Solar Wars Draw Millions in Cash in Threat to Rooftop Industry

Electrical Testing & Commissioning of Power Systems
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
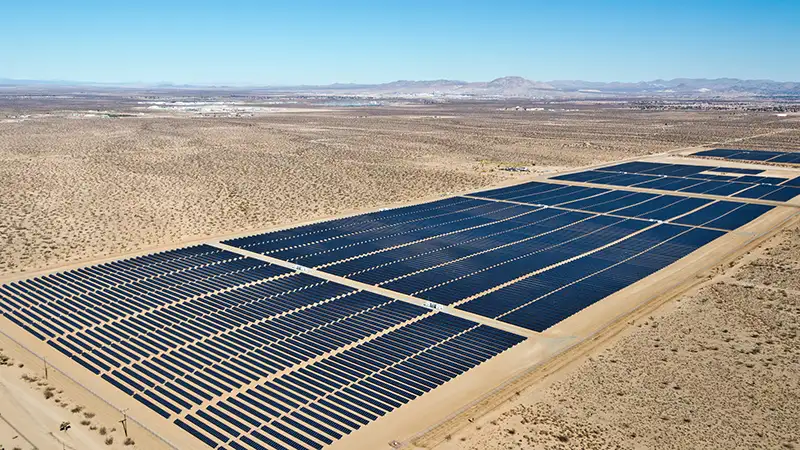
Arizona Rooftop Solar Battle intensifies as regulators weigh net metering, utility fees, and solar credits; APS, Pinnacle West, and SolarCity flood elections, shaping Arizona Corporation Commission policy and statewide renewable energy incentives.
Key Points
A high-stakes clash over net metering, utility fees, and solar credits before Arizona regulators, affecting consumers.
✅ Utilities seek higher fees and lower net metering credits
✅ Solar firms fund campaigns to sway regulator elections
✅ Decision could reshape statewide rooftop solar economics
Arizona - November 3, 2016 - There’s a war brewing over the future of rooftop solar, and Arizona is at ground zero.
Pinnacle West Capital Corp., which owns the state’s largest utility, last week said it has formed a third-party group to support candidates for an elected state board that regulates their industry. The move promises to inject $1 million into a race in which SolarCity Corp., a rooftop solar provider, is already planning to spend $2 million though a nonprofit it supports, according to officials from the two groups.
It’s the latest twist in a three-year political battle, mirrored by debates over energy freedom in the South among advocates, that’s been punctuated by charges of undue influence, an ongoing probe by the U.S. Attorney’s office and $300,000 in threatened state fines. At stake: A board ruling on a request to raise fees and drastically cut how much homeowners are paid for the solar energy they generate. It’s a decision, foes say, with the potential to hamstring a growing renewables industry.
“It’s not surprising that you are seeing campaign-style tactics in what should be a wonky policy matter because there is a lot at stake here,” said Tyson Slocum, director of the energy program at Public Citizen, a consumer advocacy group. “The rooftop solar issue has become broadly politicized.”
Utilities nationwide are pushing regulators to cut mandated solar payments, as they seek to tilt the solar market in their favor, an expense they say requires them to boost rates on non-solar customers in order to maintain the grid. Solar supporters, meanwhile, say a big drop in the amount paid to homeowners would undermine the benefits of switching to green power and imperil the industry’s double-digit annual growth.
A decision by Arizona, which last year generated the third most solar power in the U.S., could serve as a bellwether for national change at a time when as many as two dozen other states are weighing the same issue, with a Michigan push to eliminate rooftop caps highlighting the trend, according to a report by the North Carolina Clean Energy Technology Center.
In December, Nevada regulators voted to allow utilities to increase fees and reduce payments to home solar users. A month later, California rejected reduced solar credits, even as electricity pricing changes pose an existential threat to residential rooftop solar there. Now, the spotlight swings to Arizona, one of only 14 states with an elected board -- the Arizona Corporation Commission -- that sets regulatory policy and utility rates.
Arizona has long required utilities to pay consumers for solar energy they put back into the grid. In November 2013, the commission allowed utilities to assess a small connection fee to offset part of that payment. Now, the commission is being asked to consider a proposal from Pinnacle West’s Arizona Public Service unit that would almost triple the fee for some customers to $24 a month, and cut consumer credits for solar power by as much as 80 percent.
Arizona Public Service has more than 50,000 customers with home solar. To pay them, the company estimated it will have to raise bills for non-solar customers by $51 million annually starting next year. At the same time, as consumer choice in California suddenly reshapes the electricity business, a June report from Credit Suisse Group AG said approving the new proposal could make solar "uneconomic" across a state that is among the nation’s leaders in the use of home solar.
Public Debate
The issue has spurred an active public debate, pulling in homeowners from both sides of the argument.
Those without solar say they shouldn’t be paying extra for those who do. "People with solar panels on their roofs think they ought to have free electricity," said Fannalou Guggisberg, a retired military chaplain in Sun City West. "I don’t think it’s fair for them to sell back electricity and not pay any taxes on it.”
Proponents counter that charging a fee only serves to discourage the growth of home solar as a feasible energy alternative. "APS is actually battling solar people," said Russell Taylor, a cabinet maker in Goodyear. "They want a monopoly."
Meanwhile, the involvement of the companies has drawn the attention of U.S. and state authorities.
Two Subpoenas
In a U.S. filing in August, Pinnacle West said it received two grand jury subpoenas from the U.S. attorney in June seeking information on the commission’s 2014 elections. While the FBI wouldn’t discuss the specifics of the subpoenas, spokeswoman Jill McCabe confirmed the agency is investigating “certain statewide races in the 2014 election cycle.”
Alan Bunnell, a spokesman for Pinnacle West, has said the company is “cooperating fully with the U.S. Attorney’s office in this matter.”
The probe follows public complaints by a former commissioner, Sandra Kennedy, that the company sought to improperly influence the 2013 fee decision. A year later, Kennedy lost a bid to rejoin the commission in a campaign that saw two nonprofit groups spend $3.2 million in support of board candidates favorable to Pinnacle West.
Spokesmen for both non-profit groups -- Save Our Future Now, and the Arizona Free Enterprise Club -- declined to identify their benefactors, or to comment for this article. James McDonald, a spokesman for the Arizona Public Service unit, declined to say whether the company contributed to either.
"We’ve always complied with all disclosure requests," McDonald said in an e-mail. "We have an obligation to our customers and our shareholders to be politically active.”
Missed Deadlines
SolarCity, meanwhile, hasn’t gone unscathed.
Kris Mayes, president of the nonprofit group Save our AZ Solar, confirmed that SolarCity is its sole funder after the company’s spokeswoman, Suzanne Merkelson, referred calls to her. The group, which records show has received $2 million in contributions, faces fines of as much as $300,000 for missing deadlines on filing reports, according to Thomas Collins, executive director of the Arizona Citizens Clean Elections Commission.
Save our AZ Solar is trying to settle the matter with the commission for $8,000 to $15,000, Mayes said, adding that any violations were inadvertent. "We have been all about transparency and disclosure from the very beginning," she said.
For the 2016 election, Pinnacle West formed the AZ Coalition for Reliable Electricity to openly back three Republicans for board seats, the company said in an e-mailed statement on Oct. 24. Matthew Benson, the group’s spokesman, confirmed the $1 million spending target.
Robert Burns, a commissioner backed by SolarCity in his re-election bid, said he’s concerned about the amount of financing attached to the race. "But there’s nothing I can do about it," he said, noting that the commission has called on companies with business before it to refrain from funding commission campaigns. "I can’t control what they do."