renewable energy. In contrast, compressed air energy storage can be combined with renewable and non-renewable sources. For high-cycle grid services and power quality, flywheel energy storage offers durable, high-power buffering over short intervals.
Overall, energy storage technology can work with many different fuel sources, and the choice of storage technology will depend on a variety of factors, including the specific energy source being used, the amount of energy being stored, and the application for which the stored energy is being used. As renewable energy sources continue to play an increasingly important role in the energy mix, the need for energy storage systems to support their integration into the electrical power grid will only grow. These dynamics underscore why energy storage is important to building resilient, low-carbon power systems.
Related Articles

Battery Energy Storage System Technology
Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) technology stores electricity for later use, supporting renewable energy, grid stability, and peak demand management. These systems improve energy efficiency, reliability, and sustainability across power distribution networks.
What is a Battery Energy Storage System?
A Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is a technology that captures and stores electrical energy for later use, thereby enhancing grid reliability, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources, and improving energy management.
✅ Provides backup power and peak demand control
✅ Supports renewable energy sources like solar and wind
✅ Improves grid stability, efficiency, and reliability
A battery energy storage system is an energy storage solution that cost-effectively stores electricity in rechargeable batteries for later use. It is a type of energy storage (ES) system that uses batteries to store and discharge electricity.
BESS stores electricity when it is generated in excess and then releases it back into the grid or uses it when the electricity supply is limited. It can also serve as a backup power supply in the event of power outages or to stabilize the grid during periods of high demand. Our Energy Storage Channel provides a complete overview of technologies and trends shaping the future of electricity storage.
Visit our Energy Storage System Training Course Page
A battery energy storage system typically consists of a set of batteries, power conditioning equipment such as inverters, and a control system that manages the charging and discharging of the batteries. The batteries used in BESS can vary from lead-acid to lithium-ion and other advanced chemistries, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Alternative storage technologies like Capacitor Energy Storage and Flywheel Energy Storage are being developed for specialized applications.
BESS has become an increasingly important energy storage solution as renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, have become more prevalent. This can provide a means of storing energy during times of excess generation for use during periods of low demand. Additionally, BESS can help to reduce the need for fossil fuel-powered peaker plants, which are used to meet peak demand but can be expensive and environmentally damaging. BESS can store the power generated by solar power systems. Large-scale solutions such as Compressed Air Energy Storage and Gravity Energy Storage highlight the diversity of methods available for balancing the grid.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a battery energy storage system work?
A BESS works by storing electrical power in batteries for later use. The basic operation of a BESS can be broken down into several steps:
Charging: Electrical power is supplied to the battery to charge it. This can be achieved through various sources, including renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, or by utilizing the grid during periods of low demand.
Storage Technologies: Once the batteries are charged, they store the electrical energy until it is needed. The amount of power stored in the batteries depends on the system's capacity.
Discharging: The batteries release the stored power when electrical power is needed. This can be done by converting the DC power from the batteries to AC power using an inverter. The amount of energy released depends on the demand and the capacity of the system.
Monitoring and Control: The BESS is typically monitored and controlled by a control system that manages the charging and discharging of the batteries. This control system ensures that the batteries are charged and discharged safely and efficiently, and operate within their design limits.
Overall, a BESS can provide a means of storing excess power from renewable sources for later use, reducing peak demand on the grid, providing backup power during outages, and improving the stability and reliability of the electrical grid.
What are the benefits of a battery energy storage system?
There are several benefits of a BESS, including:
Renewable Energy Integration: BESS can store excess power generated by renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, for use when energy demand exceeds power generation.
Peak Demand Management: BESS can help reduce demand during peak times by peak shaving, thereby limiting the need for utilities to bring on expensive and environmentally harmful peaker plants to meet high electricity demands.
Grid Stability and Reliability: BESS can provide a stable and reliable power supply, especially during outages or emergencies. BESS can also provide ancillary services to the grid, such as frequency regulation, voltage support, and ramp rate control. To understand the broader impact, see our analysis of Energy Storage and the Grid and the Growth in Utility-Scale Energy Storage.
Cost Savings: BESS can help businesses and homeowners reduce their electricity costs by storing and utilizing cheaper off-peak electricity during peak periods.
Environmental Benefits: BESS can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by enabling the integration of more renewable power into the grid and reducing the need for fossil fuel-powered peaker plants.
Energy Independence: BESS can provide a backup power supply during power outages or emergencies, providing energy independence and reducing reliance on the grid.
