Electric Motor Protection Explained
Substation Relay Protection Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3875 Fact Sheet – Electrical PPE for Power Industry Workers

- Follow rules for rubber gloves, arc-rated PPE, and inspection procedures
- Learn employer obligations for testing, certification, and training
- Protect workers from arc flash and electrical shock injuries
Electric motor protection ensures reliable operation by preventing overloads, short circuits, overheating, and arc flash hazards. It improves safety, extends equipment lifespan, and supports efficient industrial power systems.
What is Electric Motor Protection?
Electric motor protection refers to safety measures and devices that guard motors against electrical and mechanical faults, ensuring performance, reliability, and compliance.
✅ Involves the use of overload relays, circuit breakers, and thermal protection mechanisms
✅ Minimizes downtime, reduces repair costs, and safeguards personnel and infrastructure
✅ Commonly applied in factories, commercial buildings, and critical machinery installations
Basic Protection Relay Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Understanding Electric Motor Protection
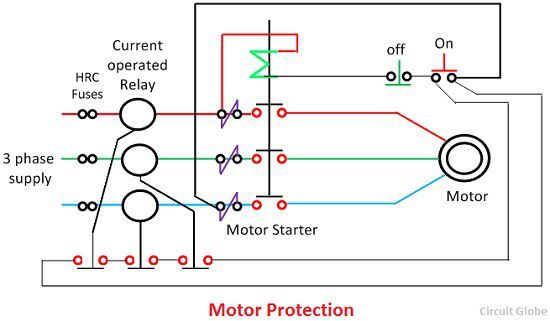
It is a critical aspect of power engineering focused on ensuring the reliability and durability of electrical motors. From small fans to massive industrial pumps, motors drive processes everywhere, and their failure can have far-reaching consequences. Protection systems defend against threats such as overload, phase failure, overheating, undervoltage, and short circuits. Modern protective schemes combine mechanical and electronic solutions to detect irregularities and disconnect power before significant damage occurs.
Electrical relay and fuse protection systems are designed to prevent damage to the motor by ensuring it operates within safe limits. Protective relays and solid-state devices can monitor the temperature to avoid overheating, while overload protection ensures the current does not exceed full load ratings. Modern systems often integrate with variable frequency drives, which provide smoother starting, improved efficiency, and added safeguards against faults that could compromise motor reliability.
Key Types of Motor Protection
-
Overload Protection: Protects motors from running at a current exceeding their rated capacity, which can cause overheating and insulation breakdown. Devices like thermal overload relays sense the heat generated and trip when necessary. Find a detailed explanation at Motor Overload Protection explained
-
Short-Circuit and Ground-Fault Protection: Circuit breakers and fuses rapidly disconnect faulty circuits, preventing catastrophic failures and fire hazards.
-
Phase Loss/Phase Imbalance Protection: Three-phase motors require a balanced supply. Phase failure relays monitor all phases and trip the motor if a disconnect or imbalance is detected.
-
Temperature Protection: Embedded thermistors or thermal switches can disengage the motor or raise an alarm if winding temperature exceeds safe limits.
-
Voltage/Current Monitoring: Undervoltage relays and current monitors prevent operation under unstable power conditions, minimizing stress on the motor’s windings.
Why Protection Matters
When a motor operates outside its designed parameters, it is vulnerable to damage that may not be immediately evident. For example, persistent overloads can degrade insulation, leading to short circuits that are costly to repair. Early detection ensures only minor repairs are necessary and helps keep operations running efficiently. Strong protective technologies also improve workplace safety by reducing the risk of fires and hazardous shocks stemming from motor faults. For more information about protection strategies and devices, visit our main Electrical Protection page.
Implementation in Real-World Applications
In industrial environments, motor protection is standard in manufacturing plants, water treatment facilities, and processing plants—anywhere motors operate for extended periods under variable loads. Typical protection setups might include:
-
Thermal overload relays in motor control centers
-
Fused disconnect switches for short-circuit protection
-
Digital protection relays that offer remote monitoring and programmable settings
-
Integrated temperature sensors for larger machines
Consistent maintenance and periodic electric motor testing ensure protective devices and circuits remain responsive and reliable.
Best Practices for Motor Protection
-
Understand the application: Determine the normal and abnormal operating conditions for each motor in your facility.
-
Proper sizing of protection devices: Overload relays and fuses must match the motor’s rating and duty cycle for optimal response.
-
Routine maintenance: Regularly inspect protection equipment, wiring, and motor health.
-
Continuous monitoring: Leverage modern monitoring systems that provide real-time alerts and diagnostics, enabling the prediction of failures before they occur.
-
Documentation and training: Maintain records of protection settings and educate operators and technicians on troubleshooting and resetting protective devices.
Incorporating these best practices extends the lifespan of equipment and minimizes lost productivity due to unexpected failures. Learn more about maintenance strategies at Electric Motor Maintenance and Diagnostics.
Electric motor protection is not merely a technical requirement—it is a foundational component of modern safety management, reliability engineering, and cost control in every sector that depends on motors. By deploying the right combination of overload protection, short-circuit devices, and temperature monitoring, organizations minimize risk and maximize operational uptime. As both equipment and protective technologies advance, regular training and upgrades will ensure systems remain robust for years to come.
Related Articles




