Smart Substation and the Evolving Grid
Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
Smart substation technology uses digital sensors, IEDs, and secure communications to automate protection, monitoring, and control, improving grid reliability, power quality, and DER integration across modern substations.
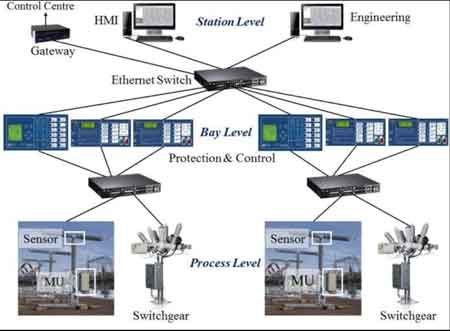
What is a Smart Substation?
A smart substation is a digitally enabled substation that applies IEC 61850, IEDs, SCADA, and analytics to automate control, protection, and data exchange.
✅ Real-time monitoring, automation, and fault response
✅ Standards-based communications (IEC 61850) for interoperability
✅ Improved reliability, cybersecurity, and DER integration
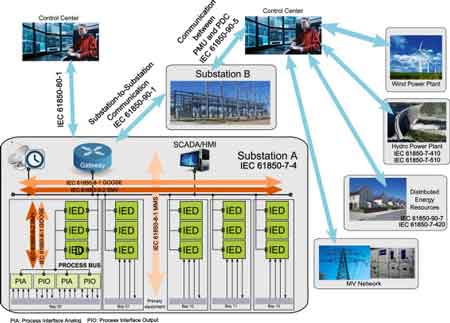
The Smart Substation and Smart Grid
The power industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by grid modernization, renewable integration, and increasing demands for resilience and efficiency. At the heart of this evolution lies the smart substation—a next-generation facility equipped with advanced sensors, digital communications, and real-time control technologies. These substations are foundational to the smart grid, serving as critical nodes that enable automated monitoring, faster fault response, and optimized power flow. For a broader look at grid modernization efforts that support smart substation deployment, visit our Smart Grid Overview.
As utilities shift from analog to digital substations, the move generates complex questions about architecture, cybersecurity, return on investment (ROI), and implementation strategy. However, the long-term value of smart substations—through improved reliability, operational efficiency, and grid intelligence—makes them an essential part of the future energy landscape. Explore how Coordinated Automation Schemes enhance system efficiency and reliability within smart substations.
What Defines a Smart Substation?
A smart substation goes beyond traditional functionality by integrating advanced digital technologies that enhance visibility, control, and automation. While conventional substations focus on mechanical protection and simple monitoring, smart substations leverage:
-
IEC 61850-based communication protocols
-
Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs)
-
Edge computing platforms
-
Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs)
-
IoT sensors and digital relays
Together, these technologies enable real-time data acquisition, remote control, and adaptive protection schemes, creating a dynamic interface between transmission, distribution, and distributed energy resources (DERs). Learn how Smart Grid Data Analytics enable predictive maintenance and adaptive fault detection at the substation level.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Edge Computing in Smart Substations
One of the core innovations in smart substations is the adoption of edge computing—processing data locally at the substation level rather than sending it all to a centralized control center. This distributed intelligence reduces latency, enhances fault response, and eases the burden on wide-area communication networks.
Edge analytics enable real-time decisions to be made closer to the source of events. For example:
-
Fault detection and isolation can be automated in milliseconds
-
Voltage control and reactive power adjustments can be localized
-
Predictive maintenance can be applied using sensor data from breakers, transformers, and other critical equipment
This shift toward decentralized intelligence supports a more agile and responsive grid, especially as DERs, electric vehicles (EVs), and variable renewables introduce complexity and volatility into power flows.
-
Discover the importance of real-time visibility in substation operations with our page on Smart Grid Monitoring.
AI and Machine Learning in Substation Operations
To manage the growing data volume generated by smart substations, utilities are turning to AI and machine learning tools. These technologies offer the ability to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and optimize system performance across various time scales.
Applications of AI in smart substations include:
-
Predictive maintenance: Using historical data to forecast equipment failure before it happens
-
Fault classification: Automatically distinguishing between transient, permanent, or nuisance faults
-
Dynamic load forecasting: Improving dispatch decisions and reducing peak demand
-
Adaptive protection schemes: Automatically adjusting relay settings based on real-time grid conditions
Machine learning models trained on substation telemetry data can evolve over time, improving accuracy and enabling data-driven decision-making. This reduces the need for manual intervention and allows grid operators to proactively address emerging issues. For insights into how SCADA systems integrate with smart substations, explore our overview of supervisory control and data acquisition.
PMUs and Synchrophasors: Enhancing Situational Awareness
Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs) and their associated data, known as synchrophasors, are another critical component of smart substation functionality. These devices measure electrical waves at high speed with precise time stamps using GPS-synchronized clocks.
PMUs improve situational awareness by:
-
Providing real-time visibility into voltage and current phase angles
-
Supporting wide-area monitoring systems (WAMS)
-
Detecting grid oscillations, frequency deviations, and angular instability
-
Enabling fast response to events like line faults or islanding
By embedding PMUs in smart substations, utilities gain a time-synchronized, wide-area view of grid dynamics, essential for maintaining stability in a system increasingly influenced by fast-changing loads and generation profiles. Understand how Improved Sensor Technology supports smart substations by enabling accurate, real-time equipment diagnostics.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, deploying smart substations involves several challenges:
-
High capital costs for retrofitting or building from scratch
-
Integration with legacy systems and analog infrastructure
-
Cybersecurity risks from increased digital exposure
-
The need for staff training in digital technologies and system interoperability
-
Ensuring compatibility with utility-wide data platforms and SCADA/EMS systems
However, the ROI of smart substations often becomes clear over time, as utilities realize gains in reliability, reduced outage durations, streamlined maintenance, and enhanced regulatory compliance. Cybersecurity is vital—see our guide on the DHS-FBI Alert to understand threats to smart substation infrastructure.
Conclusion
Smart substations are a cornerstone of the evolving smart grid, enabling faster, smarter, and more efficient control of the power system. Through technologies such as edge computing, AI and machine learning, and PMU-based situational awareness, they provide the foundation for a responsive, resilient, and data-rich energy network.
Test Your Knowledge About Smart Grid!
Think you know Smart Grid? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
As utilities continue to modernize, the implementation of smart substations will not only support immediate operational benefits but also position the grid to handle the challenges of tomorrow—from renewable integration to real-time analytics and autonomous grid operation. Investing in smart substation architecture is not just about upgrading hardware—it's about building the intelligent backbone of the future grid.
Related Articles








