What is a Ground Fault? Hazard Explained
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
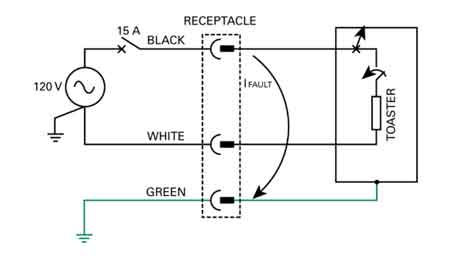
A ground fault occurs when electrical current unintentionally flows to the ground, often through a person or conductive surface. It poses serious shock and fire hazards and typically results from damaged wiring, insulation failure, or water intrusion in electrical systems.
What is a Ground Fault?
A ground fault is a potentially hazardous electrical event when an unintended electrical path forms between a live electrical conductor and a grounded surface.
✅ Occurs when electrical current flows to ground through an unintended path
✅ Commonly caused by damaged wires, insulation failure, or moisture
✅ Increases the risk of electrical shock and equipment failure
The flow of current through this unintended path, also known as earth leakage, can cause serious electrical shock hazards and damage to electrical systems. Let's examine the causes, dangers, and preventive measures associated with ground faults. Proper electrical grounding is essential to prevent ground faults, as it ensures that stray currents are safely diverted into the earth.
There are common causes of ground faults. A ground fault occurs because of several factors, including damaged insulation, incorrect wiring, or moisture in the electrical system. Damaged insulation, for example, can expose the conductor of electricity, allowing it to come into contact with a grounded surface. Additionally, moisture can create a conductive path between live conductors and the earth, thereby increasing the risk. Moisture intrusion and damaged insulation can cause faults similar to arc faults, which are discussed further in our power quality troubleshooting resource.
One of the primary dangers associated with ground faults is the risk of electrical shock. When one occurs, it can create a path to the earth through a person, leading to serious injury or even death. Additionally, they can cause overheating, sparking, and fires in electrical systems, posing a significant risk to property and life.
Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are essential devices designed to mitigate the risks associated with ground faults. GFCIs constantly monitor the flow of electrical current between the hot wire and the neutral wire. If an imbalance is detected, the GFCI quickly cuts power to the electrical circuit, preventing electrical shock and minimizing potential damage. GFCI outlets are commonly installed in areas where water is present, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor spaces, as these locations have a higher risk of ground faults. A grounding system should be regularly inspected to minimize the risk of fire and shock caused by unintentional current paths.
Preventing Ground Faults
Preventing and minimizing ground faults involves several steps. First, proper electrical grounding is critical in reducing the risk. A grounding wire connected to the electrical box creates a path for fault current to flow safely to the earth, reducing the likelihood of electrical shock. Regular inspection and maintenance of electrical systems can also help identify potential issues, such as damaged insulation or incorrect wiring, before they lead to ground faults. Additionally, using GFCI-protected outlets and circuit breakers in high-risk areas can help prevent ground faults and protect against shock hazards.
Understanding the differences between ground faults, short circuits, and arc faults is important, as they are all distinct electrical events with unique risks and causes. A short circuit occurs when a live conductor comes into contact with a neutral or grounded conductor, resulting in a sudden surge of current. This can lead to overheating, fires, or damage to electrical equipment. On the other hand, arc faults occur when an electrical arc forms between conductors, often due to damaged or frayed wiring. Arc faults can generate excessive heat and pose a fire risk.
Identifying one in an electrical system can be accomplished through visual inspection, testing, or the use of specialized equipment. For example, signs of a ground fault may include tripped GFCI outlets or circuit breakers, flickering lights, or a burning smell near electrical equipment. Additionally, testing outlets with a ground fault circuit interrupter tester or a multimeter can help determine if a ground fault is present.
Grounding is crucial in preventing ground faults and protecting against electrical shock. By providing a safe path for fault current to flow, earthing helps minimize the risk of injury and damage to electrical systems. Proper earthing involves connecting all electrical equipment, including outlets, switches, and metal boxes, to a grounding wire connected to the earth. This connection helps ensure that unintended electrical paths, such as those caused by ground faults, are safely grounded.
Understanding Ground Faults
Understanding what a ground fault is and how to prevent it is essential for ensuring electrical safety in residential and commercial settings. Proper earthing, regular inspection and maintenance of electrical systems, and the use of GFCI-protected outlets and circuit breakers are all crucial measures in reducing the risk of electrical hazards. By being aware of the dangers associated with ground faults and taking proactive steps to address them, we can help protect our homes, businesses, and loved ones from electrical hazards.
In addition to the precautions mentioned above, it's essential to exercise caution when using power tools and appliances. Many incidents occur when using power tools in damp environments. Always ensure that power tools are in good working condition, with no frayed cords or damaged insulation. Use GFCI-protected outlets or extension cords when operating them in potentially hazardous conditions.
Moreover, educating yourself and those around you about electrical safety is crucial. Understanding the risks associated with ground faults and knowing how to respond in an electrical emergency can save lives. Regularly reviewing safety procedures and ensuring that everyone in your home or workplace knows how to use GFCI outlets and reset buttons. Circuit breakers can significantly reduce the risk of injury or property damage.
Finally, don't hesitate to consult a licensed electrician if you suspect or encounter any electrical issues. Professional electricians have the knowledge and tools to diagnose and repair electrical problems safely and effectively. Attempting to resolve electrical issues without proper training can be dangerous and may lead to further complications.
By adopting a comprehensive approach to electrical safety, we can minimize risks and create a safer environment for ourselves and our communities. Awareness, preventive measures, and education are crucial in reducing the incidence of injuries and ensuring the well-being of everyone interacting with electrical systems.
Related Articles