Dielectric Fluid

Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
Dielectric fluid is an insulating liquid used in electrical equipment like transformers and capacitors to prevent arcing, dissipate heat, and ensure system reliability. It offers high dielectric strength, thermal stability, and moisture resistance for safe operation.
What is Dielectric Fluid?
Dielectric fluid is a critical component in the operation and safety of electrical equipment, especially transformers and high-voltage switchgear.
✅ Provides electrical insulation and prevents arcing in high-voltage systems.
✅ Offers excellent thermal conductivity to dissipate heat.
✅ Protects components from moisture and contamination.
For industrial electricians, understanding their role in insulation, cooling, and arc suppression is essential for ensuring system reliability and preventing electrical failures. Let's review the properties, types, and maintenance requirements of dielectric fluids, providing practical insights into how they support energy efficiency, equipment longevity, and fire safety. Readers will learn about testing procedures, contamination risks, and how proper fluid management can minimize downtime and enhance overall electrical system performance. An oil-filled transformer relies on dielectric fluid to provide both insulation and cooling, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Applications in Electrical Equipment
In the realm of electrical equipment, insulating fluids are indispensable. They serve as both insulating and cooling agents, safeguarding systems from electric discharges while effectively dissipating heat. High-voltage applications, such as transformers, capacitors, and cables, rely heavily on these fluids to maintain stability and reliability. By preventing electric breakdown in these critical components, dielectric fluid ensures the longevity and efficiency of power distribution networks, which are the backbone of modern energy systems. The quality of transformer oil is crucial because its dielectric properties directly affect breakdown voltage and reliability.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Role in Immersion Cooling
The role of dielectric fluid in immersion cooling has gained prominence with the rise of data-intensive industries. Immersion cooling involves submerging electronic components in a thermally stable dielectric liquid to enhance heat transfer and reduce energy consumption. This technique is particularly advantageous in data centers, where efficient cooling solutions are essential. By dissipating heat more effectively than traditional air-cooling methods, dielectric fluid enables high-performance computing systems to operate at optimal levels while minimizing their environmental impacts. Understanding the role of transformer core and its interaction with insulating fluids can optimize cooling and extend transformer lifespan.
Comparison with Mineral Oils
A frequent comparison in the industry is between dielectric fluid and traditional mineral oil. While both serve as insulators and coolants, advanced dielectric fluid surpasses mineral oils in terms of thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and eco-friendliness. In high-voltage applications, \fluids offer lower operating temperatures and improved system reliability, reducing failure rates and extending service life. These properties make them an ideal choice for industries seeking to strike a balance between performance and sustainability.
Comparison of Dielectric Fluids
| Fluid Type | Key Properties | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral Oil | Moderate dielectric strength, good cooling, low cost | Widely available, proven track record | Low fire point, poor biodegradability |
| Natural Ester | High dielectric strength, high fire point (>300°C) | Biodegradable, excellent moisture tolerance | Higher cost, potential oxidation if unmanaged |
| Synthetic Ester | High thermal stability, excellent oxidation resistance | Long service life, superior high-temperature performance | Expensive, less eco-friendly than natural esters |
| Nanofluids | Enhanced dielectric strength and heat transfer via nanoparticles | Improved cooling, reduced aging, and emerging technology | Still experimental, higher production cost |
Types of Dielectric Fluids – Mineral Oil, Natural Ester, Synthetic Ester, Emerging Nanofluids
Dielectric fluid is categorized into several types, each with distinct properties and applications. Mineral oil has been the traditional choice due to its low cost and reliable insulation; however, it has limitations, including low flash points and environmental concerns. Natural ester fluids, derived from vegetable oils, offer high biodegradability, excellent moisture absorption, and fire safety advantages with fire points exceeding 300°C. Synthetic esters provide superior oxidation stability and thermal performance, making them suitable for high-load and high-temperature applications. Emerging nanofluids, enhanced with nanoparticles such as graphene or titanium dioxide, are at the forefront of innovation, offering improved thermal conductivity, higher dielectric strength, and enhanced aging resistance compared to conventional fluids. Regular testing of transformer oil filling is essential to avoid contamination and maintain high dielectric strength.
