What is Single Phase Power?
Short Circuit Study & Protective Device Coordination
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.
- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA FS3529 Fact Sheet – Lockout/Tagout Safety Procedures

- Learn how to disable machines and isolate energy sources safely
- Follow OSHA guidelines for developing energy control programs
- Protect workers with proper lockout devices and annual inspections
Single phase power delivers alternating current through one sine wave, supplying energy for homes, offices, and small industries. It provides efficient, cost-effective power distribution for lighting and appliances, making it the standard system for commercial use.
What is Single Phase Power?
Single phase power is an AC electrical system that operates with one alternating voltage wave, commonly used in residential and small commercial applications.
✅ Supplies energy efficiently for homes and small businesses
✅ Simplifies wiring and reduces installation costs
✅ Supports lighting, heating, and general-purpose loads
How Single Phase Power Works (AC Waveform and Wiring)
Single phase power is an alternating current (AC) electrical system that operates with one voltage waveform. The voltage alternates polarity, producing a smooth sine wave that repeats 50 or 60 times per second—depending on the country’s standard frequency (50 Hz in most of the world, 60 Hz in North America). You can also study the structural and operational aspects of modern distribution grids in our Power System Engineering article.
Electricity is delivered through two wires: a phase (hot) wire and a neutral wire. The phase wire carries current to the load, while the neutral wire returns it to complete the circuit. This simple configuration makes single-phase systems reliable and easy to install for low-to-moderate power needs. To understand how voltage and current relationships are analyzed across electrical networks, see our guide on Load Flow Analysis.
Power System Analysis and Design Course
Arc Flash Analysis/Study Training Course
Power System Fundamentals Course
Short Circuit Analysis/Study Course
Power Calculation Formula:
For purely resistive loads: P = V × I
For loads with reactance (motors, transformers): P = V × I × PF, where PF (power factor) accounts for the phase shift between voltage and current.
The instantaneous power fluctuates twice per cycle due to the sine wave shape, meaning energy delivery varies with time. A graphical representation of this waveform helps visualize how power peaks twice each cycle. For engineers seeking a deeper understanding of power distribution models and transformer behavior, our Power System Analysis and Design section provides detailed insights.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Electrical Engineering Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Electrical Engineering Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Commercial Applications
Single phase power is the backbone of residential energy distribution. It supplies 120 V or 240 V (split-phase) to operate household devices such as lighting systems, air conditioners, ovens, and small motors. In a 120/240 V split-phase system, a center-tapped transformer provides two 120 V legs that are 180° out of phase—combined to supply 240 V for higher-demand loads like dryers or water heaters.
In small commercial environments—offices, shops, and small workshops—single-phase circuits power general-purpose outlets, HVAC systems, and small machinery. Approximately 90% of North American homes and many small businesses use single-phase electricity due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Advantages and Limitations
Single phase systems are efficient for modest electrical loads, but they have limitations for heavy-duty use. Because a single AC waveform does not produce a rotating magnetic field, motors require start capacitors or auxiliary windings to begin rotation. These systems may also experience voltage drops, load imbalance, and reduced efficiency under heavy loads.
Solutions include:
-
Installing start/run capacitors for motor applications
-
Balancing loads across circuits
-
Using power factor correction equipment
-
Upgrading to three-phase service for higher-capacity demands
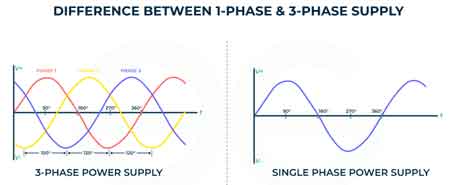
Single Phase vs Three Phase Power
| Feature | Single Phase Power | Three Phase Power |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Waveforms | 1 | 3 (120° apart) |
| Wires Required | 2 or 3 (split-phase) | 3 or 4 |
| Voltage Stability | Fluctuates with load | More constant |
| Typical Use | Homes, small offices | Industry, large facilities |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Equipment Cost | Lower | Higher |
Safety, Grounding, and Protection
Proper grounding and circuit protection are essential for safe operation. In residential wiring, the neutral is bonded to ground at the service panel to prevent overvoltage and shock hazards. Protective devices such as circuit breakers, fuses, and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) safeguard users from faults and short circuits.
Regular maintenance, load balancing, and adherence to NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code) or CSA C22.1 (Canadian Electrical Code) ensure long-term reliability and safety compliance. Finally, explore our live online Power System Training courses to develop practical skills for designing and maintaining both single-phase and three-phase power systems.
Converting and Upgrading Power Systems
Single-phase power can be derived from three-phase lines by tapping one phase and a neutral wire. Conversely, when higher loads are required, rotary phase converters or variable frequency drives (VFDs) can simulate three-phase output from a single-phase source, allowing heavier equipment to operate in small facilities.
Historical and Global Context
Single phase systems date back to the late 19th century during the evolution of alternating current distribution pioneered by Nikola Tesla. As polyphase systems emerged for industrial use, single-phase systems remained dominant in residential and small-scale applications worldwide due to their simplicity and cost efficiency.
Single phase power remains the most practical solution for everyday electricity needs. Its straightforward design, compatibility with household devices, and adaptability to local standards make it a cornerstone of modern electrical infrastructure. Understanding how it works—and its advantages, limitations, and safety practices—ensures reliable and efficient energy use in homes and businesses.
Related Articles








