Breakdown Voltage Explained
Power Transformer Maintenance Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3873 Fact Sheet – Minimum Approach Distance and Training Requirements

- Calculate MAD using voltage and overvoltage values
- Ensure proper communication between host and contract employers
- Meet OSHA training requirements for qualified electrical workers
Breakdown voltage, also known as dielectric strength, is the maximum voltage that insulating oil can withstand before it fails. In transformers, switchgear, and other high-voltage systems, it safeguards insulation, prevents arcing, and ensures electrical performance.
What is Breakdown Voltage?
Breakdown voltage is the maximum voltage at which an insulating oil loses its dielectric strength and begins to conduct electricity, which is critical for transformer reliability and electrical system safety.
✅ Indicates the dielectric strength of insulating oil
✅ Prevents electrical discharges and transformer failure
✅ Ensures safety, reliability, and system performance
The breakdown voltage of oil, also known as its dielectric strength, is a critical measure of its ability to withstand electrical stress without failing. In simpler terms, it represents the maximum voltage that can be applied across an oil sample before it loses its insulating properties and allows electricity to flow through it. This characteristic is of paramount importance in electrical systems, especially those involving high voltages, where oil is commonly employed as an insulator and coolant. Understanding dielectric fluids is essential for evaluating breakdown voltage, since these insulating oils provide both cooling and dielectric strength in transformers and other high-voltage systems.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
The Importance of Breakdown Voltage in Electrical Systems
Insulating oil plays a crucial role in high-voltage equipment like transformers, cables, and switchgear. It acts as a barrier between energized components, preventing short circuits and ensuring the system's safe and reliable operation. If the oil's breakdown voltage is insufficient, it can lead to electrical discharges, arcing, and ultimately, equipment failure. Advancements in dissolved gas analysis complement BDV testing by detecting incipient faults, providing engineers with a more comprehensive picture of transformer insulation health
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Measuring Breakdown Voltage: Methods and Standards
The breakdown voltage of oil is typically determined using a standardized procedure known as a BDV test or insulating oil test. Two electrodes are immersed in an oil sample at a specific distance apart (commonly 2.5 mm or 4 mm). A gradually increasing alternating voltage is applied until the oil fails and conducts electricity, forming an arc. The voltage at which breakdown occurs is recorded as the BDV. The fundamental dielectric characteristics of insulating oils directly influence breakdown voltage, making routine monitoring vital for ensuring safe and reliable electrical performance.
To ensure consistency, internationally recognized standards are followed:
Standards define how BDV tests are performed, ensuring that results are accurate and comparable across laboratories and different types of equipment. The most common include:
-
ASTM D1816 – Uses VDE electrodes with smaller gaps, highly sensitive to moisture and contaminants.
-
IEC 60156 – Defines electrode shapes, gap distances, and voltage rise rates for precise comparisons.
-
ASTM D877 – Uses flat electrodes and is less sensitive to moisture, often applied for screening.
Multiple breakdowns are usually performed on the same sample to account for the statistical nature of the breakdown. The average value—or sometimes a Weibull distribution analysis—is used to represent the oil’s dielectric strength and failure probability. The performance of utility transformers depends heavily on the breakdown voltage of insulating oil, which protects windings and cores from electrical stress.
Factors Influencing Breakdown Voltage
Breakdown voltage is not a fixed property. It can be reduced or improved depending on the condition of the oil and the environment in which it operates. Key influences include:
-
Conducting impurities, such as dust, dirt, or metallic particles, lower dielectric strength by creating conductive pathways.
-
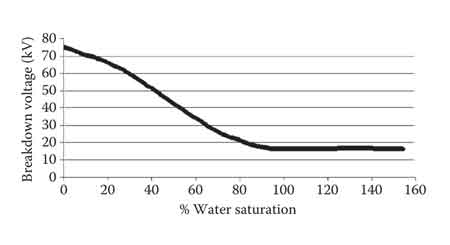
Moisture content: Even small amounts of dissolved water can drastically reduce BDV. A rise from 10 ppm to 100 ppm moisture can reduce BDV by nearly half in some studies. Water activity (relative saturation at operating temperature) is often a better predictor than ppm alone.
