B.C. Hydro predicts 'bottleneck' as electric-vehicle demand ramps-up
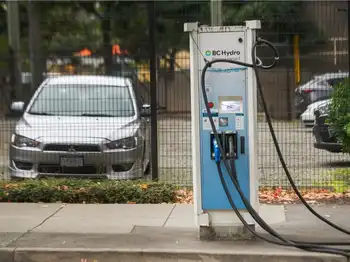
Protective Relay Training - Basic
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
B.C. EV Bottleneck signals a post-pandemic demand surge for electric vehicles amid semiconductor and lithium-ion battery shortages, driving waitlists, record sales, rebates, charging infrastructure needs, and savings on fuel and maintenance across British Columbia.
Key Points
B.C. EV bottleneck is rising demand outpacing supply from chip and battery shortages, creating waitlists.
✅ 85% delayed EV purchase; demand rebounds with reopening.
✅ Supply chain limits: chips and lithium-ion batteries.
✅ Plan ahead: join waitlists, consider used EVs, claim rebates.
B.C. Hydro is warning of a post-pandemic “EV bottleneck” as it predicts pent-up demand and EV shortages will lead to record-breaking sales for electric vehicles in 2021.
A new survey by B.C. Hydro found 85 per cent of British Columbians put off buying an electric vehicle during the pandemic, but as the province reopens, the number of people on the road commuting to-and-from work and school is expected to rise 15 per cent compared with before the pandemic.
It found about two-thirds of British Columbians are considering buying an EV over the next five years, with 60 per cent saying they would go with an EV if they can get one sooner.
“The EV market is at a potential tipping point, as demand is on the rise and will likely continue to grow long-term, with one study projecting doubling power output to meet full road electrification,” said a report about the findings released Wednesday.
The demand for EVs is prompted by rising gas prices, environmental concerns and to save money on maintenance costs like oil changes and engine repairs, said the report. At the same time, a shortage of semiconductor chips and lithium ion batteries needed for auto production is squeezing supply.
For people wanting to make the switch to electric, B.C. Hydro recommended they plan ahead and get on several waiting lists and explore networks offering faster charging options. Used EVs are also a cheaper option.
B.C. Hydro said an electric vehicle can save 80 per cent in gas expenses over a year and about $100 a month in maintenance costs compared with a gas-powered vehicle. There are also provincial and federal rebates of up to $8,000 for EV purchases in B.C., and additional charger rebates can help with installation costs.
B.C. has the highest electric vehicle uptake in North America, with zero-emission vehicles making up almost 10 per cent of all car sales in the province in 2020 as the province expands EV charging to support growth — more than double the four per cent in 2018.
According to a report by University of B.C. business Prof. Werner Antweiler on the state of EV adoption in B.C., electric vehicles are still concentrated in urban areas like Metro Vancouver and the Capital Regional District on Vancouver Island where public charging stations are more readily available.
He said electric vehicle purchases are still hampered by limited choice and a lack of charging stations, especially for people who park on the street or in condo parkades, which would require permission from strata councils to install a charging station, though rebates for home and workplace charging can ease installation.
The online survey was conducted by market researcher Majid Khoury of 800 British Columbians from May 17-19. It has a margin of error of plus-or-minus 3.5 per cent, 19 times out of 20.











