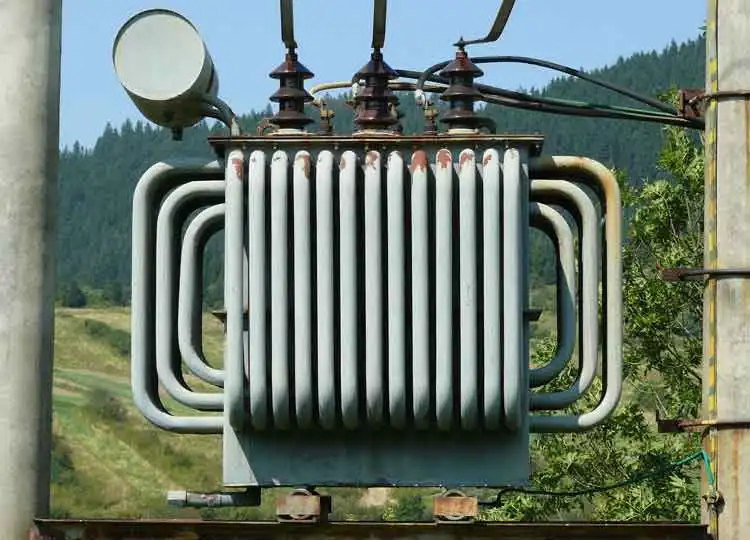
Medium Voltage Transformer
By R.W. Hurst, Editor

Substation Maintenance Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
A medium voltage transformer converts electrical energy between 1 kV and 35 kV, ensuring efficient power distribution in commercial, utility, and industrial systems. It plays a vital role in voltage regulation, energy efficiency, and protection of downstream equipment.
What is a Medium Voltage Transformer?
A medium voltage transformer is an essential component in electrical systems that manage voltages between 1 kV and 35 kV.
✅ Converts electrical energy for power distribution in utility, industrial, and commercial systems
✅ Regulates voltage to protect downstream equipment and maintain grid stability
✅ Enhances energy efficiency and supports safe, reliable electrical infrastructure
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
The medium voltage transformer is the unsung workhorse of our electrical infrastructure, playing a pivotal role in delivering electricity to homes, businesses, and industries. Operating within the medium voltage range, typically between 2.4 kV and 69 kV, this device is crucial for reducing the voltage from the distribution grid to levels suitable for various applications. Our utility transformers guide explores how AC transformers support national transmission infrastructure.
It is an electrical device designed to convert electrical energy from higher voltage levels, typically ranging between 1kV and 72.5kV, to lower voltage levels suitable for distribution and end-use applications. They are essential in managing the flow of electrical energy from transmission systems to distribution networks, ensuring that the voltage levels are appropriate for safe and efficient utilization by consumers. Proper transformer construction ensures magnetic efficiency and electrical insulation. Discover how a padmount transformer simplifies urban distribution with compact, ground-level installation.
Applications of Medium Voltage Transformers
They are used in a wide array of applications across different sectors:
-
Industrial Facilities: In manufacturing plants and factories, they supply power to large motors, machinery, and other equipment that require higher voltage levels for optimal performance.
-
Commercial Buildings: Office complexes, shopping malls, hospitals, and other commercial establishments rely on them to power lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, as well as other essential electrical loads.
-
Utility Substations: Electric utilities utilize them to step down the voltage from transmission lines to lower levels suitable for distribution to residential and commercial customers.
-
Renewable Energy Systems: Solar and wind farms often incorporate them to connect the generated electricity to the grid.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Utility Transformers Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Utility Transformers Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Medium Voltage Transformer Comparison Table
| Transformer Type | Cooling & Insulation | Common Applications | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry-Type (VPI) | Air-cooled (AN/AF), Class B/F/H | Commercial buildings, indoor substations | Low fire risk, oil-free, easy maintenance |
| Cast Resin | Air-cooled, epoxy-encapsulated | Tunnels, offshore platforms, renewable systems | Fire-resistant, moisture-proof, compact design |
| Oil-Immersed | ONAN/ONAF, mineral or synthetic oil | Utility substations, heavy industrial loads | High thermal capacity, long life, efficient cooling |
| Pad-Mounted | Oil or cast resin, sealed enclosure | Residential neighborhoods, campuses, commercial zones | Tamper-proof, ground-accessible, compact outdoor unit |
| Instrument Transformer | Low heat, epoxy or oil insulation | Protection relays, switchgear metering | High measurement accuracy, low power burden |
| Substation Transformer | ONAN/ONAF, dry-type or oil-filled | Grid step-down, renewable energy tie-in | High kVA rating, robust for long-term grid service |
Types of Medium Voltage Transformers
Medium voltage transformers come in a variety of designs to meet the diverse requirements of industrial, commercial, and utility power systems. The selection of transformer type depends on factors such as the installation environment, cooling requirements, fire safety considerations, and load characteristics. Each type offers unique advantages in terms of performance, protection, and reliability, making it essential to select the right one for your specific application. Below are the most commonly used types, along with their primary features.
