UK low-carbon electricity 2019 saw stalled growth as renewables rose slightly, wind expanded, nuclear output fell, coal hit record lows, and net-zero targets demand faster deployment to cut CO2 intensity below 100gCO2/kWh.
Key Points
Low-carbon sources supplied 54% of UK power in 2019, up just 1TWh; wind grew, nuclear fell, and coal dropped to 2%.
✅ Wind up 8TWh; nuclear down 9TWh amid outages
✅ Fossil fuels 43% of generation; coal at 2%
✅ Net-zero needs 15TWh per year added to 2030
The amount of electricity generated by low-carbon sources in the UK stalled in 2019, Carbon Brief analysis shows.
Low-carbon electricity output from wind, solar, nuclear, hydro and biomass rose by just 1 terawatt hour (TWh, less than 1%) in 2019. It represents the smallest annual increase in a decade, where annual growth averaged 9TWh. This growth will need to double in the 2020s to meet UK climate targets while replacing old nuclear plants as they retire.
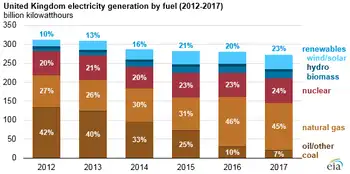
Some 54% of UK electricity generation in 2019 came from low-carbon sources, including 37% from renewables and 20% from wind alone, underscoring wind's leading role in the power mix during key periods. A record-low 43% was from fossil fuels, with 41% from gas and just 2% from coal, also a record low. In 2010, fossil fuels generated 75% of the total.
Carbon Brief’s analysis of UK electricity generation in 2019 is based on figures from BM Reports and the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS). See the methodology at the end for more on how the analysis was conducted.
The numbers differ from those published earlier in January by National Grid, which were for electricity supplied in Great Britain only (England, Wales and Scotland, but excluding Northern Ireland), including via imports from other countries.
Low-carbon low
In 2019, the UK became the first major economy to target net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, increasing the ambition of its legally binding Climate Change Act.
To date, the country has cut its emissions by around two-fifths since 1990, with almost all of its recent progress coming from the electricity sector.
Emissions from electricity generation have fallen rapidly in the decade since 2010 as coal power has been almost phased out and even gas output has declined. Fossil fuels have been displaced by falling demand and by renewables, such as wind, solar and biomass.
But Carbon Brief’s annual analysis of UK electricity generation shows progress stalled in 2019, with the output from low-carbon sources barely increasing compared to a year earlier.
The chart below shows low-carbon generation in each year since 2010 (grey bars) and the estimated level in 2019 (red). The pale grey bars show the estimated future output of existing low-carbon sources after old nuclear plants retire and the pale red bars show the amount of new generation needed to keep electricity sector emissions to less than 100 grammes of CO2 per kilowatt hour (gCO2/kWh), the UK’s nominal target for the sector.
Annual electricity generation in the UK by fuel, terawatt hours, 2010-2019. Top panel: fuel by fuel. Bottom panel: cumulative total generation from all sources. Source: BEIS energy trends, BM Reports and Carbon Brief analysis. Chart by Carbon Brief using Highcharts.
As the chart shows, the UK will require significantly more low-carbon electricity over the next decade as part of meeting its legally binding climate goals.
The nominal 100gCO2/kWh target for 2030 was set in the context of the UK’s less ambitious goal of cutting emissions to 80% below 1990 levels by 2050. Now that the country is aiming to cut emissions to net-zero by 2050, that 100gCO2/kWh indicator is likely to be the bare minimum.
Even so, it would require a rapid step up in the pace of low-carbon expansion, compared to the increases seen over the past decade. On average, low-carbon generation has risen by 9TWh each year in the decade since 2010 – including a rise of just 1TWh in 2019.
Given scheduled nuclear retirements and rising demand expected by the Committee on Climate Change (CCC) – with some electrification of transport and heating – low-carbon generation would need to increase by 15TWh each year until 2030, just to meet the benchmark of 100gCO2/kWh.
For context, the 3.2 gigawatt (GW) Hinkley C new nuclear plant being built in Somerset will generate around 25TWh once completed around 2026. The world’s largest offshore windfarm, the 1.2GW Hornsea One scheme off the Yorkshire coast, will generate around 5TWh each year.
