Why the Texas Power Grid Is Facing Another Crisis

NFPA 70e Training - Arc Flash
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Texas Power Grid Reliability faces record peak demand as ERCOT balances renewable energy, wind and solar variability, gas-fired generation, demand response, and transmission limits to prevent blackouts during heat waves and extreme weather.
Key Points
Texas Power Grid Reliability is ERCOT's capacity to meet peak demand with diverse resources while limiting outages.
✅ Record heat drives peak demand across ERCOT.
✅ Variable wind/solar need firm, flexible capacity.
✅ Demand response and reserves reduce blackout risk.
The electric power grid in Texas, which collapsed dramatically during the 2021 winter storm across the state, is being tested again as the state suffers unusually hot summer weather. Demand for electricity has reached new records at a time of rapid change in the mix of power sources as wind and solar ramp up. That’s feeding a debate about the dependability of the state’s power.
1. Why is the Texas grid under threat again?
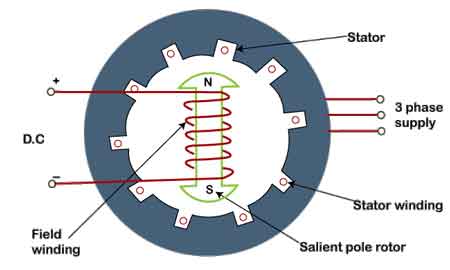
Already the biggest power user in the nation, electricity use in the second most-populous state surged to record levels during heat waves this summer. The jump in demand comes as the state becomes more dependent on intermittent renewable power sources, raising concerns among some critics that more reliance on wind and solar will leave the grid more vulnerable to disruption. Green sources will produce almost 40% of the power in Texas this year, US Energy Information Administration data show. While that trails California’s 52%, Texas is a bigger market. It’s already No. 1 in wind, making it the largest clean energy market in the US.
2. How is Texas unique?
The spirit of defiance of the Lone Star State extends to its power grid as well. The Electric Reliability Council of Texas, or Ercot as the grid operator is known, serves about 90% of the state’s electricity needs and has very few high-voltage transmission lines connecting to nearby grids. It’s a deliberate move to avoid federal oversight of the power market. That means Texas has to be mainly self-reliant and cannot depend on neighbors during extreme conditions. That vulnerability is a dramatic twist for a state that’s also the energy capital of the US, thanks to vast oil and natural gas producing fields. Favorable regulations are also driving a wind and solar boom in Texas.
3. Why the worry?
The summer of 2023 will mark the first time all of the state’s needs cannot be met by traditional power plants, like nuclear, coal and gas. A sign of potential trouble came on June 20 when state officials urged residents to conserve power because of low supplies from wind farms and unexpected closures of fossil-fuel generators amid supply-chain constraints that limited availability. As of late July, the grid was holding up, thanks to the help of renewable sources. Solar generation has been coming in close to expected summer capacity, or exceeding it on most days. This has helped offset the hours in the middle of the day when wind speeds died down in West Texas.
4. Why didn’t the grid’s problems get fixed?
There is no easy fix. The Texas system allows the price of electricity to swing to match supply and demand. That means high prices — and high profits — drive the development of new power plants. At times spot power prices have been as low as $20-$50 a megawatt-hour versus more than $4,000 during periods of stress. The limitation of this pricing structure was laid bare by the 2021 winter blackouts. Since then, state lawmakers have passed market reforms that require weatherization of critical infrastructure and changed rules to put more money in the pockets of the owners of power generation.
5. What’s the big challenge?
There’s a real clash going on over what the grid of the future should look like in Texas and across the country, especially as severe heat raises blackout risks nationally. The challenge is to make sure nuclear and fossil fuel plants that are needed right now don’t retire too early and still allow newer, cleaner technologies to flourish. Some conservative Republicans have blamed renewable energy for destabilizing the grid and have pushed for more fossil-fuel powered generators. Lawmakers passed a controversial $10 billion program providing low-interest loans and grants to build new gas-fired plants using taxpayer money, but Texans ultimately have to vote on the subsidy.
6. Why do improvements take so long?
Figuring out how to keep the lights on without overburdening consumers is becoming a greater challenge amid more extreme weather fueled by climate change. As such, changing the rules is often a hotly contested process pitting utilities, generators, manufacturers, electricity retailers and other groups against one another. The process became more politicized after the storm in 2021 with Republican Gov. Greg Abbott and lawmakers ordering Ercot to make changes. Building more transmission lines and connecting to other states can help, but such projects are typically tied up for years in red tape.
7. What can be done?
The price cap for electricity was cut from $9,000/MWh to $5,000 to help avoid the punitive costs seen in the 2021 storm, though prices are allowed to spike more easily. Ercot is also contracting for more reserves to be online to help avoid supply shortfalls and improve reliability for customers, which added $1.7 billion in consumer costs alone last year. Another rule helps some gas generators pay for their fuel costs, while a more recent reform put in price floors when reserves fall to certain levels. Many power experts say that the easiest solution is to pay people to reduce their energy consumption during times of grid stress through so-called demand response programs. Factories, Bitcoin miners and other large users are already compensated to conserve during tight grid conditions.