Advanced Nuclear Reactors redefine nuclear energy with SMRs, diverse fuels, passive safety, digital control rooms, and flexible heat and power, pairing veteran operator expertise with cost-efficient, carbon-free electricity for a resilient grid.
Key Points
SMR-based advanced reactors with passive cooling and digital controls deliver flexible power and process heat.
✅ Veteran operators transfer proven safety culture and risk management.
✅ SMRs, passive safety, and digital controls simplify operations.
✅ Flexible output: electricity, process heat, and grid support.
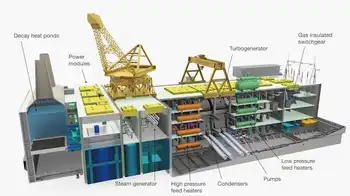
Advanced reactors will break the mold of what we think next-gen nuclear power can accomplish: some will be smaller, some will use different kinds of fuel and others will do more than just make electricity. This new technology may seem like uncharted waters, but when operators, technicians and other workers start up the first reactors of the new generation, they will bring with them years of nuclear experience to run machines that have been optimized with lessons from the current fleet.
While advanced reactors are often portrayed as the future of nuclear energy, and atomic energy is heating up across markets, its our current plants that have paved the way for these exciting innovations and which will be workhorses for years to come.
Reactor Veterans Bring Their Expertise to New Designs
Many of the workers who will operate the next generation of reactors come from a nuclear background. Even though the design of an advanced reactor may be different, the experience and instincts these operators have gained from working at the current fleet will help new plants get off to a more productive start.
They have a questioning attitude; they are always exploring what could go wrong and always understanding the notion of risk management in nuclear operations, whether its the oldest design or the newest design, said Chip Pardee, the president of Terrestrial Energy USA, who is the former chief operating officer at two nuclear utilities, Exelon Corp. and the Tennessee Valley Authority.
They have respect for the technology and a bias towards conservative decision-making.
Jhansi Kandasamy, vice president of engineering at GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, agrees. She said that the presence of industry veterans will benefit the new modelslike the 300 megawatt boiling water reactor her company is developing.
From the beginning, a new reactor will have people who have touched it, worked on it, and experienced it, she said.
Theyre going to be able to tell you if something doesnt look right, because theyve lived through it.
Experience Informs New Reactor Design
Advanced reactors are designed by engineers who are fully familiar with existing plants and can use that experience to optimize the new ones, like a family building a house and wanting the kitchen just so. New reactors will be simpler to operate because of insights gained from years of operations of the current fleet, and some designs even integrate molten salt energy storage to enhance flexibility.
NuScale Power LLC, for example, has a very different design from the current fleet amid an advanced nuclear push that is reshaping development: up to 12 small reactorsinstead of one or two large reactorsmanaged from a single digital control roominstead of one full of analog switches and dials. When the company designed its control room, it brought in industry veterans who had collectively worked at more than two dozen nuclear plants.
The experts that NuScale brought in critiqued everything, even down to the shape of the symbols on the computer screens to make them easier to read for operators who sometimes need to quickly interpret lots of incoming data. The control panels for NuScales small modular reactor (SMR) present information according to its importance and automatically call up appropriate procedures for operators.
Many advanced reactors are also smaller than those currently operating, which makes their components simpler and less expensive. Kandasamy pointed out that the giant mechanical pumps in todays reactors generate a lot of heat and require a lot of supporting systems, including air conditioning in the rooms that house them.
GE Hitachis SMR design relies more on passive cooling so it needs fewer pumps, and those that remain use magnets, so they generate less heat. Fewer, smaller pumps means a smaller building and less cost.
Advanced Nuclear Will Further the Work of Current Reactors
Advanced reactors promise improved flexibility and the ability to do more kinds of work, including nuclear beyond electricity applications, to displace carbon and stabilize the climate. And they will continue nuclear energys legacy of providing reliable, carbon-free electricity, as a recent new U.S. reactor startup illustrates in practice. As new designs come on line over the next decade, we will continue to rely on operating plants which provide nearly 55 percent of the countrys carbon-free electricity.
The world will need all the carbon-free generation it can get for many years to come, as companies, states and countries aim for zero emissions by mid-century and pursue strategies like the green industrial revolution to accelerate deployment. That means it will need wind, solar, advanced reactors and current plants.
Related News