Several types are available, each suited to specific applications:
-
Dry-Type Transformers: These are air-cooled and do not use liquid insulation. They are suitable for indoor applications where fire safety is a concern.
-
Oil-Immersed Transformers: These use oil for cooling and insulation, making them ideal for outdoor installations and higher power ratings. Learn more about the structure and parts that make up these units in our detailed guide on transformer components.
-
Pad-Mounted Transformers: These are enclosed in tamper-resistant housings and installed on concrete pads, commonly used in residential and commercial areas. To understand the role of enclosure and accessibility in commercial settings, read about padmount transformer designs.
-
Cast Resin Transformers: These transformers have windings encapsulated in resin, providing excellent fire resistance and suitability for both indoor and outdoor use.
-
Instrument Transformers: These are used for measuring and protection purposes, ensuring accurate voltage and current readings in power systems.
Selecting the Right Medium Voltage Transformer
Selecting the right medium voltage transformer is critical for ensuring reliable performance, operational safety, and long-term efficiency. Because transformers must integrate seamlessly into electrical systems, a range of technical and environmental factors must be carefully evaluated. From voltage and power ratings to insulation materials and cooling methods, each specification plays a vital role in matching the transformer to its intended application. The following considerations can help guide the selection process for optimal results.
Choosing the appropriate one involves careful consideration of several factors:
-
Voltage Rating: The transformer's primary and secondary voltage levels must match the system requirements to ensure proper operation and safety.
-
Power Rating (kVA): The transformer should be sized to handle the maximum load of the connected equipment or system.
-
Insulation Type: The choice between liquid-filled and dry-type transformers depends on environmental conditions, space constraints, and safety considerations.
-
Cooling Method: Various cooling methods, including natural air, forced air, natural oil, and forced oil, are available, and the selection depends on the transformer's location and load profile. Learn how proper transformer insulation can extend service life and enhance safety in medium-voltage environments.
When selecting a medium voltage transformer, several factors must be taken into account:
-
Load Requirements: Assess the power needs of the application, including peak and average load demands, to ensure it can handle the required capacity.
-
Voltage Levels: Determine the input and output voltage levels to ensure compatibility with the existing electrical infrastructure.
-
Cooling Method: Choose between dry-type and oil-immersed transformers based on the installation environment and cooling requirements.
-
Environmental Conditions: Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to corrosive elements when selecting the type of transformer and its materials.
-
Regulatory Standards: Ensure the transformer complies with relevant industry standards and regulations to guarantee safety and reliability.
Safety Precautions
Working with them demands strict adherence to safety protocols. They carry high voltages and pose significant electrical hazards. Only qualified and trained personnel should handle or work on these devices. Always de-energize them and ensure proper grounding before conducting any maintenance or repairs. Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulating gloves and safety glasses, is crucial for ensuring personal safety. The 3 phase transformers design enables balanced power distribution across industrial loads.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Working with medium voltage transformers involves several safety precautions:
-
Proper Training: Ensure that all personnel handling them are adequately trained and certified in electrical safety practices.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers should wear appropriate PPE, such as insulated gloves, helmets, and protective clothing, to prevent electrical shock and injury.
-
Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine inspections and maintenance to identify and address potential issues before they lead to failures or hazards.
-
Clear Signage and Barriers: Mark transformer installations with clear warning signs and barriers to prevent unauthorized access and accidental contact.
-
Emergency Procedures: Establish and communicate clear emergency procedures for responding to electrical incidents, including shutdown protocols and first aid measures.
They are indispensable components of our electrical infrastructure. Their ability to efficiently and safely transform voltage levels is vital for ensuring the reliable delivery of electricity to our homes, businesses, and industries. By understanding their types, applications, and safety considerations, we can appreciate the crucial role they play in powering our modern world. Explore how transformer core design impacts magnetic flux flow and voltage conversion efficiency.
Related Articles