Arc Flash Study
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
Arc Flash Training CSA Z462 - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA FS3529 Fact Sheet – Lockout/Tagout Safety Procedures

- Learn how to disable machines and isolate energy sources safely
- Follow OSHA guidelines for developing energy control programs
- Protect workers with proper lockout devices and annual inspections
Arc flash study identifies electrical hazards, calculates incident energy, and defines PPE requirements. Following NFPA 70E, OSHA, and IEEE 1584 standards, it ensures workplace electrical safety, compliance, and protection against arc flash injuries.
What is an Arc Flash Study?
An arc flash study is a detailed engineering analysis of a facility’s electrical system to identify potential arc flash and shock hazards.
✅ Identifies electrical hazards and shock risk levels
✅ Defines PPE categories and approach boundaries
✅ Ensures compliance with NFPA 70E, CSA Z462, and OSHA regulations
An effective arc flash study forms the foundation of every electrical safety program. It measures system conditions—fault current, arc duration, and working distance—to determine the thermal energy released during an arc fault. These results guide PPE selection, equipment labeling, and risk reduction strategies that protect workers and minimize equipment damage.
Understanding the Arc Flash Study Process
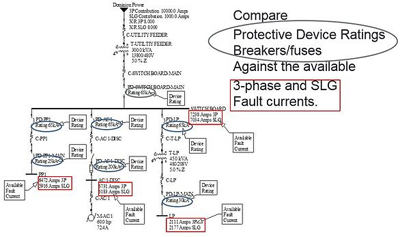
Performing a full arc flash study involves systematic data collection, short circuit analysis, and coordination studies to evaluate the performance of protective devices. The process ensures that incident energy levels are accurately measured, documented, and mitigated using IEEE 1584-2018 methodology.
Request a Free Training Quotation
This process quantifies potential exposure to hazardous energy and verifies that circuit breakers, fuses, and relays operate in proper sequence. The findings support labeling, safe work permits, and PPE selection—linking engineering data directly to on-site electrical safety.
To complete a compliant arc flash study, engineers must first conduct a short circuit analysis to determine fault current, arc duration, and working distance. These values form the foundation for incident energy calculations—defining the thermal output of an arc fault and ensuring accurate PPE categorization.
Test Your Knowledge About Arc Flash!
Think you know Arc Flash? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Following IEEE 1584 ensures standardized calculations and consistent results across all electrical equipment. Facilities must evaluate each component for potential exposure to hazardous energy and assign PPE levels based on actual incident energy values. The study results are later used to meet NFPA 70E labeling and documentation requirements, which are detailed in our Arc Flash Study Requirements Guide.
A full assessment enhances worker safety while fulfilling legal and regulatory obligations under NFPA 70E, OSHA, and CSA Z462. Facilities that proactively manage electrical hazards reduce downtime, injury risk, fines, and insurance costs.
Key Components of an Arc Flash Study
Short Circuit Study for Electrical Hazard Assessment
The short circuit analysis determines available fault current and verifies that protective devices are properly rated. Identifying weaknesses allows engineers to coordinate breakers and fuses correctly, reducing the risk of excessive fault energy and improving reliability.
Protective Device Coordination Study
This study ensures that fuses, breakers, and relays operate in sequence to limit arc duration and fault energy. Proper coordination minimizes hazard exposure and prevents nuisance tripping, crucial in environments like hospitals, data centers, and manufacturing facilities.
Arc Flash Risk Assessment
The arc flash risk assessment evaluates where and how arc flash events might occur. It calculates incident energy for each location, determines PPE levels, and defines safe approach distances. This process also considers maintenance practices and human factors to prioritize high-risk areas.
Arc Flash Hazard Evaluation and Incident Energy Calculation
Incident energy analysis establishes PPE levels and safe boundaries. This step also determines labelling requirements and informs mitigation measures such as barriers, remote switching, and alternative work procedures. The results provide actionable safety data for every system component.
