Renewable Energy Sources Explained
_1497100159.webp)
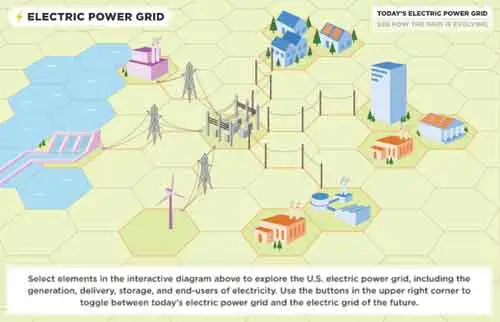
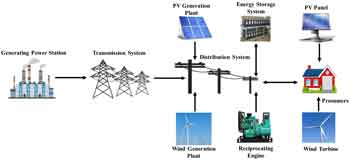
Renewable energy sources power modern grids via solar photovoltaics, wind turbines, and hydropower, using power electronics, inverters, smart grid controls, and energy storage to enhance reliability, grid integration, load balancing, and efficient transmission.
What Are Renewable Energy Sources?
Systems that convert solar, wind, and hydro energy into electricity using inverters and controls for grid compatibility.
✅ Employs power electronics: MPPT, PWM inverters, and converters
✅ Integrates with smart grids for frequency, voltage, and VAR control
✅ Requires storage (batteries, flywheels) for intermittency mitigation
Renewable Energy Sources are any renewable energy source that can be turned into the generation of electricity. Most renewable energy systems depend on natural souces of energy such as solar energy, wave energy, water energy, wind energy, etc that takes advantage of these energy souces to facilitate the conversion of those energies through the mechanical action of a generator to manufacture electricity. Also energy in the form of heat from deep in the crust of the Earth can be converted into electric power. This is known as "geothermal energy" production. There are other instances in which electricity can be generated from biofuel energy and fuel cell technology. The main advantage of renewable energy sources is that they are considered non-polluting but some can be unreliable, depending on when the sun shines and the wind blows, which is not how electricity is consumed. For a broader overview of definitions and technologies, see this guide to what renewable energy entails for additional context.
Despite inherent problems with the technology behind renewable energy sources, increasing environmental pressure is forcing development at an increasing pace. By the end of 2002, worldwide wind-power generation had exceeded 30 megawatts and had reached an annual growth rate of 25 per cent. Further insights into generation trends are summarized in this overview of renewable electricity with data on deployment.
Renewable Energy Sources
For readers comparing technologies, this summary of the main forms of alternative energy outlines typical applications.
Wind Energy Wind Energy Researchers recently calculated wind power's global potential. They have concluded that wind at many specific locations could produce more than enough electric power to meet world electricity demand. Comparative resource maps and case studies are available in this overview of alternative energy sources for deeper exploration.
Solar Energy The amount of solar energy by any measure is also enormous. Every hour more energy strikes the surface of the Earth than is consumed globally in a year.14 According to the DOE’s Solar Energy Technologies Program, there is on average between 2.8 and 6.2 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of sunlight available per square meter (m2) each day.15 The exact amount of sunlight depends on the region and the season. In the United States, the annual average is 4.8 kWh/m2 per day. Regional insolation data and technology basics are summarized in this renewable energy facts explainer for reference.
Advanced Hydro Hydro-electric power generation currently produces 10 per cent of the electricity production in the United States and is a clean source of renewable energy. However, mega dams and stations have a history of causing negative environmental impacts. Emerging fish-friendly designs and storage options are profiled in this overview of alternative energy solutions addressing environmental trade-offs.
Biomass Biomass is the burning of organic matter – typically agricultural crops and grasses – to produce heat or electricity. Biomass, which is different than solar and wind energy, does contribute significantly to world carbon dioxide emission levels. These emissions, on the other hand, can be offset through plantations of new crops and forests, which absorb carbon dioxide. For biomass to be a significant source of non-carbon emitting renewable energy, plants must be raised with little cultivation and fertilizer, and then transported over short distances, and harvested by methods that do not spoil the environment. Broader market trends and policy drivers are discussed in this guide to renewable alternative energy with practical examples.
Importantly, renewable energy sources produce virtually no greenhouse gas emissions and can effectively address climate change. If unchecked, the disruption of the earth’s atmosphere poses the greatest threat to humankind in our lifetimes. Continuing to fill the atmosphere with greenhouse gases will melt the ice caps, increase sea levels around the world, bring on more intense weather patterns, and adversely affect and disrupt food production, while destroying vast areas of the biosphere. Millions of inhabitants may be without food, shelter and clean water, which could cause political and social revolution and chaos. According to a studies, renewable energy souces, combined with industrial, commercial and institutional energy efficiency measures could decrease greenhouse gas emission pollution by as much as 70 per cent. With relatively little capital and short times for deployment, renewable energy sources could start to positively address global climate issues more rapidly than, say, nuclear power.