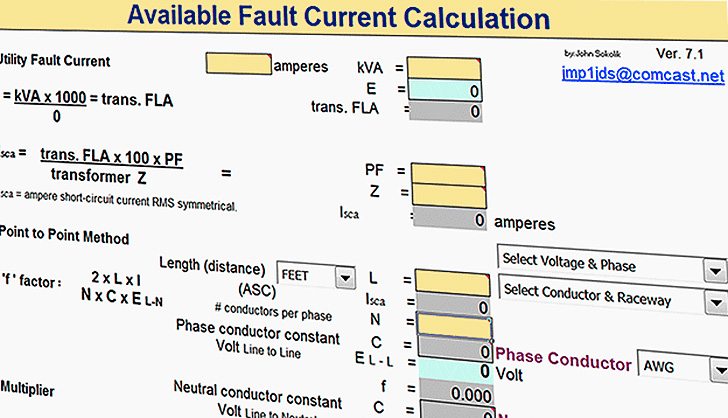
Single Phase Transformer Explained

Substation Maintenance Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
A single phase transformer is an electrical device that transfers power between circuits using electromagnetic induction. Common in residential, commercial, and industrial systems, it steps voltage up or down to ensure safe, reliable, and efficient energy distribution.
What is a Single Phase Transformer?
A single phase transformer is an electrical device that steps voltage up or down in power systems using a single alternating current.
✅ Converts high or low voltage levels for safe and efficient distribution
✅ Operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction
✅ Commonly used in residential, lighting, and small industrial loads
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
It is a vital component in the distribution of electrical power, playing a crucial role in converting voltage levels in alternating current (AC) systems. Unlike more complex three-phase transformers, single phase transformers are designed to operate on residential and light commercial circuits. By stepping voltage up or down, these transformers ensure that electrical power is delivered efficiently and safely to end users. A utility transformer plays a vital role in delivering power from generation stations to end users, with one phase transformers serving as an essential part of this system.
In the context of utility power, these units are essential for powering everyday appliances, lighting, and smaller electrical devices. Their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them key players in ensuring stable and consistent electrical delivery, particularly in low-power systems where efficiency is critical. Understanding the role of these transformers is important for anyone involved in electrical engineering, from technicians to homeowners, as they are foundational to how electricity is distributed worldwide. For higher demand facilities, three phase transformers are more common, these models remain essential where loads are smaller.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Definition and Functionality
A single phase transformer is an electrical device designed to operate on an alternating current system, primarily used to step voltage levels up or down in AC circuits. It plays a crucial role in distributing power by adjusting voltage levels, making it suitable for residential and small industrial applications. These transformers rely on the principle of mutual inductance, where energy is transferred between the primary winding and secondary winding through the magnetic field generated by the core. In essence, a one-phase unit takes high voltage from the primary winding and lowers it to a more usable level at the secondary winding, or vice versa, depending on the design. Understanding the construction of transformers helps explain how primary and secondary windings, cores, and insulation work together to ensure efficient performance. To learn the fundamentals behind voltage conversion and efficiency, see our guide on how transformers work, which explains the principles of electromagnetic induction in simple terms.
It typically consists of a core-type construction, where the magnetic core serves as the foundation for the windings. The primary winding generates a magnetic field that flows through the magnetic circuit of the core, creating flux. This flux links with the secondary winding, inducing an electromotive force (EMF) through electromagnetic induction. The efficient transfer of energy between the windings relies on the integrity of the magnetic circuit and the coupling of the flux between primary and secondary coils. A single phase transformer is widely used in residential and small-scale industrial applications to step voltage up or down efficiently. Engineers and technicians often study transformer components in detail to maintain reliable operation and extend equipment lifespan in both residential and industrial applications.
Applications of Single Phase Transformers
| Application Area | Typical Use Cases | Benefits of Using Single Phase Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Power Supply | Appliances, lighting, HVAC, small heating systems | Safe voltage levels, reliable performance, cost-effective |
| Commercial Buildings | Offices, shops, restaurants, small businesses | Adequate for low to medium loads, simple installation |
| Industrial Equipment | Pumps, motors, generators, small-scale manufacturing | Efficient power conversion for smaller industrial loads |
| Utility Distribution | Step-down from power lines for local supply | Provides usable low-voltage electricity for end users |
| Specialized Applications | Isolation, autotransformers, laboratory/medical devices | Electrical safety, noise reduction, voltage stability |
The functionality of a single phase transformer is essential in delivering electrical power in various settings, from homes to small businesses. A single supply system, which uses only one alternating current, is generally sufficient for low-power needs. The most common application is in residential areas where it supplies power to household appliances, lighting, and small heating systems. Its efficiency and relatively simple design make it ideal for low-load applications. Compared to more complex systems, such as three-phase transformers, single-supply designs are cost-effective and capable of meeting residential demand. In smaller commercial settings, they serve the same purpose, powering office buildings, shops, and restaurants, where the demand does not exceed what a single phase transformer can offer.
