What is the Load Factor in Electrical?
Substation Grounding Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
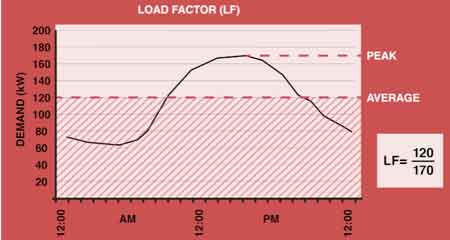
Load factor in electrical systems measures how efficiently electrical energy is used compared to the system’s maximum capacity. It reflects demand consistency, energy consumption, and system performance over a specific time period.
What is the Load Factor in Electrical?
The load factor in power systems compares the average load to the peak load, showing how consistently energy is used over time.
✅ Indicates electrical energy efficiency and utilization
✅ Helps optimize demand and reduce energy costs
✅ Used in power system analysis and utility planning
Load factor is a key metric used to measure the efficiency of a power system by analyzing its energy usage over a period of time. It is an important indicator for commercial and industrial facilities, as it helps determine how effectively power is being used. In simple terms, load factor compares the electricity demand over time to the system’s maximum potential load. To understand how power quality affects overall system efficiency, explore how voltage stability, harmonics, and demand patterns influence load factor performance.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
Understanding Load Factor
Load factor is a key metric used to measure the efficiency of a power system by analyzing its energy usage over a period of time. It helps determine how effectively power is being used in residential, commercial, or industrial facilities. In simple terms, it compares the total electricity consumed over time to the system’s maximum potential load.
Formula:
Load Factor = (Total kilowatt-hours used during the billing period) ÷ (Peak kilowatts × Hours in the billing period)
Example:
If a facility uses 100,000 kWh during a 30-day billing cycle and its peak demand is 250 kW, then:
Test Your Knowledge About Power Quality!
Think you know Power Quality? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
100,000 ÷ (250 × 720) = 0.56, or 56 %.
This means the power system was operating at 56 % of its potential capacity on average throughout the period.
Why Load Factor Matters
Load factor is a direct measure of energy efficiency, demand management, and operational performance. A high level reflects steady, predictable energy use, which minimizes utility demand charges and extends equipment life. Conversely, a low load factor signals irregular or intermittent use—costing more per kilowatt-hour and straining power infrastructure. A strong power factor correction program can directly improve load factor by reducing reactive current and optimizing energy use across industrial systems.
For utilities, customers with a high level of help stabilize grid operations and reduce the need for costly peak-generation capacity. For businesses, it translates into lower bills and more sustainable energy use.
Typical Load Factors by Sector
| Sector | Typical Load Factor | Usage Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | 25 – 40 % | Morning and evening peaks |
| Commercial | 40 – 60 % | Consistent daytime loads |
| Industrial | 60 – 80 % | Continuous manufacturing |
| Data Centers | 80 – 95 % | Constant 24/7 operation |
| Hospitals | 70 – 85 % | Critical systems always active |
These benchmarks reveal that continuous operations, such as data centers, tend to achieve near-optimal levels, while residential or office environments fluctuate more sharply throughout the day.
Factors That Influence Load Factor
Load factor varies due to several conditions: equipment efficiency, maintenance scheduling, automation, and process timing. Seasonal temperature changes, production shifts, or irregular equipment startups can create peaks that lower the ratio. Even weather events or power interruptions can distort the pattern. Monitoring real-time load curves helps engineers detect and correct inefficiencies before they increase costs. Learn how to use a power factor calculator to evaluate system performance and identify inefficiencies that contribute to low levels.
How to Improve Load Factor
Improving load factor begins with energy awareness and system planning. Key strategies include:
-
Load shifting: Schedule high-energy processes during off-peak hours.
-
Peak shaving: Use on-site generators or batteries to limit demand spikes.
-
Demand response programs: Adjust consumption when utilities request load reductions.
-
Automation and forecasting: Use smart meters and controls to stabilize load.
-
Efficient equipment upgrades: Replace aging motors, drives, and lighting with high-efficiency alternatives.
Each method smooths the energy profile, lowers demand charges, and enhances overall power quality. Understanding apparent power and its relationship to real and reactive power is essential for accurately assessing system capacity and calculating true efficiency.
Related Concepts
Load factor interacts with several other important performance indicators:
-
Power Factor: Measures how effectively current is converted into real power.
-
Demand Factor: Ratio of maximum demand to total connected load; indicates actual utilization.
-
Diversity Factor: Sum of individual maximum demands divided by the system’s total maximum demand.
-
Utilization Factor: Average load compared to rated capacity.
Understanding these differences allows engineers to analyze systems holistically and design solutions that improve efficiency and reliability. Explore how automatic power factor controllers help maintain stable voltage and minimize energy losses, key factors that directly enhance electrical load factor.
Limitations and Real-World Considerations
Perfect load factors are nearly impossible to achieve. Even well-optimized facilities experience fluctuations from maintenance, downtime, or seasonal variation. Meter accuracy, data intervals, and random events can all influence recorded values. Engineers often calculate a loss factor, the relationship between load factor and system losses, to identify hidden inefficiencies and improve audit precision. Effective electrical grounding ensures system safety and reliable current flow, both of which are critical for achieving stable demand and consistent load profiles.
The load factor is one of the most revealing indicators of how effectively power systems use energy. Understanding it in electrical systems helps engineers, facility managers, and utility planners measure efficiency, control costs, and enhance performance. By calculating and improving it, organizations can lower energy bills, reduce peak demand, and achieve more reliable, sustainable operations across every hour of the day. For a broader understanding of energy distribution and performance measurement beyond load factor, review our guide on what is power quality to see how these principles connect in maintaining efficient power systems.
Related Articles