Overall, BESS can help improve the electrical grid's efficiency, reliability, and sustainability while providing businesses and homeowners with cost savings and energy independence.
How efficient is BESS?
The efficiency of a BESS can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of chemistry used, the temperature and operating conditions, and the efficiency of the power electronics and control systems used to manage the batteries.
Generally, the round-trip efficiency of a BESS, which is the ratio of the power output to the power input, can range from around 70% to 95%. This means that if you put 100 units of power into the battery, you may get anywhere from 70 to 95 units of power back out, depending on the system's efficiency.
Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in BESS applications, have a round-trip efficiency of around 80-90%, while lead-acid batteries have a round-trip efficiency of about 70-80%. Other types of batteries, such as flow batteries, may have higher round-trip efficiencies of up to 95%.
It's important to note that efficiency is not the only factor to consider when evaluating the performance of a BESS. Other factors such as cost, lifespan, safety, and environmental impact are also important considerations.
Related Articles
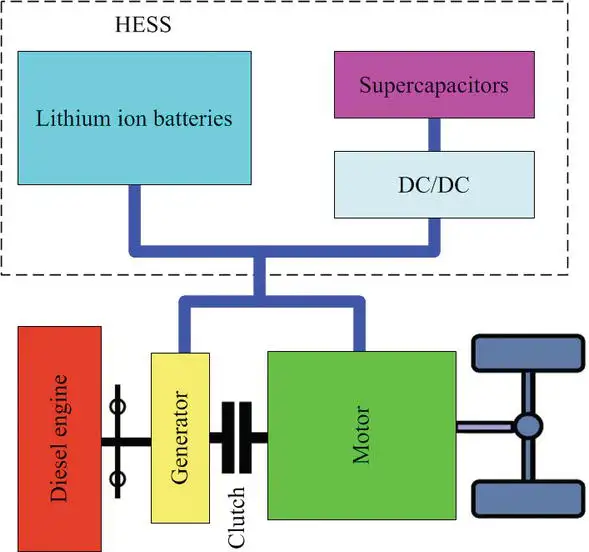
Hybrid Energy Storage System Explained
A hybrid energy storage system combines batteries, supercapacitors, and other technologies to optimize electricity supply, integrate renewable energy, and enhance grid stability while balancing rapid response with long-duration needs for efficiency and reliability.
What is a Hybrid Energy Storage System?
A hybrid energy storage system (HESS) integrates various storage technologies to deliver both high power and long-duration capacity, ensuring reliable energy use.
✅ Optimizes grid stability and renewable energy integration
✅ Provides fast response and long-term electricity supply
✅ Increases efficiency, flexibility, and storage system reliability
Energy Storage Systems Training
Why a Hybrid Energy Storage System Matters
The power grid faces challenges from the increasing penetration of renewable energy sources and growing energy demand. A single storage technology cannot always meet these diverse requirements. Lithium-ion batteries, for example, offer excellent energy density but degrade under frequent cycling, while supercapacitors excel at fast response yet lack long-duration capacity. To understand how hybrid designs fit into the broader energy landscape, see our overview of energy storage, which explains the essential role storage plays in modern power systems.
A HESS, which combines multiple storage and generation technologies, solves this issue by distributing the workload. They are especially valuable in remote regions where access to the grid is limited. With rising fossil fuel costs and the urgency of reducing carbon emissions, hybrid systems are positioned as a practical and cost-effective solution for resilient power delivery.
Technology Combinations
Different hybrid designs are tailored to specific needs, each offering distinct advantages:
-
Battery + Supercapacitor: Batteries provide steady, long-duration power, while supercapacitors manage sudden surges and fast transients. This pairing is common in electric vehicles and renewable smoothing.
-
Battery + Flow Battery: Flow batteries offer scalability and long cycle life, but a slower response. Adding conventional batteries provides faster reaction and flexible operation at the grid scale.
-
Battery + Hydrogen Storage: Batteries handle short-term demand, while hydrogen storage supplies seasonal or long-duration backup. Projects in Europe and Asia demonstrate how this design stabilizes microgrids during extended periods of renewable energy shortfalls.
These combinations demonstrate how system designers pair technologies to overcome the limitations of any single option, thereby creating storage architectures that are efficient, durable, and adaptable. Since batteries remain the backbone of most hybrid solutions, our detailed guide on battery energy storage systems explores their performance, applications, and integration with other technologies.
