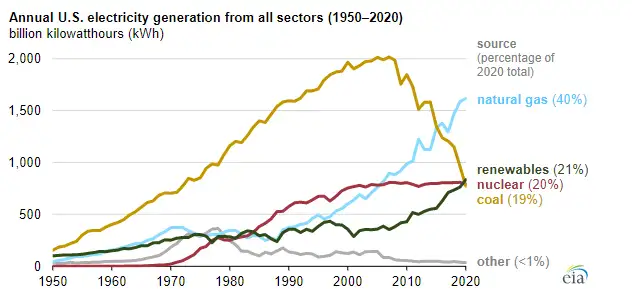
Renewables became the second-most prevalent U.S. electricity source in 2020
Arc Flash Training CSA Z462 - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
2020 U.S. Renewable Electricity Generation set a record as wind, solar, hydro, biomass, and geothermal produced 834 billion kWh, surpassing coal and nuclear, second only to natural gas in nationwide power output.
Key Points
The record year when renewables made 834 billion kWh, topping coal and nuclear in U.S. electricity.
✅ Renewables supplied 21% of U.S. electricity in 2020
✅ Coal output fell 20% y/y; nuclear slipped 2% on retirements
✅ EIA forecasts renewables rise in 2021-2022; coal rebounds
In 2020, renewable energy sources (including wind, hydroelectric, solar, biomass, and geothermal energy) generated a record 834 billion kilowatthours (kWh) of electricity, or about 21% of all the electricity generated in the United States. Only natural gas (1,617 billion kWh) produced more electricity than renewables in the United States in 2020. Renewables surpassed both nuclear (790 billion kWh) and coal (774 billion kWh) for the first time on record. This outcome in 2020 was due mostly to significantly less coal use in U.S. electricity generation and steadily increased use of wind and solar generation over time, amid declining consumption trends nationwide.
In 2020, U.S. electricity generation from coal in all sectors declined 20% from 2019, while renewables, including small-scale solar, increased 9%. Wind, currently the most prevalent source of renewable electricity in the United States, grew 14% in 2020 from 2019, and the EIA expects solar and wind to be larger sources in summer 2022, reflecting continued growth. Utility-scale solar generation (from projects greater than 1 megawatt) increased 26%, and small-scale solar, such as grid-connected rooftop solar panels, increased 19%, while early 2021 January power generation jumped year over year.
Coal-fired electricity generation in the United States peaked at 2,016 billion kWh in 2007 and much of that capacity has been replaced by or converted to natural gas-fired generation since then. Coal was the largest source of electricity in the United States until 2016, and 2020 was the first year that more electricity was generated by renewables and by nuclear power than by coal (according to our data series that dates back to 1949). Nuclear electric power declined 2% from 2019 to 2020 because several nuclear power plants retired and other nuclear plants experienced slightly more maintenance-related outages.
We expect coal-fired generation to increase in the United States during 2021 as natural gas prices continue to rise and as coal becomes more economically competitive. Based on forecasts in our Short-Term Energy Outlook (STEO), we expect coal-fired electricity generation in all sectors in 2021 to increase 18% from 2020 levels before falling 2% in 2022. We expect U.S. renewable generation across all sectors to increase 7% in 2021 and 10% in 2022, and in 2021, non-fossil fuel sources accounted for about 40% of U.S. electricity. As a result, we forecast coal will be the second-most prevalent electricity source in 2021, and renewables will be the second-most prevalent source in 2022. We expect nuclear electric power to decline 2% in 2021 and 3% in 2022 as operators retire several generators.