-
Age and oxidation: As oil ages, it oxidizes, forming acids, sludge, and other byproducts that degrade dielectric properties.
-
Temperature: Elevated oil temperatures reduce dielectric strength by accelerating molecular activity.
-
Electrical stress and gases: Prolonged high-voltage operation or partial discharges introduce gases that weaken the insulating medium.
-
Handling and storage: Exposure to humid air during sampling, transport, or storage can lower BDV significantly before the oil even enters service.
These influences demonstrate why proper oil management—from sampling to operation—is crucial for maintaining breakdown voltage. Effective condition monitoring programs utilize BDV testing in conjunction with dissolved gas analysis to assess insulation health and predict potential failures.
Typical Breakdown Voltage Values for Transformer Oil
Different operating conditions and oil qualities produce different BDV values. Industry standards provide benchmarks that help engineers decide whether oil is suitable for continued use:
-
New transformer oil typically exceeds 60 kV, as specified in IEC 60156.
-
In-service oil may be acceptable in the 30–50 kV range, depending on voltage class and equipment criticality.
-
Critical equipment often requires values significantly above the baseline for added safety margins.
A common threshold is 30 kV minimum, below which the oil is considered unsuitable. Utilities often maintain their own BDV acceptance limits tailored to voltage class, reliability needs, and risk tolerance. In high-voltage transformers, maintaining a strong dielectric barrier is critical to prevent arcing and ensure long-term reliability.
Breakdown Voltage Under Different Voltage Stresses
Insulating oil may be exposed to different kinds of electrical stress. Each has unique implications for breakdown behavior:
Test Your Knowledge About Utility Transformers!
Think you know Utility Transformers? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
-
AC stress – The most common laboratory test, representing steady sinusoidal operation.
-
DC stress – Oils may exhibit different insulating strengths when exposed to a constant polarity voltage.
-
Impulse stress – Surges from switching operations or lightning cause streamer propagation, often resulting in lower BDV than under AC tests.
These differences explain why engineers employ a range of oil dielectric tests to evaluate performance under real-world conditions.
Maintaining and Improving Breakdown Voltage
Because BDV directly reflects the health of insulating oil, utilities and industrial operators implement several strategies to maintain or restore dielectric strength:
-
Purification: Filtration, vacuum dehydration, or degassing removes moisture and impurities.
-
Regular testing: Trending BDV over time highlights degrading conditions before catastrophic failure occurs.
-
Proper storage and handling: Keep oil sealed, dry, and free from contamination during sampling and transfer.
-
Reconditioning: Chemical reclamation reduces acidity and sludge, improving insulating strength.
-
Replacement: If degradation is irreversible, fresh oil must be introduced.
Proper transformer insulation design and maintenance have a direct influence on breakdown voltage, thereby extending service life and safeguarding system performance.
Oil Types and Emerging Technologies
While mineral oil has traditionally been the insulating medium of choice, alternatives are becoming increasingly important in modern power systems:
-
Synthetic esters and natural esters (vegetable oils) – Often higher BDV values and more eco-friendly.
-
Silicone oils – Excellent thermal stability, but more expensive.
-
Nanoparticle-enhanced oils – Experimental dielectric fluids with TiO₂, SiO₂, or graphene nanoparticles. Research shows that BDV gains of 20–30% can be achieved by delaying dielectric breakdown and enhancing insulating strength.
Regular testing of transformer oil helps maintain dielectric strength, prevent breakdowns, and ensure safe operation under demanding electrical loads.
Breakdown Voltage and System Reliability
Breakdown voltage is just one measure of oil health, but it is most powerful when interpreted in conjunction with other diagnostics. Taken together, these tests give engineers a complete picture of transformer condition:
-
Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) – Detects incipient faults.
-
Acidity and sludge tests – Indicate oxidation.
-
Tan δ / dissipation factor – Measures dielectric losses.
-
Moisture analysis – Tracks water contamination.
A decline in BDV, combined with high moisture or gas levels, signals urgent maintenance action. For this reason, BDV is often treated as a first-line indicator of insulation health in transformer oil management programs.
Related Articles











