Short Circuit Protection Explained
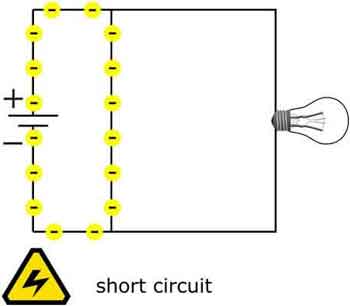
Substation Relay Protection Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
Short circuit protection safeguards electrical systems by interrupting excessive current flow caused by faults. It prevents equipment damage, fire risks, and personal injury by using fuses, breakers, or relays to quickly detect and isolate dangerous short circuits.
What is Short Circuit Protection?
Short circuit protection safeguards electrical systems and devices from potential hazards.
✅ Interrupts excessive current flow during faults to prevent hazards
✅ Protects equipment and wiring from overheating and damage
✅ Uses breakers, fuses, or relays to isolate the short circuit quickly
Basic Protection Relay Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Users can effectively mitigate risks associated with short circuits by understanding the various protection devices available, their applications, and the maintenance requirements for each. Through continuous learning, adherence to best practices, and the application of the appropriate protection devices, a safer and more reliable electrical environment can be achieved for all. Understanding the basics of electrical protection is essential for designing systems that prevent damage from short circuits and overcurrent events.
In today's world, electrical systems have become an essential part of our daily lives. They are used in homes, offices, industries, and other sectors. With the widespread usage of electrical systems, ensuring their safety and stability is crucial. One of the key aspects of electrical safety is safeguarding against electrical faults. Let's explore the concept of short circuit protection, its significance, how it operates, and the devices involved. Devices such as circuit protection devices are designed to detect faults and isolate affected sections, ensuring safety and reliability.
It is a method to safeguard electrical devices and systems from damage caused by a sudden and excessive flow of current, commonly referred to as an electrical fault. A short circuit occurs when an unintended path for electricity forms, typically through a low-resistance path. The importance lies in its ability to prevent damage to electrical devices and systems, minimize the risk of fire, and ensure user safety.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Several devices and mechanisms are in place to protect electrical systems from electrical faults. These devices typically work by detecting an overcurrent and interrupting the flow of electricity. The most commonly used devices include fuses, circuit breakers, and resettable fuses.
Fuses are one of the oldest and most widely used forms of overcurrent protection. They contain a thin wire or strip of metal that melts when the current exceeds a specified limit, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. Fuses are usually inexpensive and require replacement after a single use. Understanding the role of current-limiting fuses can help reduce the energy loss during a short-circuit event.
Comparative Devices and Their Functions
| Device | Primary Function | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Fuse | Melts to break the circuit when current exceeds safe limits | Residential panels, simple low-cost systems |
| Circuit Breaker | Detects and interrupts overcurrent; can be reset | Commercial and industrial power distribution |
| Resettable Fuse | Increases resistance to limit current, then resets after cooling | Consumer electronics, telecom equipment |
| Protective Relay | Monitors current and activates breakers during fault conditions | Substations, industrial control systems |
| Current Limiter | Restricts fault current to safe levels | High-voltage transmission and distribution |
On the other hand, circuit breakers are reusable electromechanical devices that detect overcurrent and automatically interrupt the flow of electricity. In addition, they can be manually reset once the fault has been resolved. Circuit breakers come in various types, such as thermal-magnetic, electronic, and hybrid. Selecting the correct circuit breaker type is crucial for effective short-circuit fault mitigation, particularly in industrial and high-load environments.
Resettable fuses, also known as polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PPTC) devices, offer an alternative approach to overcurrent protection. These devices have a conductive polymer that heats up and changes resistance when the current exceeds a certain level. This change in resistance interrupts the circuit, and the device resets itself after cooling down.
Other Forms of Protection
Aside from these primary devices, other forms of fault mitigation are employed to address different aspects of electrical safety. For instance, thermal protection prevents devices from overheating, while voltage protection safeguards against voltage surges or drops. Surge protection, however, protects devices from transient voltage spikes that can cause damage.
Choosing the right protective device for your application involves considering factors such as the type of load, the operating voltage and current, and the expected fault conditions. Additionally, it is crucial to understand the specifications and limitations of each device to ensure adequate fault mitigation.
Preventing damage to electrical devices is a primary goal. By detecting and interrupting overcurrents, these protection mechanisms can minimize the potential for fires, equipment damage, and costly downtime. Fuses and circuit breakers play a significant role in this regard, as they are designed to respond quickly and efficiently to electrical fault conditions.
Innovations in Protection
Innovations in protective devices also offer more sophisticated and efficient solutions to address specific challenges in various industries. For instance, power supply protection is particularly crucial for sensitive equipment and systems, ensuring they continue to operate safely and efficiently even under challenging conditions. Modern systems benefit from protective relays and multifunction relays, which offer fast and intelligent responses to electrical faults.
Educating oneself on the best practices for electrical safety is a vital step toward ensuring the well-being of both users and equipment. By understanding the potential hazards associated with electrical faults and implementing the appropriate protective measures, individuals and organizations can prevent costly damage, reduce downtime, and maintain the overall reliability of their electrical systems. Learning about different types of short circuit faults in power systems helps ensure that your protective strategy matches your application’s fault characteristics.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my system’s protection is adequate?
A thorough short circuit analysis, combined with regular system testing and review of fault current ratings, is essential. Consulting with an electrical engineer ensures your protective devices are correctly rated and coordinated for your specific load and environment.
Test Your Knowledge About Electrical Protection!
Think you know Electrical Protection? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Can modern smart breakers replace traditional devices?
Yes, smart breakers with integrated sensors and communication capabilities can enhance protection. They provide real-time monitoring, automated diagnostics, and remote reset capabilities, which can reduce downtime and improve safety in advanced systems.
How often should devices be tested or replaced?
It depends on the environment and usage. Industrial systems typically test equipment annually. Fuses are single-use and need to be replaced after operation, while breakers and relays should be tested periodically for both mechanical and functional integrity.
Does short circuit protection affect system efficiency?
Not directly. These devices stay dormant until a fault occurs. However, poor coordination or incorrect device selection can lead to nuisance tripping or underprotection, which may result in unexpected downtime or equipment wear.
What’s the difference from surge protection?
Short circuit protection deals with high currents resulting from internal faults, while surge protection addresses sudden voltage spikes caused by external events, such as lightning or switching surges. Both are necessary for comprehensive system safety.
Related Articles