TVA looks to renewable sources
By Knoxville News Sentinel
NFPA 70e Training - Arc Flash
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
TVA has just signed a 20-year contract with Waste Management to buy 4.8 megawatts of power from a landfill-biogas facility at Camden in West Tennessee. That contract is the first in TVA's new renewable standard offer initiative.
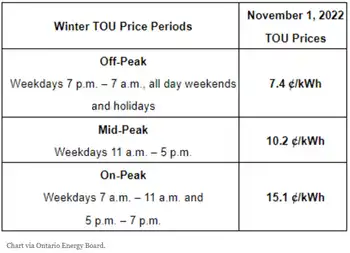
TVA pays a set price — or a "standard offer" — for renewable power based on the time of day the electricity is available to the TVA power grid. TVA's Renewable Standard Offer initially will be limited to a total of 100 megawatts from all participants, with no single renewable technology representing more than 50 megawatts of the total.
The Chestnut Ridge facility along the Knox-Anderson county line has been providing electricity for about 1,600 homes that are KUB customers. TVA and Waste Management have been partners in the Chestnut Ridge power contract for nearly 20 years.
TVA also buys power — 3 megawatts — from methane facilities at Middle Point Landfill in Murfreesboro, Tenn., and 8 megawatts from the city of Memphis wastewater treatment plant.
TVA spokesman Mike Bradley said the agency does not discuss pricing for the renewable energy contracts, citing the information as "business sensitive."
TVA, which also gets renewable energy from wind, solar and biomass and customers, has an agreement with the state of Tennessee to buy up to 5 megawatts of electricity from a solar farm being built in Haywood County in West Tennessee. The University of Tennessee and the state are developing that facility.
The agency has added 1,625 megawatts of wind energy — 300 megawatts from an Illinois company and 29 megawatts from the Buffalo Mountain turbines near Oliver Springs.
TVA's Generation Partners program — for very small power producers — includes more than 560 participants that produce about 65 megawatts of power from solar biomass, wind and low-impact hydro generation.