Equipment Labelling, PPE Boundaries, and Documentation
Labels display critical information: boundary distances, fault current, incident energy, and PPE requirements. Clear, consistent labelling helps workers instantly recognize hazards and comply with OSHA standards.
For detailed labelling criteria, see our Arc Flash Study Requirements Guide.
Arc Flash Study Deliverables, Timeline, and Cost Overview
| Item | What’s Included | Typical Timeline | Cost Range* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Line Electrical Model | Updated diagram of your facility’s electrical distribution system | 1–2 weeks (data collection & drafting) | Included |
| Incident Energy Calculation Table | Detailed results for each piece of equipment, in cal/cm² | 1 week after data collection | Included |
| Breaker/Fuse Setting Review | Study and adjustment recommendations for protective devices | Integrated into study | Included |
| Arc Flash Labels | Printed and/or digital labels for all applicable equipment | Upon final approval | Included |
| Mitigation Recommendations | List of practical steps to reduce incident energy levels | Included in final report | Included |
| Training & Review Session | Walkthrough of results and compliance guidance for your team | 1–2 hours, scheduled after delivery | Optional, quoted separately |
| Full Project | All items above | 2–4 weeks total | $X,XXX – $XX,XXX |
Note: *Cost range varies depending on facility size, equipment quantity, and complexity.
Related Compliance Standards
An arc flash study often forms part of a larger NFPA 70E compliance initiative, including electrical hazard assessments, PPE boundary mapping, and OSHA Electrical Safety procedures. Together, these practices create a safer, more compliant workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should an arc flash study be updated?
NFPA 70E recommends updating your electrical hazard assessment every five years, or sooner if there are significant changes to your electrical system, such as new equipment, altered protective device settings, or facility expansions. Calculations should follow the IEEE 1584-2018 standard to ensure accurate results based on fault current, working distance, and system configuration.
How much does an Arc Flash Study cost?
Costs typically range from $X,XXX to $XX,XXX depending on facility size, complexity, and number of electrical assets. A detailed quotation is provided after reviewing your system layout and requirements.
How long does it take to complete?
Most projects take 2–4 weeks from the initial site data collection to delivery of the final report, labels, and recommendations. Larger facilities may require additional time.
Who is responsible for preparing the site for the arc flash study?
The facility owner or manager is responsible for ensuring safe access to all electrical equipment, providing accurate single-line diagrams (if available), and coordinating with maintenance staff to support data collection.
What standards are used to perform the study?
Arc flash studies are typically performed in accordance with IEEE 1584 for incident energy calculations, NFPA 70E or CSA Z462 for safety compliance, and applicable OSHA regulations.
What deliverables are included?
Deliverables typically include an updated single-line diagram, incident energy calculation tables, breaker/fuse setting review, arc flash labels, and a list of recommended mitigation measures.
How does it improve safety?
By identifying hazard levels and proper PPE requirements, an NFPA 70E compliance study helps reduce the risk of injury, ensures compliance with safety standards, and improves overall electrical system reliability.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Don't Forget Training
Even the best report is useless without qualified workers. Proper training ensures that your staff understands the results of your incident energy evaluation and how to respond. Our arc flash study training course prepares your team to interpret assessment data, apply labels, and use PPE effectively.
Training also reinforces a culture of safety. When workers understand the “why” behind PPE, labelling, and procedures, they’re more likely to comply and make safer decisions on the job. Ongoing education supports long-term risk reduction.
Take the Next Step
If you're ready to build or update your arc flash study, our resources can help:
-
Start with our incident energy analysis guide.
-
Review how to set safe distances in our arc flash boundary overview.
-
Learn how OSHA requirements apply on our OSHA Electrical Safety page.
Or get in touch to request a group training quotation tailored to your facility.
An arc flash study is more than just a compliance task—it’s a proactive measure that saves lives and protects infrastructure. The Electricity Forum is here to help you stay safe, informed, and fully prepared.
Explore More Arc Flash Topics:
Explore our Arc Flash Training Programs or contact us to Request a Free Training Quotation for group safety sessions and PPE consultation.