Performance and Comparisons
| Storage Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Power Density (W/kg) | Efficiency (%) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion Battery | 100–250 | 250–340 | 90–95 | 2,000–7,000 |
| Supercapacitor | 5–10 | 1,000–10,000 | 95–98 | 100,000+ |
| Flow Battery | 20–50 | 50–150 | 65–85 | 10,000–20,000 |
| Hydrogen Storage | 33–39 (per kg H2) | Variable | 30–50 | Very high |
By combining technologies, for example, pairing the high energy density of lithium-ion with the rapid responsiveness of supercapacitors, hybrid systems overcome the weaknesses of individual storage methods. Capacitors often complement batteries in hybrid setups, and our article on the capacitor energy storage formula explains how stored electrical charges contribute to fast-response performance.
Control and Optimization
The effectiveness of a hybrid energy storage system depends heavily on its control strategy. Passive hybrids, which directly connect different technologies, are simple but limited in flexibility. Semi-active systems incorporate additional control electronics, whereas fully active systems utilize advanced converters and controllers to optimize energy sharing.
Modern hybrid energy storage systems often employ intelligent algorithms to determine which technology should supply power at any given time. For instance, supercapacitors might be assigned to absorb short bursts during peak loads, while batteries deliver steady output. Some systems now utilize model predictive control or machine learning to optimize efficiency and extend lifespan, thereby ensuring the optimal balance between components. For large-scale, long-duration applications, many hybrid models incorporate compressed air energy storage, which provides substantial capacity for balancing electricity supply and demand.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, hybrid energy storage systems face barriers that slow wider adoption. Costs remain high due to the need for multiple technologies and a complex control infrastructure. Integration challenges, such as mismatched lifespans and varying maintenance requirements, also add difficulty.
There are also regulatory and safety concerns. Different storage technologies have varying standards for installation, monitoring, and disposal, which complicates compliance. While hybrids can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, they must also overcome issues of scaling, degradation, and long-term system management before becoming universal solutions. A hybrid system also supports broader grid reliability, as described in our discussion of energy storage and the grid, where storage solutions help stabilize voltage and frequency.
One of the main advantages hybrid energy storage systems offer is their ability to combine multiple energy storage technologies into a single platform, creating flexible and resilient energy storage solutions. By integrating batteries with supercapacitors, flow batteries, or hydrogen storage, a hybrid energy storage system can provide both rapid response for short-term fluctuations and capacity for long-term energy needs. This dual capability makes hybrid systems especially valuable for modern grids that must balance daily demand swings with seasonal renewable variability, ensuring efficiency, stability, and reliability across diverse applications.
Future Trends
The future of hybrid energy storage is tied to ongoing innovation. Research is advancing in new battery chemistries, such as solid-state designs, and improved power electronics that reduce conversion losses. Intelligent, AI-driven control systems are emerging to fine-tune hybrid operations in real time. Hydrogen is another promising element in hybrid configurations, and our page on hydrogen energy storage highlights its potential for seasonal and long-duration backup.
In addition, the range of hybrid combinations is expanding. Beyond batteries and supercapacitors, researchers are exploring combinations with thermal storage, compressed air, and even next-generation hydrogen systems. Integration with smart grids promises more dynamic management, enabling hybrid systems to play a crucial role in reducing emissions while delivering affordable and reliable energy.
Real-World Applications
Hybrid energy storage systems are already proving their value in practice. Microgrids in island communities and remote villages rely on solar, batteries, and hydrogen storage to ensure continuous power. Public transit systems, such as electric buses, use battery–supercapacitor hybrids to capture regenerative braking and support acceleration. On a larger scale, utility projects in Germany and China demonstrate how hybrid systems can stabilize national grids while accommodating high levels of renewable energy penetration.
Hybrid energy storage systems offer the flexibility, resilience, and efficiency necessary to meet the challenges of modern energy demands. By combining the complementary strengths of different technologies, they ensure that renewable energy can be integrated at scale without sacrificing reliability. As innovations in control, design, and materials continue, hybrids will become central to the transition toward a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. To explore the future of the industry, review our insights on growth in utility-scale energy storage, which demonstrate how hybrid systems are shaping the integration of large-scale renewable energy sources.
Related Articles
Where are energy storage systems operating in the United States?
Energy Storage Systems in the USA enable grid-scale resilience, integrating renewables with battery storage, BESS, inverters, and power electronics for peak shaving, frequency regulation, microgrids, and smart grid reliability across sectors.
Key Concepts of Energy Storage Systems in the USA
Where are energy storage systems operating in the United States?