Construction and Components
A single phase transformer consists of two primary components: the magnetic core and the windings. The core is usually made of iron or another ferromagnetic material, which helps to concentrate and direct the magnetic field. The primary winding is connected to the input voltage, typically from a power grid, while the secondary winding delivers the transformed voltage to the load. The copper windings in each coil facilitate the flow of electrical current, ensuring efficient transfer. The relationship between these components is critical in determining the efficiency, voltage ratio, and overall performance in a power system.
Operation Principle of Single Phase Transformer
The operation of a single phase transformer is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, which explains how energy is transferred between the primary and secondary windings. When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces a current in the secondary winding. This process of mutual induction allows for the transformation of electrical power from one circuit to another, either stepping voltage up or down. The specific ratio of voltage between the primary and secondary windings depends on the number of turns of wire in each coil, a design feature that makes these units versatile for different voltage levels.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Utility Transformers Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Utility Transformers Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Comparison with Three Phase Transformer
One of the main advantages of a single phase transformer is its simplicity and ease of use in household and light commercial systems. However, it is important to note the differences between single-supply and three-phase transformers. While one-phase units are designed for residential and small commercial loads, three-phase transformers are used in more complex, industrial-grade applications where higher power demands exist. A three-line system uses three separate AC waveforms, making it more efficient for large-scale transmission and distribution. In contrast, single-supply transformers are better suited for homes and smaller businesses where the load does not justify a three-phase design.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a single phase transformer and how does it work?
A single phase transformer is an electrical device used to transfer energy between two circuits using alternating current (AC). It operates on a single supply, meaning it uses one alternating current waveform to provide power. It consists of two main components: the primary winding and the secondary winding, connected through a magnetic core. When current flows through the primary winding, it generates a magnetic field that induces a current in the secondary winding through mutual induction. This allows them to step voltage up or down depending on the winding ratio. The efficiency of the unit is influenced by the design of the core, the materials used, and the winding configuration.
What are the main applications of single phase transformers?
Single phase transformers are primarily used in residential and small commercial applications where power demands are relatively low. Common applications include supplying power to household appliances, lighting systems, and small heating or air conditioning units. They are widely used in utilities to step down high voltage from power lines to safe and usable levels for homes and businesses. Additionally, they are used in small industrial equipment, pumps, and generators. In rural areas where three-phase systems are not practical, single phase transformers provide electricity for essential infrastructure.
What is the difference between a single phase and a three phase transformer?
The main difference between a single-supply and a three-phase transformer lies in the number of AC waveforms used for power transmission. A single phase transformer works with one alternating current waveform and is common in residential and light commercial applications. A three-phase transformer, by contrast, is used in industrial and heavy-duty applications where higher power demand exists. A three-phase unit provides a continuous, balanced supply of power, resulting in greater efficiency for large-scale distribution. While a single phase transformer simpler and more cost-effective for lower loads, three-phase transformers are essential for heavy industry and high-power systems.
Can a transformer convert three phase to single phase?
A three-phase to single-supply conversion involves using a transformer with a specific winding configuration. In this process, one or two of the three-phase windings are used to create one output. Methods include:
-
Using a Three-Phase Unit with a Tapped Winding: The primary winding connects to a three-phase supply, while the secondary winding can be tapped to provide a one output.
-
Using a Bank: A bank of three transformers can be configured to deliver a single-supply output from a three-phase system, often using two transformers from the bank.
-
Phase Converter Devices: Another option is using a phase converter, which converts a multi-phase supply into one waveform output.
What are the common types?
There are several types of single phase transformer, each suited to specific applications:
-
Step-up: Increases voltage from the primary side to the secondary side. Common in transmission networks.
-
Step-down: Decreases voltage from the primary to the secondary side. Widely used in residential areas to reduce power line voltage.
-
Autotransformer: Uses one winding that serves as both primary and secondary. Compact and efficient, often used in motor starting.
-
Isolation: Isolates equipment from the supply, providing safety and reducing electrical interference. Used in medical and laboratory settings.
Each type is tailored to specific electrical needs, enhancing safety, efficiency, and reliability across applications.
A single phase transformer is an essential electrical device used to step voltage levels up or down in AC systems, typically for residential and small commercial applications. Operating on one alternating current supply, it consists of two primary components: the windings and magnetic core, which transfer energy through induction. These units are crucial for delivering power to appliances, lighting, and small equipment, ensuring voltage remains at a safe and usable level. While ideal for low-power needs, they are simpler and more cost-effective compared to three-phase designs. With their reliable construction and versatile uses, they remain a cornerstone of electrical distribution systems worldwide.
Related Articles