What is Core Balance Current Transformer?
Substation Maintenance Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3875 Fact Sheet – Electrical PPE for Power Industry Workers

- Follow rules for rubber gloves, arc-rated PPE, and inspection procedures
- Learn employer obligations for testing, certification, and training
- Protect workers from arc flash and electrical shock injuries
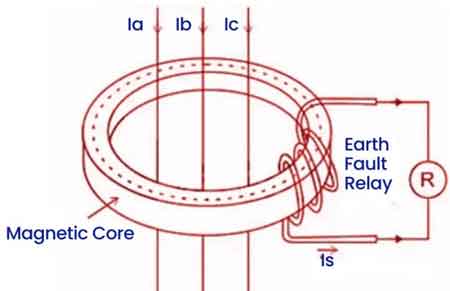
Core Balance Current Transformer (CBCT) detects earth leakage, residual current, and ground faults. It safeguards electrical distribution, prevents equipment damage, and enhances worker safety by detecting faults and operating protective relays.
What is Core Balance Current Transformer
A Core Balance Current Transformer (CBCT) is a protective device that detects leakage or residual current in power systems, ensuring safety and reliability.
✅ Provides ground fault protection in electrical networks
✅ Enhances insulation monitoring and system safety
✅ Supports reliable fault detection and energy distribution
A Core Balance Current Transformer (CBCT) is a protective device that senses leakage or residual current in power systems. Operating on the zero-sequence current principle, CBCTs improve ground fault protection, activate earth fault relays, and support compliance with safety standards in industrial and utility applications. For a broader perspective on transformer technology, visit our Utility Transformers Channel covering design, function, and safety applications.
CBCTs play a critical role in enhancing safety and minimizing equipment damage in industrial settings, where precision and rapid fault detection are essential. By identifying earth leakage and earth fault conditions, CBCTs protect electrical power systems, ensuring safety for electrical workers and reducing downtime due to potential faults. Understanding the working principle and applications of CBCTs helps professionals maintain efficient and safe electrical operations. Many CBCTs are installed alongside distribution transformers to provide ground fault protection in medium-voltage systems.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Key Differences Between Core Balance Current Transformer and Regular Current Transformers (CT)
While a regular CT provides current measurement for metering and protective systems, a CBCT specializes in identifying current imbalance and earth faults, making it indispensable for residual current detection in safety-critical environments. A regular current transformer monitors the magnitude of current flowing through a circuit, offering measurements used for metering and general protection. CBCTs, on the other hand, are dedicated to detecting earth faults by identifying current imbalances within a three-phase system. Unlike standard CTs, CBCTs rely on a secondary winding through which the three-phase conductors pass, providing a balanced system under normal conditions. When an imbalance occurs, indicating a potential fault, the CBCT detects it and signals protective devices to address the issue. To understand how three-phase systems interact with protective devices like CBCTs, see our guide on 3-phase transformers.
Test Your Knowledge About Electrical Transformers!
Think you know Electrical Transformers? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Applications and Benefits of Core Balance Current Transformer
Core Balance Current Transformers are essential in applications where earth fault protection is critical. These transformers are typically used in industrial motors and medium-voltage electrical systems, where the risk of earth leakage or fault can have significant consequences. The CBCT design allows it to promptly detect and relay information about imbalances, enhancing operational safety. Electrical workers benefit from CBCTs because they reduce the risk of equipment damage, protect personnel from electrical hazards, and help maintain compliance with safety regulations in sensitive environments. Residual current detection is critical for electrical substation transformers, where earth faults can compromise large-scale power reliability.
Working Principle of Core Balance Current Transformer
The CBCT functions on the zero-sequence current principle, which is similar to Kirchhoff’s Current Law. In balanced conditions, the sum of the three-phase currents (Ia + Ib + Ic) equals zero. This results in no magnetic flux in the CBCT core, leaving the secondary winding unaffected. However, when a ground fault or earth leakage disrupts the balance, a residual or zero-sequence current is generated. This current flows through the CBCT’s secondary winding, triggering the earth fault relay to isolate the system. This action minimizes the potential for electrical fires, equipment damage, or personnel injury. CBCTs are widely applied in motor feeders, switchgear assemblies, and cable systems to detect earth leakage early, reducing arc flash hazards and insulation failures. Their use supports safety compliance and helps facilities maintain uptime in energy-intensive operations. The role of CBCTs complements protective strategies such as transformer overcurrent protection, ensuring systems remain safe and stable.
CBCT Features and Selection Criteria
Core Balance Current Transformers are chosen for their high sensitivity, reliability, and ease of installation. Key characteristics include a nominal CT ratio adequate to detect even minor ground faults, a minimal ground leakage current requirement, and sufficient knee voltage to activate the earth fault relay. Choosing a CBCT with the correct internal diameter ensures compatibility with the specific cable size in use. These transformers must also provide consistent performance, ensuring protection across various industrial applications where electrical power safety is paramount.
Selection depends on the accuracy of CT ratio, sensitivity to low fault currents, proper relay coordination, and compatibility with cable diameters. Easy installation and low maintenance also make CBCTs practical for long-term industrial safety strategies.
CBCTs are invaluable in industrial and medium-voltage applications for their unique ability to detect ground faults and earth leakages that could compromise electrical systems. By utilizing a zero-sequence current detection method, CBCTs offer rapid and reliable protection against faults, enhancing the safety and integrity of electrical systems. This makes CBCTs a crucial tool for electrical workers, contributing to safer work environments and extending the life of equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does a Core Balance Current Transformer Detect Ground Faults?
CBCTs operate on the principle of zero-sequence current balance, meaning they detect residual current that arises when there's an imbalance among the phases in a three-phase system. Normally, the vector sum of the currents in each phase is zero, indicating balanced conditions without any earth leakage or fault. When an earth fault or leakage occurs, however, this balance is disrupted, resulting in residual current. The CBCT’s secondary winding, connected to an earth fault relay, registers this current and activates the relay. This detection triggers safety mechanisms to isolate the faulty circuit, minimizing risks associated with fault conditions. For insight into how transformer performance is monitored, explore condition monitoring in an age of modernization.
Where is a Core Balance Current Transformer used?
A Core Balance Current Transformer (CBCT) is widely used in industrial plants, medium-voltage switchgear, motor feeders, and cable systems. It provides earth fault detection, residual current monitoring, and insulation protection in environments where electrical safety and reliability are critical.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
What is the difference between CBCT and Earth Leakage Relay?
A CBCT detects residual or leakage current caused by an imbalance in a three-phase system, while an Earth Leakage Relay (ELR) is the protective device that receives the CBCT signal and trips the circuit. Together, they provide effective earth fault protection and system safety.
Related Articles