Deepwater Wind Eyeing Massachusetts’ South Coast for Major Offshore Wind Construction Activity

NFPA 70e Training - Arc Flash
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
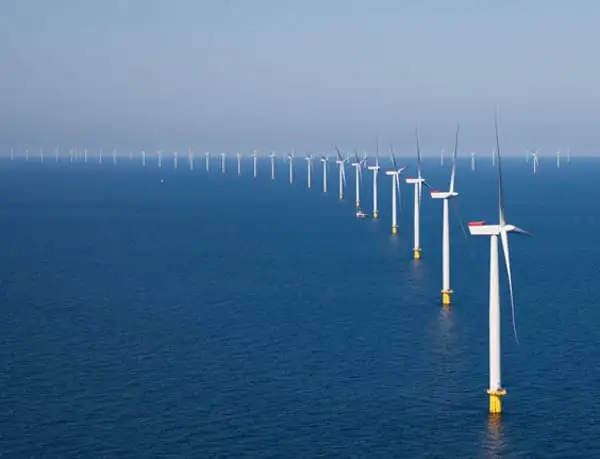
Revolution Wind Massachusetts will assemble turbine foundations in New Bedford, Fall River, or Somerset, building a local offshore wind supply chain, creating regional jobs, and leveraging pumped storage and an offshore transmission backbone.
Key Points
An offshore wind project assembling MA foundations, building a local supply chain, jobs, and peak clean power.
✅ 400 MW offshore wind; local fabrication of 1,500-ton foundations
✅ 300+ direct jobs, 600 indirect; MA crew vessel builds and operations
✅ Expandable offshore transmission; pumped storage for peak power
Deepwater Wind will assemble the wind turbine foundations for its Revolution Wind in Massachusetts, and it has identified three South Coast cities – New Bedford, Fall River and Somerset – as possible locations for this major fabrication activity, the company is announcing today.
Deepwater Wind is committed to building a local workforce and supply chain for its 400-megawatt Revolution Wind project, now under review by state and utility officials as Massachusetts advances projects like Vineyard Wind statewide.
“No company is more committed to building a local offshore wind workforce than us,” said Deepwater Wind CEO Jeffrey Grybowski. “We launched America’s offshore wind industry right here in our backyard. We know how to build offshore wind in the U.S. in the right way, and our smart approach will be the most affordable solution for the Commonwealth. This is about building a real industry that lasts.”
#google#
The construction activity will involve welding, assembly, painting, commissioning and related work for the 1,500-ton steel foundations supporting the turbine towers. This foundation-related work will create more than 300 direct jobs for local construction workers during Revolution Wind’s construction period. An additional 600 indirect and induced jobs will support this effort.
In addition, Deepwater Wind is now actively seeking proposals from Massachusetts boat builders for the construction of purpose-built crew vessels for Revolution Wind. Several dozen workers are expected to build the first of these vessels at a local boat-building facility, and another dozen workers will operate this specialty vessel over the life of Revolution Wind. (Deepwater Wind commissioned America’s only offshore wind crew vessel – Atlantic Wind Transfer’s Atlantic Pioneer – to serve the Block Island Wind Farm.)
The company will issue a formal Request for Information to local suppliers in the coming weeks. Deepwater Wind’s additional wind farms serving Massachusetts will require the construction of additional vessels, as will growth along Long Island’s South Shore in the coming years.
These commitments are in addition to Deepwater Wind’s previously-announced plans to use the New Bedford Marine Commerce Terminal for significant construction and staging operations, and to pay $500,000 per year to the New Bedford Port Authority to use the facility. During construction, the turbine marshaling activity in New Bedford is expected to support approximately 700 direct regional construction jobs.
“Deepwater Wind is building a sustainable industry on the South Coast of Massachusetts,” said Matthew Morrissey, Deepwater Wind Vice President Massachusetts. “With Revolution Wind, we are demonstrating that we can build the industry in Massachusetts while enhancing competition and keeping costs low.”
The Revolution Wind project will be built in Deepwater Wind’s federal lease site, under the BOEM lease process, southwest of Martha’s Vineyard. If approved, local construction work on Revolution Wind would begin in 2020, with the project in operations in 2023. Survey work is already underway at Deepwater Wind’s offshore lease area.
Revolution Wind will deliver “baseload” power, allowing a utility-scale renewable energy project for the first time to replace the retiring fossil fuel-fired power plants closing across the region, a transition echoed by Vineyard Wind’s first power milestones elsewhere.
Revolution Wind will be capable of delivering clean energy to Massachusetts utilities when it’s needed most, during peak hours of demand on the regional electric grid. A partnership with FirstLight Power, using its Northfield Mountain hydroelectric pumped storage in Northfield, Massachusetts, makes this peak power offering possible. This is the largest pairing of hydroelectric pumped storage and offshore wind in the world.
The Revolution Wind offshore wind farm will also be paired with a first-of-its-kind offshore transmission backbone. Deepwater Wind is partnering with National Grid Ventures on an expandable offshore transmission network that supports not just Revolution Wind, but also future offshore wind farms, as New York’s biggest offshore wind farm moves forward across the region, even if they’re built by our competitors.
This cooperation is in the best interest of Massachusetts electric customers because it will reduce the amount of electrical infrastructure needed to support the state’s 1,600 MW offshore wind goal. Instead of each subsequent developer building its own standalone cable network, other offshore wind companies could use expandable infrastructure already installed for Revolution Wind, reducing project costs and saving ratepayers money.