Russian Cyberattacks on U.S. Critical Infrastructure target energy grids, nuclear plants, water systems, and aviation, DHS and FBI warn, using spear phishing, malware, and ICS/SCADA intrusion to gain footholds for potential sabotage and disruption.
Key Points
State-backed hacks targeting U.S. energy, nuclear, water and aviation via phishing and ICS access for sabotage.
✅ DHS and FBI detail multi-stage intrusion since 2016
✅ Targets include energy, nuclear, water, aviation, manufacturing
✅ TTPs: spear phishing, lateral movement, ICS reconnaissance
Russia is attacking the U.S. energy grid, with reported power plant breaches unfolding alongside attacks on nuclear facilities, water processing plants, aviation systems, and other critical infrastructure that millions of Americans rely on, according to a new joint analysis by the FBI and the Department of Homeland Security.
In an unprecedented alert, the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and FBI have warned of persistent attacks by Russian government hackers on critical US government sectors, including energy, nuclear, commercial facilities, water, aviation and manufacturing.
The alert details numerous attempts extending back to March 2016 when Russian cyber operatives targeted US government and infrastructure.
The DHS and FBI said: “DHS and FBI characterise this activity as a multi-stage intrusion campaign by Russian government cyber-actors who targeted small commercial facilities’ networks, where they staged malware, conducted spear phishing and gained remote access into energy sector networks.
“After obtaining access, the Russian government cyber-actors conducted network reconnaissance, moved laterally and collected information pertaining to industrial control systems.”
The Trump administration has accused Russia of engineering a series of cyberattacks that targeted American and European nuclear power plants and water and electric systems, and could have sabotaged or shut power plants off at will.
#google#
United States officials and private security firms saw the attacks as a signal by Moscow that it could disrupt the West’s critical facilities in the event of a conflict.
They said the strikes accelerated in late 2015, at the same time the Russian interference in the American election was underway. The attackers had compromised some operators in North America and Europe by spring 2017, after President Trump was inaugurated.
In the following months, according to the DHS/FBI report, Russian hackers made their way to machines with access to utility control rooms and critical control systems at power plants that were not identified. The hackers never went so far as to sabotage or shut down the computer systems that guide the operations of the plants.
Still, new computer screenshots released by the Department of Homeland Security have made clear that Russian state hackers had the foothold they would have needed to manipulate or shut down power plants.
“We now have evidence they’re sitting on the machines, connected to industrial control infrastructure, that allow them to effectively turn the power off or effect sabotage,” said Eric Chien, a security technology director at Symantec, a digital security firm.
“From what we can see, they were there. They have the ability to shut the power off. All that’s missing is some political motivation,” Mr. Chien said.
American intelligence agencies were aware of the attacks for the past year and a half, and the Department of Homeland Security and the F.B.I. first issued urgent warnings to utility companies in June, 2017. Both DHS/FBI have now offered new details as the Trump administration imposed sanctions against Russian individuals and organizations it accused of election meddling and “malicious cyberattacks.”
It was the first time the administration officially named Russia as the perpetrator of the assaults. And it marked the third time in recent months that the White House, departing from its usual reluctance to publicly reveal intelligence, blamed foreign government forces for attacks on infrastructure in the United States.
In December, the White House said North Korea had carried out the so-called WannaCry attack that in May paralyzed the British health system and placed ransomware in computers in schools, businesses and homes across the world. Last month, it accused Russia of being behind the NotPetya attack against Ukraine last June, the largest in a series of cyberattacks on Ukraine to date, paralyzing the country’s government agencies and financial systems.
But the penalties have been light. So far, President Trump has said little to nothing about the Russian role in those attacks.
The groups that conducted the energy attacks, which are linked to Russian intelligence agencies, appear to be different from the two hacking groups that were involved in the election interference.
That would suggest that at least three separate Russian cyberoperations were underway simultaneously. One focused on stealing documents from the Democratic National Committee and other political groups. Another, by a St. Petersburg “troll farm” known as the Internet Research Agency, used social media to sow discord and division. A third effort sought to burrow into the infrastructure of American and European nations.
For years, American intelligence officials tracked a number of Russian state-sponsored hacking units as they successfully penetrated the computer networks of critical infrastructure operators across North America and Europe, including in Ukraine.
Some of the units worked inside Russia’s Federal Security Service, the K.G.B. successor known by its Russian acronym, F.S.B.; others were embedded in the Russian military intelligence agency, known as the G.R.U. Still others were made up of Russian contractors working at the behest of Moscow.
Russian cyberattacks surged last year, starting three months after Mr. Trump took office.
American officials and private cybersecurity experts uncovered a series of Russian attacks aimed at the energy, water and aviation sectors and critical manufacturing, including nuclear plants, in the United States and Europe. In its urgent report in June, the Department of Homeland Security and the F.B.I. notified operators about the attacks but stopped short of identifying Russia as the culprit.
By then, Russian spies had compromised the business networks of several American energy, water and nuclear plants, mapping out their corporate structures and computer networks.
They included that of the Wolf Creek Nuclear Operating Corporation, which runs a nuclear plant near Burlington, Kan. But in that case, and those of other nuclear operators, Russian hackers had not leapt from the company’s business networks into the nuclear plant controls.