Energy storage systems operate in various locations throughout the United States, with many states actively promoting the deployment of energy storage to support the integration of renewable energy sources into the electrical power grid. Some states leading the way in energy storage deployment include California, Texas, and Hawaii. For readers new to the concept, this overview of what energy storage is provides helpful context for policy and deployment trends.
California has been one of the most active states in promoting the deployment of energy storage, with a target of 1,325 MW of energy storage capacity by 2024. The state has several large-scale energy storage projects, including the 300 MW/1,200 MWh Moss Landing Energy Storage Facility, one of the world's largest battery energy storage systems. In addition, the state is also home to many smaller-scale energy storage systems, such as residential and commercial battery systems. Given the state's vast solar resources, this primer on solar energy storage explains how batteries capture midday generation for evening demand.
Texas is another state that has been actively promoting the deployment of energy storage, with a goal of 5 GW of energy storage capacity by 2030. The state has several large-scale energy storage projects, including the 495 MW/1,993 MWh Samson Energy Storage Project, which will be the largest energy storage project in the United States when it is completed. In addition, the state is also home to several smaller-scale energy storage projects, including battery systems for residential and commercial use. The rapid growth in utility-scale energy storage is reshaping ERCOT's resource mix and ancillary services.
Hawaii has set a goal of achieving 100% renewable energy by 2045, and energy storage is an integral part of the state's strategy to achieve this goal. The state has several large-scale energy storage projects, including the 36 MW/144 MWh Kapolei Energy Storage Project, Hawaii's largest energy storage project. In addition, the state is also home to many smaller-scale energy storage projects, including residential and commercial battery systems. Isolated island grids also benefit from advances in long-duration energy storage that can ride through prolonged cloudy or low-wind periods.
Other states that have been actively promoting the deployment of energy storage include New York, Massachusetts, and Arizona. In New York, the state has a goal of 3 GW of energy storage capacity by 2030. It has several large-scale energy storage projects, including the 20 MW/20 MWh Hecate Energy Queens Lithium-ion Battery Storage System. Massachusetts has set a goal of 1,000 MWh of energy storage capacity by 2025 and has several energy storage projects in operation, including a 20 MW/20 MWh battery storage project in Worcester. Arizona has several large-scale energy storage projects, including the 100 MW/400 MWh Sonoran Energy Center Battery Storage Facility, one of the most significant battery storage projects in the United States. Across these regions, the interaction between energy storage and the grid helps balance peaks, reduce curtailment, and enhance resilience.
Overall, energy storage systems are operating in various locations throughout the United States, with many states actively promoting their deployment to support the integration of renewable energy sources and improve the stability and reliability of the electrical power grid. Analysts track the expanding sector in reports on how big the energy storage market is, highlighting investment trends across technologies. Ultimately, understanding why we need energy storage underscores its value for reliability, decarbonization, and cost efficiency.
Related Articles

Solar Energy Storage: Explained
Solar energy storage captures excess solar power in batteries or thermal systems. It balances electricity supply and demand, supports renewable energy integration, and ensures reliable, sustainable backup for businesses, homes, and the power grid.
What is Solar Energy Storage?
Solar energy storage is the process of storing electricity generated by solar panels for later use, thereby enhancing the reliability and integration of renewable energy sources.
✅ Stores excess solar power for use during night or cloudy periods
✅ Improves grid stability and renewable energy efficiency
✅ Reduces reliance on fossil fuels and peak demand costs
Energy Storage Systems Training
Why Solar Energy Storage Matters
Solar energy storage (SES) is a critical component of the U.S. clean energy transition. By storing excess solar energy, SES systems provide a reliable source of power even when the sun isn’t shining, reducing dependence on traditional power plants and fossil fuels. Battery storage is the most widely used form of SES, but other technologies, such as thermal and pumped hydro, are also important in large-scale applications. Our overview of energy storage and the grid explains how SES interacts with transmission, distribution, and demand management.
The U.S. solar storage market is experiencing rapid growth. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, installed battery storage capacity surpassed 16 GW in 2024, with projections indicating it will triple by 2030. States like California, Texas, and Arizona are leading the way in deployments, as high solar penetration drives demand for reliable storage solutions. Many forms of long-term energy storage complement solar by providing reliable electricity for days or weeks when renewable generation is limited.
U.S. Solar Storage Incentives and Policy
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 provided a significant boost to solar and storage projects by extending a 30% federal tax credit, known as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), for both residential and commercial installations. Many states also offer incentives:
-
California’s SGIP program supports home batteries and resiliency upgrades.
