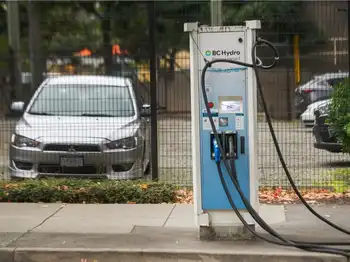EV shortages, wait times amid high gasoline prices

NFPA 70b Training - Electrical Maintenance
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Canada EV demand surge is driven by record gas prices, zero-emission policies, and tight dealer inventory, while microchip shortages, ZEV mandates abroad, and lithium supply concerns extend wait times for new and used models.
Key Points
Canada EV demand surge is rising interest in zero-emission cars due to high gas prices and limited EV supply.
✅ Gas at $2/litre spurs zero-emission interest
✅ Dealer inventory scarce; waits up to 3 years
✅ Microchip and lithium constraints limit output
Price shock at the pump is driving Canadians toward buying an ev. But manufacturers are having trouble keeping up with consumer demand, even as the U.S. auto sector pivots to EVs across North America.
In parts of the country, gas prices exceeded $2 per litre last month amid strong global demand for oil combined with Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Halifax-based electric vehicle salesperson Jeremie Bernardin said he's noticed an explosion of interest in zero-emission vehicles since the price of fuel started to take off.
"I think there's a lot of people that were considering electric vehicles for a very long time, and they needed that extra little push," Bernardin, who is also the president of the Electric Vehicle Association of Atlantic Canada, where Atlantic EV demand has lagged the national average, told CTVNews.ca over the phone on Wednesday.
With so few electric vehicles on dealership lots, Canadians looking to buy a brand-new zero-emission car will have to put down a deposit and get onto a waiting list. Bernardin said the wait times can be as long as three years, depending on the manufacturer and the dealership.
Tesla, which makes Canada's best-selling electric car according to the automotive publication Motor Illustrated, says delivery times for its vehicles range between three months to one year, depending on the model. But some manufacturers like Nissan have already completely sold out of their electric vehicle inventory for the 2022 model year, though recent EV assembly deals in Canada aim to expand capacity over time.
Shortages of electric vehicles have been around long before the recent spike in gas prices. In March 2021, a report commissioned by Transport Canada found that more than half of Canadian dealerships had no electric vehicles in stock. The report also found that wait times exceeded six months at 31 per cent of dealerships that had no zero-emission cars in their inventory.
Interest in used electric vehicles has also surged amid the high gas prices. Used car marketplace AutoTrader.ca says searches for electric cars in March 2022 increased 89 per cent compared to the previous year, while the number of inquiries sent to electric vehicle sellers through its platform jumped 567 per cent.
"It's understandable that when the gas prices are expensive, consumers are looking to buy and get into electric vehicles, though upfront cost remains a major barrier for many buyers today," Baris Akyurek, AutoTrader.ca's director of marketing intelligence, told CTVNews.ca in a phone interview on Wednesday.
SUPPLY CHAIN ISSUES PERSIST
The surging interest in electric vehicles also comes at a time when pandemic-induced shortages of microchips have been affecting the automotive industry at large since late 2020. Modern automobiles can have hundreds of microchips that control everything from the air conditioning to the power steering system, and a shortage of these crucial components have resulted in fewer vehicles being manufactured.
"Electric vehicles are subject to supply chain issues, just like anything else. Right now, the COVID pandemic has disrupted global supply chains. The auto industry specifically is seeing a microchip shortage that it's been struggling with for the past year or two. So those things are at play," said Joanna Kyriazis, senior policy advisor with Simon Fraser University’s Clean Energy Canada, in a phone interview with CTVNews.ca on Tuesday.
On top of that, Kyriazis says more than 80 per cent of the world's supply of electric vehicles are shipped to consumers in China and the European Union.
China has a strict zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) mandate that requires automakers to ensure that a certain minimum percentage of their vehicles are electric or hydrogen-powered. In Europe, automakers are also forced to sell more electric vehicles there in order to meet the EU's stringent fleetwide emissions standards, and in Canada, Ottawa is preparing EV sales regulations to guide adoption in the coming years.
"We don't have the same aggressive regulations in place yet to really force automakers to prioritize the Canadian market when they're deciding where to allocate their EV inventory and where to sell EVs," said Kyriazis, though Ottawa's 2035 EV mandate remains debated by some industry observers today.
Kyriazis also said she believes it's possible that a shortage of lithium and other minerals required for battery production could be a potential issue within the next five years.
"But my understanding is that the global market is not hitting a supply crunch just yet," she said. "There could be a near-term supply issue. But we're not there yet."
In order to ensure adequate supply of minerals for battery production, the federal government in its most recent budget committed to providing up to $3.8 billion over eight years to create "Canada's first critical minerals strategy." The strategy is aimed at boosting extraction and production of Canadian nickel, lithium and other minerals used as components in electric vehicles and their batteries, and it aligns with opportunities for Canada-U.S. collaboration as companies electrify.
"Canada has a lot of natural resources and a lot of experience with natural resource extraction. We really can stand to be a leader in battery production," said Harry Constatine, president of the Vancouver Electric Vehicles Association, in an interview with CTVNews.ca over the phone on Monday.