Forensic analysis suggested that Russian spies were looking for inroads — although it was not clear whether the goal was to conduct espionage or sabotage, or to trigger an explosion of some kind.
In a report made public in October, Symantec noted that a Russian hacking unit “appears to be interested in both learning how energy facilities operate and also gaining access to operational systems themselves, to the extent that the group now potentially has the ability to sabotage or gain control of these systems should it decide to do so.”
The United States sometimes does the same thing. It bored deeply into Iran’s infrastructure before the 2015 nuclear accord, placing digital “implants” in systems that would enable it to bring down power grids, command-and-control systems and other infrastructure in case a conflict broke out. The operation was code-named “Nitro Zeus,” and its revelation made clear that getting into the critical infrastructure of adversaries is now a standard element of preparing for possible conflict.
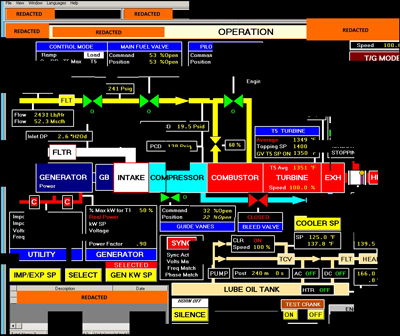
Reconstructed screenshot fragments of a Human Machine Interface that the threat actors accessed, according to DHS
Sanctions Announced
The US treasury department has imposed sanctions on 19 Russian people and five groups, including Moscow’s intelligence services, for meddling in the US 2016 presidential election and other malicious cyberattacks.
Russia, for its part, has vowed to retaliate against the new sanctions.
The new sanctions focus on five Russian groups, including the Russian Federal Security Service, the country’s military intelligence apparatus, and the digital propaganda outfit called the Internet Research Agency, as well as 19 people, some of them named in the indictment related to election meddling released by special counsel Robert Mueller last month.
In announcing the sanctions, which will generally ban U.S. people and financial institutions from doing business with those people and groups, the Treasury Department pointed to alleged Russian election meddling, involvement in the infrastructure hacks, and the NotPetya malware, which the Treasury Department called “the most destructive and costly cyberattack in history.”
The new sanctions come amid ongoing criticism of the Trump administration’s reluctance to punish Russia for cyber and election meddling. Sen. Mark Warner (D-Va.) said that, ahead of the 2018 mid-term elections, the administration’s decision was long overdue but not enough. “Nearly all of the entities and individuals who were sanctioned today were either previously under sanction during the Obama Administration, or had already been charged with federal crimes by the Special Counsel,” Warner said.
Warning: The Russians Are Coming
In an updated warning to utility companies, DHS/FBI officials included a screenshot taken by Russian operatives that proved they could now gain access to their victims’ critical controls, prompting a renewed focus on protecting the U.S. power grid among operators.
American officials and security firms, including Symantec and CrowdStrike, believe that Russian attacks on the Ukrainian power grid in 2015 and 2016 that left more than 200,000 citizens there in the dark are an ominous sign of what the Russian cyberstrikes may portend in the United States and Europe in the event of escalating hostilities.
Private security firms have tracked the Russian government assaults on Western power and energy operators — conducted alternately by groups under the names Dragonfly campaigns alongside Energetic Bear and Berserk Bear — since 2011, when they first started targeting defense and aviation companies in the United States and Canada.
By 2013, researchers had tied the Russian hackers to hundreds of attacks on the U.S. power grid and oil and gas pipeline operators in the United States and Europe. Initially, the strikes appeared to be motivated by industrial espionage — a natural conclusion at the time, researchers said, given the importance of Russia’s oil and gas industry.
But by December 2015, the Russian hacks had taken an aggressive turn. The attacks were no longer aimed at intelligence gathering, but at potentially sabotaging or shutting down plant operations.
At Symantec, researchers discovered that Russian hackers had begun taking screenshots of the machinery used in energy and nuclear plants, and stealing detailed descriptions of how they operated — suggesting they were conducting reconnaissance for a future attack.
Eventhough the US government enacted sanctions, cybersecurity experts are still questioning where the Russian attacks could lead, given that the United States was sure to respond in kind.
“Russia certainly has the technical capability to do damage, as it demonstrated in the Ukraine,” said Eric Cornelius, a cybersecurity expert at Cylance, a private security firm, who previously assessed critical infrastructure threats for the Department of Homeland Security during the Obama administration.
“It is unclear what their perceived benefit would be from causing damage on U.S. soil, especially given the retaliation it would provoke,” Mr. Cornelius said.
Though a major step toward deterrence, publicly naming countries accused of cyberattacks still is unlikely to shame them into stopping. The United States is struggling to come up with proportionate responses to the wide variety of cyberespionage, vandalism and outright attacks.
Lt. Gen. Paul Nakasone, who has been nominated as director of the National Security Agency and commander of United States Cyber Command, the military’s cyberunit, said during his recent Senate confirmation hearing, that countries attacking the United States so far have little to worry about.
“I would say right now they do not think much will happen to them,” General Nakasone said. He later added, “They don’t fear us.”
Related News