Watt’s Law - Power Triangle
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
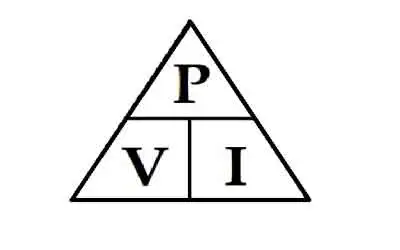
Watt’s Law defines the relationship between power (watts), voltage (volts), and current (amps): Power = Voltage × Current. It’s used in electrical calculations to determine energy usage, system efficiency, and safe equipment ratings in both residential and industrial systems.
What is: Watt’s Law?
Watt’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering:
✅ Calculates electrical power as the product of voltage and current
✅ Helps design efficient and safe electrical systems
✅ Used in both residential and industrial applications
Watt’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that defines the relationship between power, voltage, and current in an electrical circuit. James Watt invented the law. It states that the power (measured in watts) of an electrical device is equal to the product of the voltage (measured in volts) and the current (measured in amperes) flowing through it. In other words, the watt's law formula is expressed as: Power = Voltage × Current. This simple equation is essential for understanding how electrical components consume and distribute energy in a circuit.
For example, consider a light bulb connected to an electrical circuit. The electrical potential (voltage) pushes the electric charge through the filament of the bulb, creating a flow of electrons (current). As the electrons flow, they generate heat and light, representing the bulb’s power in a circuit. By knowing the voltage and current, you can easily calculate the power output of the bulb. The wattage of the bulb indicates the energy consumed per second.
Practical applications of this formula are vast. This equation is especially useful in designing safe and efficient electrical systems. For instance, designing the wiring for both small devices and large power systems requires a thorough understanding of the relationship between voltage, current, and power. The formula helps ensure that systems are capable of delivering the required energy without causing failures or inefficiencies.
Ohm’s Law and this principle are often used together in electrical engineering. While power focuses on the relationship between voltage and current, Ohm’s Law deals with the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance (measured in ohms). Ohm’s Law states that voltage equals current multiplied by resistance (Voltage = Current × Resistance). By combining Ohm’s Law and this power equation, you can analyze an electrical system more comprehensively. For example, if you know the voltage and resistance in a circuit, you can calculate the current and then determine the power in the circuit. To fully understand Watt's Law, it helps to explore how voltage and current electricity interact in a typical electrical circuit.

Georg Simon Ohm – German physicist and mathematician (1787–1854), known for Ohm's Law, relating voltage, current, and resistance.
What is Watt's Law and how is it used in electrical circuits?
Watt’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that defines the relationship between power, voltage, and current in an electrical circuit. The formula is expressed as:
Power (Watts) = Voltage (Volts) × Current (Amperes)
In simpler terms, Watt’s Law states that the electrical power consumed by a device (measured in watts) is the product of the electrical potential difference (voltage) and the current flowing through the circuit. Accurate calculations using Watt’s Law often require a voltage-drop calculator to account for line losses in long-distance wiring. Comparing voltage drop and voltage sag conditions illustrates how slight changes in voltage can have a substantial impact on power output.

James Watt – Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer (1736–1819), whose improvements to the steam engine led to the naming of the watt (unit of power).
How is it used? Watt’s Law is widely used to determine the amount of power an electrical device or system consumes. This is especially important for designing electrical circuits, optimizing power distribution, and ensuring the efficiency of devices. Here are a few examples of how it’s applied:
-
Electrical Circuit Design: Engineers use it to calculate the power consumption of devices and ensure that circuits can handle the expected electrical load. This helps prevent overloads and ensures that the wiring is safe.
-
Power Output Calculations: Using this formula, you can calculate the power output of a generator, appliance, or device, enabling you to match the right components to your system's requirements.
-
Energy Efficiency: Understanding power consumption in appliances and devices helps consumers make informed choices, such as selecting energy-efficient options. Devices like wattmeters and watthour meters measure power and energy usage based directly on the principles of Watt’s Law. For a deeper look at how devices like ammeters help measure current, see how their readings plug directly into Watt’s Law calculations.
How is Watt's Law different from Ohm's Law?
Watt’s Law and Ohm’s Law are both fundamental principles in electrical engineering, but they deal with different aspects of electrical systems:
-
Watt’s Law defines the relationship between power, voltage, and current. It focuses on the amount of energy used by a device in a given circuit. The formula is:
Power = Voltage × Current
-
Ohm’s Law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. Ohm’s Law explains how the current is affected by the voltage and the resistance present in the circuit. The formula for Ohm’s Law is:
Voltage = Current × Resistance
Key Differences:
-
Focus: It focuses on power, while Ohm’s Law focuses on the flow of electricity in a circuit, particularly how resistance affects current.
-
Watt’s Law is used to determine the amount of power a device is consuming. Ohm’s Law, on the other hand, is used to calculate current, voltage, or resistance in a circuit depending on the other known variables.
-
Applications: It is applied when designing systems that require power management, such as calculating the power output or efficiency of devices. Ohm’s Law is used more in analyzing how current behaves in a circuit when different resistive elements are present.
By combining both laws, electrical engineers can gain a comprehensive understanding of how electrical systems function, ensuring that devices operate efficiently and safely. When used with Ohm’s Law, Watt's Law enables engineers to analyze both energy consumption and electrical resistance.
One key area of application is in energy consumption. By understanding the voltage and current values for a specific device, engineers can monitor the amount of energy the device consumes. This is especially important for managing energy usage in homes, businesses, and power systems. By applying the formula, you can identify inefficient devices and make more informed decisions about energy efficiency.
In renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, this principle plays a critical role in optimizing energy output. Engineers use the formula to calculate how much electrical energy is being generated and distributed. This is crucial for ensuring that power systems operate efficiently and minimize excess energy loss.
Another practical application of this formula is in the automotive industry. It is used to design vehicle charging systems and battery technologies. For example, electric vehicle (EV) charging stations depend on understanding voltage, current, and power to ensure efficient charging times. Engineers use the equation to calculate the charging capacity required for EV batteries, helping to create optimal charging solutions.
In large facilities like data centers, this Watt’s Law formula is used to ensure power distribution is efficient. By applying the relationship between power, voltage, and current, engineers can effectively manage power systems, thereby reducing energy consumption and operational costs. Proper energy management in data centers is crucial, as high power usage can result in significant energy costs.
This power formula is indispensable for electrical engineers and technicians. The applications of Watt’s Law extend across various industries and are utilized in everything from designing power system wiring to developing renewable energy technologies. By combining Ohm’s Law and this principle, electrical engineers can optimize the performance of electrical components, ensuring energy efficiency and system reliability. Understanding the role of a resistor in a circuit can reveal how power is dissipated as heat, a key concept derived from Watt’s Law.
Finally, visual tools like the Watt's Law triangle are often used to simplify the application of this principle, helping both professionals and students understand how to apply the formula. As technology advances and energy demands grow, this formula remains a key element in electrical engineering, guiding the development of more efficient systems for the future.
















_1497153600.webp)