-
New York’s NY-Sun program provides rebates for residential and commercial solar + storage systems.
-
Massachusetts SMART program offers performance-based incentives for solar systems paired with storage.
These federal and state policies are key drivers of adoption, making solar storage more accessible and financially attractive. For a broader context, see our growth in utility-scale energy storage report, which shows how large solar projects are driving expansion across the United States.
Cost of Battery Storage
Battery storage costs in the U.S. have dropped significantly, with lithium-ion systems now averaging around $300 per kWh for utility-scale installations, down from over $1,000 a decade ago. Residential solar batteries typically cost between $10,000 and $20,000 installed, depending on the capacity and brand. As costs decline, payback periods shorten, especially in states with high electricity rates or time-of-use pricing.
Core Components of SES Systems
Battery storage is the most common SES technology. Lithium-ion batteries are favoured due to their efficiency, high energy density, and long service life. To ensure proper operation, charge controllers regulate the flow of electricity from panels to batteries, preventing overcharging and deep discharging.
Hybrid solar systems, which combine solar panels with battery storage, are gaining popularity in the U.S. They enable homes and businesses to utilize solar power immediately while storing excess energy for later use, making them particularly valuable in states with frequent power outages or variable sunlight.
Emerging and Long-Duration Storage Technologies
Beyond lithium-ion, the U.S. is investing heavily in research for long-duration storage. Flow batteries, hydrogen storage, compressed air, and solid-state batteries are being developed to extend storage times from hours to days. Thermal storage systems, including molten salt, are also utilized in concentrated solar power plants in states such as Nevada. These technologies will play a crucial role in balancing the grid as renewable energy penetration increases. Many forms of long-term energy storage complement solar by providing reliable electricity for days or weeks when renewable generation is limited.
Case Studies and Applications
-
California leads the nation with large-scale projects, such as Moss Landing (750 MW / 3,000 MWh), one of the world's largest battery storage facilities.
-
Texas has rapidly expanded solar + storage projects to stabilize its independent ERCOT grid, which faces extreme weather challenges.
-
Arizona and Nevada are pioneering solar-plus-storage to support desert solar farms and provide evening peak power.
-
At the residential level, hybrid solar + storage systems are increasingly used for resiliency against outages caused by storms, wildfires, and grid instability.
Advances in thermal energy storage and hydrogen energy storage highlight the diversity of methods being developed to complement solar power.
Technical Limitations and Trade-Offs
Like any technology, SES has trade-offs. Lithium-ion systems degrade over time, with cycle life and depth of discharge influencing performance. Recycling and disposal of batteries pose environmental challenges, while large-scale systems must address the complexities of land use, permitting, and grid integration. These factors shape the total cost of ownership and long-term sustainability. Technologies such as compressed air energy storage and gravity energy storage are emerging as scalable solutions to support the integration of solar energy on the grid.
Smart Controls, Software, and Grid Services
Modern U.S. storage projects rely on advanced battery management systems (BMS) and grid integration software. These tools optimize performance, extend battery life, and allow storage to provide valuable grid services. Storage can now generate revenue through peak shaving, demand response, and frequency regulation, making it both a resiliency tool and a financial asset.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does solar battery storage cost in the U.S.?
Residential solar batteries typically range from $10,000 to $20,000 in installation costs. Utility-scale projects average around $300 per kWh, with prices continuing to decline.
What incentives are available for solar + storage?
The federal ITC provides a 30% tax credit, and many states, such as California, New York, and Massachusetts, offer additional rebates or performance incentives.
How long do solar batteries last?
Most lithium-ion systems last between 10 and 15 years. New technologies, such as flow batteries, may extend lifespans with reduced degradation.
Can solar storage systems provide backup power?
Yes. Hybrid solar + storage systems can power essential appliances during outages. Whole-home backup is possible with larger battery banks and inverters.
What role does solar energy storage play in the U.S. clean energy future?
SES is essential for integrating more renewable energy, ensuring grid reliability, and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Large-scale projects in California and Texas demonstrate how storage supports the transition to clean energy.
SES is no longer optional—it is central to Canada’s clean energy transition. By combining declining costs, supportive policy, and advancing technology, SES empowers households, businesses, and utilities to achieve energy independence, reduce costs, and contribute to a sustainable future. Our overview of energy storage and the grid explains how SES interacts with transmission, distribution, and demand management.
Related Articles