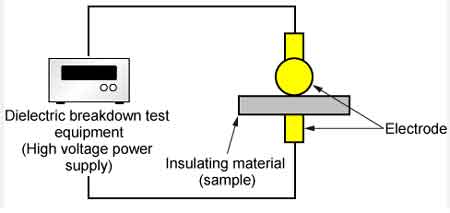
Material Compatibility & Impregnation – Testing Standards, Handling Guidance, Temperature Considerations
The interaction of dielectric fluids with insulation materials, gaskets, and seals plays a vital role in system performance. Certain fluids can cause swelling, shrinkage, or chemical degradation of elastomer-based gaskets, leading to leaks or compromised insulation. Modern ester fluids often require gasket materials that are highly resistant to hydrolysis and oxidation, such as nitrile or fluorocarbon elastomers, which offer superior stability compared to standard rubber seals.
Solid dielectrics, like pressboard or paper insulation, are directly affected by fluid absorption and impregnation. A properly selected fluid not only insulates but also strengthens these materials by filling microscopic voids and preventing moisture ingress. Poor fluid-material compatibility can reduce dielectric strength and lead to premature equipment failure.
The impregnation process, often carried out using vacuum-pressure cycles, ensures that the fluid thoroughly saturates the cellulose insulation. Vacuum impregnation removes trapped air and moisture before fluid introduction, improving dielectric performance and reducing the risk of partial discharges. Heating the fluid slightly during impregnation enhances its flow properties and ensures deep penetration. Standards like ASTM D3455 are used to verify material compatibility, while strict handling guidelines prevent contamination and degradation during storage. Proper transformer insulation depends on the fluid’s ability to prevent arcing and maintain thermal stability under load.
Material Compatibility and Impregnation Guidelines
| Aspect | Key Details | Recommended Standards/Tests | Notes and Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gasket Compatibility | Evaluates swelling, shrinkage, and chemical stability of elastomers | ASTM D3455 (Compatibility Testing) | Use nitrile or fluorocarbon gaskets for ester-based fluids |
| Solid Dielectrics | Interaction with pressboard, paper, or cellulose insulation | IEC 60296 (Insulating Liquids) | Ensure low-moisture fluids to prevent insulation breakdown |
| Impregnation Process | Saturation of solid insulation with dielectric fluid | Vacuum-Pressure Impregnation Methods | Perform multi-cycle vacuum drying for optimal saturation |
| Handling Guidance | Preventing contamination during storage and transfer | ASTM D923 (Sampling Insulating Liquids) | Use sealed containers and moisture-proof handling systems |
| Temperature Control | Managing viscosity and flow during impregnation | ASTM D3487 (Transformer Oils) | Preheat fluid slightly (40–60°C) for better impregnation |
Influence on Gaskets and Dielectric Materials
The compatibility of insulating fluids with gaskets, seals, and solid dielectric materials is critical for the long-term reliability of electrical equipment. Certain fluids can cause swelling, shrinkage, or chemical degradation of elastomer-based gaskets, leading to leaks or compromised insulation. Modern natural and synthetic ester fluids often require gasket materials that are highly resistant to hydrolysis and oxidation, such as nitrile or fluorocarbon elastomers, which offer superior stability compared to standard rubber seals.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Dielectric Fluids Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Dielectric Fluids Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Solid dielectrics, like pressboard or paper insulation, are directly affected by fluid absorption and impregnation. A properly selected fluid not only insulates but also strengthens these materials by filling microscopic voids and preventing moisture ingress. Poor fluid-material compatibility can reduce dielectric strength and lead to premature equipment failure.
Performance Metrics & Diagnostics – Presenting Typical Values, Standards, and Testing Procedures
Key performance metrics for insulating fluids include dielectric breakdown voltage, moisture content, viscosity, thermal conductivity, and flash point. Testing standards such as IEC 60156 (breakdown voltage), ASTM D877/D1816 (oil testing), and IEC 60247 (dielectric dissipation factor) are widely used to evaluate fluid health. Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) is another critical tool that monitors the condition of transformer oils by detecting gases produced during thermal or electrical faults.
Regular diagnostic testing allows early detection of contamination, oxidation, or moisture ingress. By tracking these values, maintenance teams can take corrective action before failures occur, extending equipment life and ensuring uninterrupted service.
