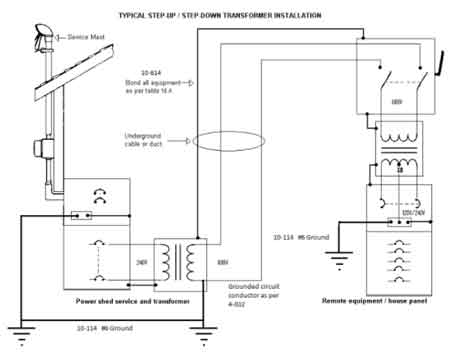
Transformer Grounding Diagram Explained
Substation Relay Protection Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
A transformer grounding diagram illustrates safe electrical connections, showing grounding methods, fault current paths, and protective bonding. It improves safety, stability, and code compliance in power systems across utility and industrial settings.
What is a Transformer Grounding Diagram?
A transformer grounding diagram is a schematic that shows how transformers are grounded to ensure safety, stability, and compliance with electrical codes.
✅ Illustrates grounding connections for fault protection
✅ Enhances power system reliability and stability
✅ Ensures compliance with NFPA, NEC, and IEEE standards
A transformer grounding diagram is a critical tool used in the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems. It provides detailed information on how a transformer is grounded to protect both the system and personnel from electrical faults. Proper grounding (sometimes referred to as "earthing") ensures that the neutral point of the system is stabilized, which is essential for preventing damage and enhancing system reliability. This article examines the role of a grounding diagram, its benefits during installation, and the potential problems it helps identify. Understanding a transformer’s basic design is the first step before studying grounding diagrams, since earthing methods depend on how windings and cores are constructed.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Purpose of a Transformer Grounding Diagram
A grounding diagram serves a clear purpose: to demonstrate the configuration of the earthing system. Grounding controls fault currents when a ground fault occurs, directing the current safely into the earth while stabilizing system voltage by holding the neutral point at ground potential. In high-voltage systems, this function is indispensable. A well-drawn grounding diagram allows engineers to predict system performance during faults and to design protective devices accordingly. In one real-world example, an industrial facility with a 13.8 kV substation experienced damaging neutral overvoltages. Reviewing the grounding diagram revealed an undersized earthing conductor. Once corrected, neutral voltages dropped dramatically during faults, preventing relay misoperations and ensuring compliance with IEEE Std. 142, known as the Green Book. When specifying equipment, transformer grounding diagrams should be reviewed along with transformer sizing calculations to ensure both electrical performance and safety compliance.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Common Grounding Problems in Transformers
Like any part of an electrical system, earthing can suffer from weaknesses that a diagram helps identify. Poor connections at the neutral point, incorrectly sized conductors, or failures in earthing transformers within ungrounded systems can all create instability and hazards. Improper earthing often leads to elevated voltages, increasing the risk of equipment failure. Engineers commonly use calculation checks to avoid these pitfalls. For example, when sizing a neutral grounding resistor (NGR), the fault current is determined using the formula:
I = V / R
where I is the fault current, V is the line-to-neutral voltage, and R is the chosen resistance. Selecting improper values may result in dangerously high fault currents or ineffective protection. In distribution networks, earthing is critical for single phase transformer connections, ensuring system stability and reducing the risk of neutral shift.
Key Components in a Grounding Diagram
Every transformer grounding diagram shares certain key components. These include the neutral point where transformer windings connect to ground, the grounding electrode itself, and the conductors that form the fault current path. In delta-connected systems, the diagram often shows an earthing transformer—such as a zigzag configuration—that provides a return path for ground faults where a direct neutral does not exist. Technicians use these diagrams not only to ensure correct installation but also to verify the system's condition during periodic maintenance. Industry standards such as NEC Article 250 and IEEE Std. 81 recommends testing methods, including fall-of-potential and clamp-on ground resistance tests, often with a goal of less than 25 ohms of resistance, or under 5 ohms for critical substations. For power quality and protection, instrument transformers rely on correct earthing of secondary windings to prevent dangerous overvoltages.
