How Does a VFD Work?
By William Conklin, Associate Editor
Motor Control Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
A VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) controls AC motor speed by adjusting the frequency and voltage of electrical power. It improves energy efficiency, reduces mechanical stress, and offers precise motor control for HVAC systems, conveyors, pumps, and other industrial automation applications.
How Does a VFD Work?
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) regulates motor speed and torque through electronic control:
✅ Converts incoming AC power to DC and back to variable-frequency AC
✅ Controls motor speed to match load requirements and optimize energy use
✅ Enhances process control, system reliability, and equipment lifespan
Electric Motor Testing Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
The question "How Does a VFD Work?" is a common question in our VFD training course. There are also many questions about type and proper sizing that electrical engineers and maintenance professionals ask.
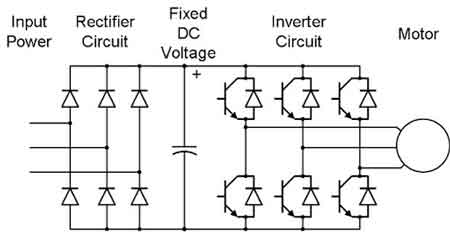
First, let me explain that a Variable Frequency Drive is an electronic device used to control the speed of AC induction motors. By varying the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor, the motor's speed and torque can be regulated precisely.
At the heart of a VFD is the inverter, which converts the DC voltage from the rectifier back into AC voltage at the desired frequency and voltage. The inverter uses Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) to switch the DC voltage on and off at high frequencies, which creates a series of voltage pulses. The width of these voltage pulses is controlled using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), allowing the control to regulate the speed and torque of the motor. To understand how speed regulation fits into broader motor systems, see our guide on electric motor control, which covers the fundamentals of managing torque, current, and direction.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
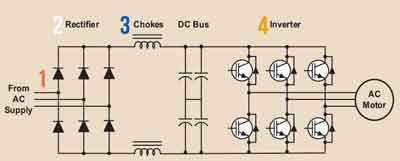
The control also includes a DC bus and a buffer between the rectifier and inverter. The DC bus stores the DC voltage from the rectifier and provides a constant voltage to the inverter, ensuring a steady supply of power to the motor. The control system regulates the voltage supplied to the DC bus and the frequency and voltage output of the inverter, allowing precise control of the motor speed. When precise speed control is needed in HVAC or industrial systems, consider the role of a variable frequency drive (VFD) in optimizing AC motor performance.
One of the benefits of using a controller is its ability to control motor speed and torque accurately. Adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, a VFD can regulate the speed and torque to match the load requirements. This flexibility allows the motor to operate efficiently under varying load conditions, reducing energy consumption and extending the motor's lifespan.
The VFD also offers benefits in terms of electric motor efficiency. Controlling the speed of the motor, a control reduces energy consumption, improving the overall efficiency of the motor. Additionally, the use of PWM reduces harmonic distortion in the motor, further improving motor efficiency.
Another essential component of control is the AC motor. AC motors are widely used in industrial applications due to their high efficiency and low maintenance requirements. A VFD can control the speed and torque of an AC motor by regulating the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor. The number of poles in the motor also affects the speed of the motor, allowing for additional control over the motor's operation.
If you’re just starting to explore the field, our overview of how electric motors work offers a solid foundation for understanding speed modulation principles.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of How a VFD Works
| Stage | Function | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1. AC Power Input | Receives standard AC electrical supply | The VFD connects to the power source (typically 230V, 460V, or higher 3-phase AC). |
| 2. Rectifier Stage | Converts AC to DC | A diode or SCR-based rectifier changes the incoming AC voltage to DC. |
| 3. DC Bus (Link) | Filters and smooths the DC voltage | Capacitors and inductors store and regulate the DC power, reducing voltage ripple. |
| 4. Inverter Stage | Converts DC back to controlled AC | IGBT or MOSFET switches rapidly to produce variable-frequency, variable-voltage AC. |
| 5. Motor Control | Sends controlled AC power to the motor | The output frequency and voltage determine motor speed and torque. |
| 6. Feedback/Monitoring | Optional sensors provide feedback for better control | Advanced VFDs use feedback to optimize performance and protect the motor (e.g., PID control). |
Variable Frequency Drive Basics
A VFD regulates the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to an AC motor. This regulation is accomplished using an inverter, which converts DC voltage from the rectifier back into AC voltage at the desired frequency and voltage. PWM is used to control the width of the voltage pulses, allowing the control to regulate the speed and torque of the motor precisely. By controlling the motor speed and torque, a VFD reduces energy consumption, improves motor efficiency, and extends the motor's lifespan. Overall, motor control is essential for efficient and reliable motor control in various industrial applications. For deeper insight into how motor structure affects control strategies, visit our page on electric motor design and its influence on speed and torque behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a VFD control a 3-phase Motor?
A motor controller can control the speed of a single-phase motor by regulating the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor. The VFD does this by converting the incoming AC power supply to DC power using a rectifier, storing the DC power in a DC bus, and then converting the DC power back to AC power at the desired frequency and voltage utilizing an inverter.
How Does a VFD Start and Stop a Motor?
The motor control can start and stop the motor by controlling the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor. When the motor control receives a start command, it increases the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor until it reaches the desired speed. Similarly, when the motor control receives a stop command, it gradually reduces the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor until it reaches a complete stop.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Motors and Drives Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Motors and Drives Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
How Does a VFD Slow Down a Motor?
To slow down a motor using a VFD, the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor are gradually reduced until the desired speed is reached. The motor control achieves this by using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to regulate the width of the voltage pulses supplied to the motor. By reducing the width of these pulses, the motor control can reduce the speed of the motor.
How Does a VFD Reduce Frequency?
The motor control reduces the frequency of the power supplied to the motor by adjusting the speed of the inverter switching. This switching is controlled by the VFD control system, which regulates the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor using PWM.
How Does a VFD Control the Speed of an AC Motor?
The motor controller controls the speed of an AC motor by regulating the power supply's frequency and voltage. By adjusting the frequency and voltage, the motor control can precisely control the speed and torque of the motor, ensuring optimal performance under varying load conditions.
What are the Different Components of a VFD?
The components of a VFD include a rectifier, DC bus, inverter, and control system. The rectifier converts the incoming AC power supply to DC power stored in the DC bus. The inverter uses IGBTs to convert the DC voltage to AC voltage with the desired frequency and voltage. Finally, the control system regulates the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor using PWM, allowing precise motor speed and torque control.
How Do You Select the Right VFD for Your Application?
Selecting the right motor control for your application depends on several factors, including motor horsepower, voltage and current rating, environmental conditions, and application requirements. Therefore, it is important to consider these factors carefully when selecting a VFD to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Enhancing system performance goes beyond speed adjustment—proper electric motor maintenance ensures long-term reliability and efficiency.
How Do You Program a VFD?
Programming a motor control involves inputting the desired setpoints for motor speed and torque into the VFD control system. The control system then adjusts the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor using PWM to achieve the desired setpoints.
What are the Safety Considerations When Working with VFDs?
Safety considerations when working with motor controls include following proper installation and wiring procedures, ensuring adequate grounding, and using appropriate personal protective equipment. It is also important to follow manufacturer guidelines for programming and operation and to use caution when working around live electrical components.
Related Articles