Innovations – Nanofluids and Sustainability Trends
The development of nanofluids is revolutionizing dielectric technology. By suspending nanoparticles like Al₂O₃, SiO₂, or graphene in base fluids, engineers have achieved significant improvements in dielectric strength, heat transfer, and thermal stability. These advanced fluids operate under higher electrical stress while maintaining lower temperatures, leading to greater reliability and efficiency.
Sustainability trends favor the use of natural and synthetic esters due to their biodegradability, reduced greenhouse gas footprint, and compliance with modern fire safety and environmental standards. As industries shift toward eco-friendly energy solutions, insulating fluids are being optimized to deliver both performance and environmental benefits. Monitoring breakdown voltage helps evaluate the condition of dielectric fluids and ensures they can withstand high voltages.
Practical Guidance – Selection Criteria Based on Fire Safety, Environmental Regulations, Maintenance Strategy, and Transformer Design Optimization
Choosing the right fluid involves striking a balance between technical performance and safety and environmental requirements. Fire safety considerations often favour natural esters, which have much higher fire points than mineral oils. Environmental regulations are increasingly encouraging fluids with low toxicity and high biodegradability to minimize ecological risks. A maintenance strategy also plays a role; fluids with greater oxidation stability and moisture tolerance can extend maintenance intervals, thereby lowering overall operating costs. Ultimately, transformer design optimization—including heat transfer requirements, viscosity, and load profiles—may dictate which fluid type offers the best efficiency and long-term reliability. Core parts of transformer components are submerged in dielectric fluid to minimize electrical discharge and control temperature.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Critical Components for Industrial Electricians?
Understanding the intricacies of electrical power distribution transformers is paramount for industrial electricians. These vital components play a pivotal role in the efficient and reliable delivery of electrical power to industries and businesses worldwide. By delving into the fundamental concepts of transformer operation, types, maintenance, and future trends, industrial electricians can gain valuable insights to optimize electrical systems, troubleshoot potential issues, and ensure a reliable and uninterrupted power supply. Insulating oil is essential for preventing electric discharges in high-voltage equipment. By immersing electrical components in these fluids, manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of arcing and short circuits. Techniques like immersion cooling utilize insulating oil to effectively dissipate heat generated by high-power components, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
What are the key characteristics of an effective electrical insulating oil?
The primary function of electrical insulating oil is to provide electrical insulation. Filling the gaps between electrical components prevents arcing and short circuits, which can lead to equipment failure and potentially hazardous situations. Additionally, dielectric fluid excels at dissipating heat generated by electrical equipment, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
What are the most common types of electrical insulating oil, and where are they used?
Electrical insulating oil comes in various types, each with its unique properties and applications. Historically, mineral oil has been the most commonly used dielectric fluid, offering a balance of cost-effectiveness and reliability. However, its environmental impact and susceptibility to degradation have led to the development of alternative options. Synthetic esters, for instance, provide superior dielectric properties, thermal stability, and biodegradability, making them a more environmentally friendly choice. Silicone fluids, renowned for their exceptional thermal stability and resistance to oxidation, are frequently employed in high-voltage applications where reliability and long-term performance are crucial. While perfluorinated fluids offer exceptional dielectric strength and thermal stability, their high cost and potential environmental impact limit their widespread use.
The performance of electrical insulating oil is influenced by several factors. A crucial factor is dielectric strength, which measures the fluid's ability to withstand high voltages without breaking down. Additionally, the fluid's thermal stability is essential for maintaining its insulating properties under varying temperature conditions. Chemical stability is also important, as it ensures the fluid's resistance to degradation and oxidation. Furthermore, a low flash point and flammability rating are crucial for safety, especially in enclosed environments. Lastly, the environmental impact of the fluid, including its biodegradability and toxicity, is becoming increasingly significant in the selection of dielectric fluids.
How does transformer oil impact sustainability?
Regular testing and maintenance are crucial to ensure the optimal performance of insulating oil. These tests evaluate critical properties, including dielectric strength, moisture content, and acidity level. By monitoring these parameters, engineers can identify potential issues and take corrective actions to prevent equipment failures. This proactive approach helps maintain the reliability and safety of electrical systems.
Dielectric fluid is an essential component in high-voltage electrical systems. They provide critical insulation and cooling properties, preventing electrical breakdowns and ensuring the reliable operation of equipment. By understanding the properties and applications of different dielectric fluids, engineers and technicians can select the most suitable fluid for specific applications and optimize system performance.
Related Articles