Arc Flash Burn Explained
CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
Arc flash burn results from electrical arc faults, high incident energy, and arc blast in switchgear; NFPA 70E risk assessment, IEEE 1584 calculations, proper PPE, and labeling mitigate thermal injury in power systems.
What Is an Arc Flash Burn?
A thermal injury from high incident energy during an electrical arc fault, harming skin and eyes.
✅ Caused by arc faults, high fault current, low impedance path.
✅ Severity predicted with IEEE 1584 and incident energy analysis.
✅ Mitigation: NFPA 70E PPE, labeling, arc-resistant gear, safe work.
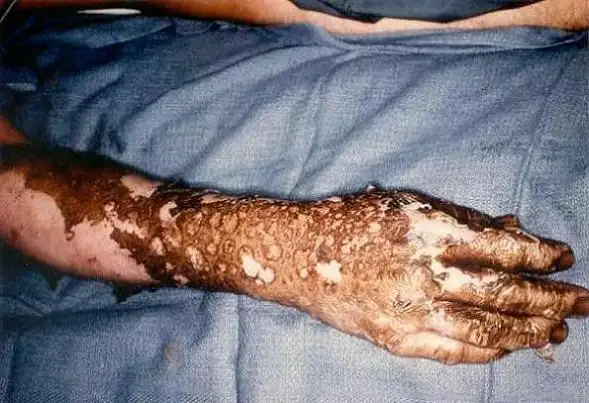
An arc flash burn can be devastating, depending on the intensity of the arc flash explosion or arc blast, the proximity of the electrical worker to the source of the arc flash explosion and the level of personal protective equipment (PPE) that is worn, if any. As outlined in the injuries associated with arc flash, workers face thermal, blast, and radiation hazards beyond electric shock.
Arc Flash Burns Can Include:
- 3rd-degree (irreversible) arc flash burn caused by extreme heat and molten splatter
- Loss of sight due to electromagnetic radiation
- Internal burns and intoxication due to the inhalation of hot toxic gases
- Permanent hearing damage due to explosion
- Other physical and emotional trauma caused by the explosion (blast pressure and flying molten metal)
- Loss of life
Comprehensive summaries of typical outcomes are available in this arc flash injuries overview, which details mechanisms, severity, and recovery considerations.
Real-world case imagery in these arc flash pictures can help safety teams communicate the consequences of inadequate controls.
When you think of electrical arc burns, you often think about hazards from direct contact with current – shocking experiences. However, remember that electrical burns are often compounded by thermal or heat burns from blasts or “electrical arc flashes.” Understanding how an electrical explosion propagates through air and ignites materials clarifies why layered PPE and boundaries are essential.
Test Your Knowledge About Arc Flash!
Think you know Arc Flash? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
An arc flash occurs when high voltage differences exist across a gap between two conductive surfaces. With mighty current, the electrical energy will travel through the air. Large amounts of energy are released when it reaches the second conductor, and temperatures reaching 36,000 degrees Fahrenheit have been reported. This rapid energy release often drives an arc blast that produces intense pressure, noise, and shrapnel hazards.
Arc burns caused by arc flash and arc blast are typically severe, 2nd-degree (partial thickness) or 3rd-degree (total thickness) burns. Clothing may catch on fire, which will contribute to the burn area, further increasing the already high risk of mortality. Skin grafts are not uncommonly required. A pressure wave of molten metal may throw the victim with a force of a half-ton, and physical harm can occur this way. Hearing loss can also occur from an arc flash blast wave. Such events can escalate into a full arc flash blast explosion, compounding thermal injury with fragmentation and impact trauma.
Victims of arc flash blast incidents often have terrible scarring and chronic pain. In addition, they may suffer severe psychological symptoms, such as post-traumatic stress disorder. Medical costs and loss of income can be substantially damaging, and workman’s comp will typically pay only a portion of the cost. Guidance for responding and supporting an arc flash victim underscores the need for immediate medical evaluation and long-term rehabilitation planning.