The new Conservative government is targeting 40GW of offshore wind by 2030, up from today’s figure of around 8GW. If policies are put in place to meet this goal, then it could keep power sector emissions below 100gCO2/kWh, depending on the actual performance of the windfarms built.
However, new onshore wind and solar, further new nuclear or other low-carbon generation, such as gas with carbon capture and storage (CCS), is likely to be needed if demand is higher than expected, or if the 100gCO2/kWh benchmark is too weak in the context of net-zero by 2050.
The CCC says it is “likely” to “reflect the need for more rapid deployment” of low-carbon towards net-zero emissions in its advice on the sixth UK carbon budget for 2033-2037, due in September.
Trading places
Looking more closely at UK electricity generation in 2019, Carbon Brief’s analysis shows why there was so little growth for low-carbon sources compared to the previous year.
There was another increase for wind power in 2019 (up 8TWh, 14%), with record wind generation as several large new windfarms were completed including the 1.2GW Hornsea One project in October and the 0.6GW Beatrice offshore windfarm in Q2 of 2019. But this was offset by a decline for nuclear (down 9TWh, 14%), due to ongoing outages for reactors at Hunterston in Scotland and Dungeness in Kent.
(Analysis of data held by trade organisation RenewableUK suggests some 0.6GW of onshore wind capacity also started operating in 2019, including the 0.2GW Dorenell scheme in Moray, Scotland.)
As a result of these movements, the UK’s windfarms overtook nuclear for the first time ever in 2019, becoming the country’s second-largest source of electricity generation, and earlier, wind and solar together surpassed nuclear in the UK as momentum built. This is shown in the figure below, with wind (green line, top panel) trading places with nuclear (purple) and gas (dark blue) down around 25% since 2010 but remaining the single-largest source.
Annual electricity generation in the UK by fuel, terawatt hours, 2010-2019. Top panel: fuel by fuel. Bottom panel: cumulative total generation from all sources. Source: BEIS energy trends, BM Reports and Carbon Brief analysis. Chart by Carbon Brief using Highcharts.
The UK’s currently suspended nuclear plants are due to return to service in January and March, according to operator EDF, the French state-backed utility firm. However, as noted above, most of the UK’s nuclear fleet is set to retire during the 2020s, with only Sizewell B in Suffolk due to still be operating by 2030. Hunterston is scheduled to retire by 2023 and Dungeness by 2028.
Set against these losses, the UK has a pipeline of offshore windfarms, secured via “contracts for difference” with the government, at a series of auctions. The most recent auction, in September 2019, saw prices below £40 per megawatt hour – similar to current wholesale electricity prices.
However, the capacity contracted so far is not sufficient to meet the government’s target of 40GW by 2030, meaning further auctions – or some other policy mechanism – will be required.
Coal zero
As well as the switch between wind and nuclear, 2019 also saw coal fall below solar for the first time across a full year, echoing the 2016 moment when wind outgenerated coal across the UK, after it suffered another 60% reduction in electricity output. Just six coal plants remain in the UK, with Aberthaw B in Wales and Fiddlers Ferry in Cheshire closing in March.
Coal accounted for just 2% of UK generation in 2019, a record-low coal share since centralised electricity supplies started to operate in 1882. The fuel met 40% of UK needs as recently as 2012, but has plummeted thanks to falling demand, rising renewables, cheaper gas and higher CO2 prices.
The reduction in average coal generation hides the fact that the fuel is now often not required at all to meet the UK’s electricity needs. The chart below shows the number of days each year when coal output was zero in 2019 (red line) and the two previous years (blue).
Cumulative number of days when UK electricity generation from renewable sources has been higher than that from fossil fuels. Source: BEIS energy trends, BM Reports and Carbon Brief analysis. Chart by Carbon Brief using Highcharts.
The 83 days in 2019 with zero coal generation amount to nearly a quarter of the year and include the record-breaking 18-day stretch without the fuel.
Great Britain has been running for a record TWO WEEKS without using coal to generate electricity – the first time this has happened since 1882.
The country’s grid has been coal-free for 45% of hours in 2019 so far.https://www.carbonbrief.org/countdown-to-2025-tracking-the-uk-coal-phase-out …
Coal generation was set for significant reductions around the world in 2019 – including a 20% reduction for the EU as a whole – according to analysis published by Carbon Brief in November.
