$453M Manitoba Hydro line to Minnesota could face delay after energy board recommendation
Electrical Testing & Commissioning of Power Systems
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
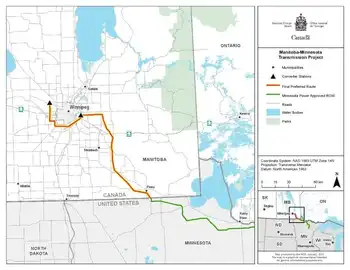
Manitoba-Minnesota Transmission Project faces NEB certificate review, with public hearings, Indigenous consultation, and cross-border approval weighing permit vs certificate timelines, potential land expropriation, and Hydro's 2020 in-service date for the 308-MW intertie.
Key Points
A cross-border hydro line linking Manitoba and Minnesota, now under NEB review through a permit or certificate process.
✅ NEB recommends certificate with public hearings and cabinet approval
✅ Stakeholders cite land, health, and economic impacts along route
✅ Hydro targets May-June 2020 in-service despite review
A recommendation from the National Energy Board could push back the construction start date of a $453-million hydroelectric transmission line from Manitoba to Minnesota.
In a letter to federal Natural Resources Minister Jim Carr, the regulatory agency recommends using a "certificate" approval process, which could take more time than the simpler "permit" process Manitoba Hydro favours.
The certificate process involves public hearings, reflecting First Nations intervention seen in other power-line debates, to weigh the merits of the project, which would then go to the federal cabinet for approval.
The NEB says this process would allow for more procedural flexibility and "address Aboriginal concerns that may arise in the circumstances of this process."
The Manitoba-Minnesota Transmission Project would provide the final link in a chain that brings hydroelectricity from generating stations in northern Manitoba, through the Bipole III transmission line and, like the New England Clean Power Link project, across the U.S. border as part of a 308-megawatt deal with the Green Bay-based Wisconsin Public Service.
When Hydro filed its application in December 2016, it had expected to have approval by the end of August 2017 and to begin construction on the line in mid-December, in order to have the line in operation by May or June 2020.
Groups representing stakeholders along the proposed route of the transmission line had mixed reactions to the energy board's recommendation.
A lawyer representing a coalition of more than 120 landowners in the Rural Municipality of Taché and around La Broquerie, Man., welcomed the opportunity to have a more "fulsome" discussion about the project.
"I think it's a positive step. As people become more familiar with the project, the deficiencies with it become more obvious," said Kevin Toyne, who represents the Southeast Stakeholders Coalition.
Toyne said some coalition members are worried that Hydro will forcibly expropriate land in order to build the line, while others are worried about potential economic and health impacts of having the line so close to their homes. They have proposed moving the line farther east.
When the Clean Environment Commission — an arm's-length provincial government agency — held public hearings on the proposed route earlier this year, the coalition brought their concerns forward, echoing Site C opposition voiced by northerners, but Toyne says both the commission and Hydro ignored them.
Hydro still aiming for 2020 in-service date
The Manitoba Métis Federation also participated in those public hearings. MMF president David Chartrand worries about the impact a possible delay, as seen with the Site C work halt tied to treaty rights, could have on revenue from sales of hydroelectric power to the U.S.
"I know that a lot of money, billions have been invested on this line. And if the connection line is not done, then of course this will be sitting here, not gaining any revenue, which will affect every Métis in this province, given our Hydro bill's going to go up," Chartrand said.The NEB letter to Minister Carr requests that he "determine this matter in an expedited manner."
Manitoba Hydro spokesperson Bruce Owen said in an email that the Crown corporation will participate in whatever process, permit or certificate, the NEB takes.
"Manitoba Hydro does not have any information at this point in time that would change the estimated in-service date (May-June 2020) for the Manitoba-Minnesota Transmission Project," he said.
The federal government "is currently reviewing the NEB's recommendation to designate the project as subject to a certificate, which would result in public hearings," said Alexandre Deslongchamps, a spokesperson for Carr.
"Under the National Energy Board Act, an international power line requires either the approval by the NEB through a permit or approval by the Government of Canada by a certificate. Both must be issued by the NEB," he wrote in an email to CBC News.
By law, the certificate process is not to take longer than 15 months.