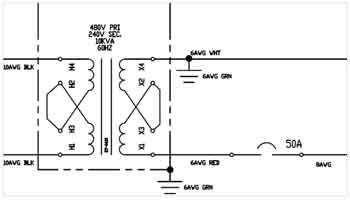
One of the two output conductors can be connected to ground, designating it as the neutral, while the other remains the energized line.
Types of Transformer Grounding Configurations
There are several grounding configurations that engineers may select, and diagrams help distinguish their applications. Solid grounding directly connects the neutral to earth, creating a low-impedance path that ensures fast fault clearing but results in high fault currents. Resistance earthing, whether low or high impedance, introduces a resistor between neutral and ground, thereby limiting fault currents to safer levels. High-resistance grounding, in particular, is effective for reducing arc flash hazards but requires careful insulation coordination. Zigzag earthing transformers, commonly applied to delta systems, provide a path for zero-sequence currents while maintaining balanced voltages.
Each method carries its own benefits and limitations:
-
Solid grounding enables fast fault clearing but can produce destructive current magnitudes.
-
Low-resistance grounding provides balance by allowing fault detection with limited current.
-
High-resistance grounding minimizes current and arc energy but requires system insulation upgrades.
-
Zigzag grounding offers flexibility in ungrounded systems, providing a fault current path without altering voltage balance.
Engineers also review earthing considerations when installing dry type transformers, especially in indoor locations where insulation and fault paths must be tightly controlled.
Comparison of Transformer Grounding Methods
| Grounding Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid | Fast fault clearing; stable voltage reference | High fault current can damage equipment | Utilities, high-voltage transmission |
| Low-Resistance | Limits current while allowing detection; protects equipment | Resistors require maintenance; moderate fault currents remain | Industrial distribution systems |
| High-Resistance | Reduces arc flash risk; minimizes equipment stress | Requires higher insulation; limits fault detection sensitivity | Sensitive process plants, mining, and data centers |
| Zigzag Grounding Transformer | Provides a path for zero-sequence currents in delta systems; maintains voltage balance | Added cost and complexity; not needed if neutral is already available | Delta-connected systems, substations |
Installation, Testing, and Maintenance of Earthing Systems
Beyond initial installation, grounding diagrams play an important role in maintenance. They help technicians trace connections, verify the integrity of earthing, and plan inspections of conductors and electrodes. For example, clamp-on resistance testers can confirm whether bonding conductors remain intact, while step-and-touch potential measurements can identify dangerous ground voltage gradients. These checks help detect weaknesses before they evolve into failures. Proper earthing plays a major role in the accuracy of a current transformer, since any imbalance in the fault return path can distort measurement signals. In low-voltage control circuits, a control transformer often requires careful earthing practices to prevent nuisance faults and ensure safe operation of sensitive equipment.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Risks, Failure Modes, and Protective Strategies
Grounding diagrams also act as tools for anticipating risks. If a delta system is shown without a grounding transformer, this may indicate that no proper return path for ground faults exists. Such omissions can lead to transient overvoltages, ferroresonance, or neutral shift, all of which increase stress on transformer insulation and protective devices. IEEE Std. C62.92 notes that poorly configured earthing systems may even amplify switching surges. By identifying these risks in the design phase, diagrams help prevent downtime, damage, and hazards.
Why Grounding Diagrams Matter
Ultimately, a transformer grounding diagram is more than a schematic—it is a safeguard for safe and efficient operation. It documents how the transformer is connected to ground, provides the reference for installation, and guides maintenance practices throughout the system’s life. By ensuring correct earthing, these diagrams stabilize system voltage, control fault currents, and uphold both personnel safety and equipment reliability. When integrated with proper testing, adherence to NEC, IEEE, and IEC standards, and ongoing maintenance, grounding diagrams become a cornerstone of electrical safety engineering.
Related Articles