Notably, overall UK electricity generation fell by another 9TWh in 2019 (3%), bringing the total decline to 58TWh since 2010. This is equivalent to more than twice the output from the Hinkley C scheme being built in Somerset. As Carbon Brief explained last year, falling demand has had a similar impact on electricity-sector CO2 emissions as the increase in output from renewables.
This is illustrated by the fact that the 9TWh reduction in overall generation translated into a 9TWh (6%) cut in fossil-fuel generation during 2019, with coal falling by 10TWh and gas rising marginally.
Increasingly renewable
As fossil-fuel output and overall generation have declined, the UK’s renewable sources of electricity have continued to increase. Their output has risen nearly five-fold in the past decade and their share of the UK total has increased from 7% in 2010 to 37% in 2019.
As a result, the UK’s increasingly renewable grid is seeing more minutes, hours and days during which the likes of wind, solar and biomass collectively outpace all fossil fuels put together, and on some days wind is the main source as well.
The chart below shows the number of days during each year when renewables generated more electricity than fossil fuels in 2019 (red line) and each of the previous four years (blue lines). In total, nearly two-fifths of days in 2019 crossed this threshold.
Cumulative number of days when the UK has not generated any electricity from coal. Source: BEIS energy trends, BM Reports and Carbon Brief analysis. Chart by Carbon Brief using Highcharts.
There were also four months in 2019 when renewables generated more of the UK’s electricity than fossil fuels: March, August, September and December. The first ever such month came in September 2018 and more are certain to follow.
National Grid, which manages Great Britain’s high-voltage electricity transmission network, is aiming to be able to run the system without fossil fuels by 2025, at least for short periods. At present, it sometimes has to ask windfarm operators to switch off and gas plants to start running in order to keep the electricity grid stable.
Note that biomass accounted for 11% of UK electricity generation in 2019, nearly a third of the total from all renewables. Some two-thirds of the biomass output is from “plant biomass”, primarily wood pellets burnt at Lynemouth in Northumberland and the Drax plant in Yorkshire. The remainder was from an array of smaller sites based on landfill gas, sewage gas or anaerobic digestion.
The CCC says the UK should “move away” from large-scale biomass power plants, once existing subsidy contracts for Drax and Lynemouth expire in 2027.
Using biomass to generate electricity is not zero-carbon and in some circumstances could lead to higher emissions than from fossil fuels. Moreover, there are more valuable uses for the world’s limited supply of biomass feedstock, the CCC says, including carbon sequestration and hard-to-abate sectors with few alternatives.
Methodology
The figures in the article are from Carbon Brief analysis of data from BEIS Energy Trends chapter 5 and chapter 6, as well as from BM Reports. The figures from BM Reports are for electricity supplied to the grid in Great Britain only and are adjusted to include Northern Ireland.
In Carbon Brief’s analysis, the BM Reports numbers are also adjusted to account for electricity used by power plants on site and for generation by plants not connected to the high-voltage national grid. This includes many onshore windfarms, as well as industrial gas combined heat and power plants and those burning landfill gas, waste or sewage gas.
By design, the Carbon Brief analysis is intended to align as closely as possible to the official government figures on electricity generated in the UK, reported in BEIS Energy Trends table 5.1.
Briefly, the raw data for each fuel is in most cases adjusted with a multiplier, derived from the ratio between the reported BEIS numbers and unadjusted figures for previous quarters.
Carbon Brief’s method of analysis has been verified against published BEIS figures using “hindcasting”. This shows the estimates for total electricity generation from fossil fuels or renewables to have been within ±3% of the BEIS number in each quarter since Q4 2017. (Data before then is not sufficient to carry out the Carbon Brief analysis.)
For example, in the second quarter of 2019, a Carbon Brief hindcast estimates gas generation at 33.1TWh, whereas the published BEIS figure was 34.0TWh. Similarly, it produces an estimate of 27.4TWh for renewables, against a BEIS figure of 27.1TWh.
National Grid recently shared its own analysis for electricity in Great Britain during 2019 via its energy dashboard, which differs from Carbon Brief’s figures.
Related News