Electricity News in January 2018

Hydro One wants to spend another $6-million to redesign bills
Hydro One Bill Redesign Spending sparks debate over Ontario Energy Board regulation, rate applications, privatization, and digital billing upgrades, as surveys cite confusing invoices under the Fair Hydro Plan for residential, commercial, and industrial customers.
Key Points
$15M project to simplify Hydro One bills, upgrade systems, and improve digital billing for commercial customers.
✅ $9M spent; $6M proposed for C&I and large-account changes.
✅ OEB to rule amid rate application and privatization scrutiny.
✅ Survey: 40% of customers struggled to understand bills.
Ontario's largest and recently privatized electricity utility has spent $9-million to redesign bills and is proposing to spend an additional $6-million on the project.
Hydro One has come under fire for spending since the Liberal government sold more than half of the company, notably for its CEO's $4.5-million pay.
Now, the NDP is raising concerns with the $15-million bill redesign expense contained in a rate application from the formerly public utility.
"I don't think the problem we face is a bill that people can't understand, I think the problem is rates that are too high," said energy critic Peter Tabuns. "Fifteen million dollars seems awfully expensive to me."
But Hydro One says a 2016 survey of its customers indicated about 40 per cent had trouble understanding their bills.
Ferio Pugliese, the company's executive vice-president of customer care and corporate affairs, said the redesign was aimed at giving customers a simpler bill.
"The new format is a format that when tested and put in front of our customers has been designed to give customers the four or five salient items they want to see on their bill," he said.
About $9-million has already gone into redesigning bills, mostly for residential customers, Pugliese said. Cosmetic changes to bills account for about 25 per cent of the cost, with the rest of the money going toward updating information systems and improving digital billing platforms, he said.
The additional $6-million Hydro One is looking to spend would go toward bill changes mostly for its commercial, industrial and large distribution account customers.
Energy Minister Glenn Thibeault noted in a statement that the Ontario Energy Board has yet to decide on the expense, but he suggested he sees the bill redesign as necessary alongside legislation to lower electricity rates introduced by the province.
"With Ontarians wanting clearer bills that are easier to understand, Hydro One's bill redesign project is a necessary improvement that will help customers," he wrote.
"Reductions from the Fair Hydro Plan (the government's 25 per cent cut to bills last year) are important information for both households and businesses, and it's our job to provide clear, helpful answers whenever possible."
The OEB recently ordered Hydro One to lower a rate increase it had been seeking for this year to 0.2 per cent down from 4.8 per cent.
The regulator also rejected a Hydro One proposal to give shareholders all of the tax savings generated by the IPO in 2015 when the Liberal government first began partially privatizing the utility. The OEB instead mandated shareholders receive 62 per cent of the savings while ratepayers receive the remaining 38 per cent.
Related News

Several Milestones Reached at Nuclear Power Projects Around the World
Nuclear Power Construction Milestones spotlight EPR builds, Hualong One steam generators, APR-1400 grid integration, and VVER startups, with hot functional testing, hydrostatic checks, and commissioning advancing toward fuel loading and commercial operation.
Key Points
Key reactor project steps, from testing and grid readiness to startup, marking progress toward safe commercial operation.
✅ EPR units advance through cold and hot functional testing
✅ Hualong One installs 365-ton steam generators at Fuqing 5
✅ APR-1400 and VVER projects progress toward grid connection
The world’s nuclear power industry has been busy in the new year, with several construction projects, including U.S. reactor builds, reaching key milestones as 2018 began.
EPR Units Making Progress
Four EPR nuclear units are under construction in three countries: Olkiluoto 3 in Finland began construction in August 2005, Flamanville 3 in France began construction in December 2007, and Taishan 1 and 2 in China began construction in November 2009. Each of the new units is behind schedule and over budget, but recent progress may signal an end to some of the construction difficulties.
EDF reported that cold functional tests were completed at Flamanville 3 on January 6. The main purpose of the testing was to confirm the integrity of primary systems, and verify that components important to reactor safety were properly installed and ready to operate. More than 500 welds were inspected while pressure was held greater than 240 bar (3,480 psi) during the hydrostatic testing, which was conducted under the supervision of the French Nuclear Safety Authority.
With cold testing successfully completed, EDF can now begin preparing for hot functional tests, which verify equipment performance under normal operating temperatures and pressures. Hot testing is expected to begin in July, with fuel loading and reactor startup possible by year end. The company also reported that the total cost for the unit is projected to be €10.5 billion (in 2015 Euros, excluding interim interest).
Olkiluoto 3 began hot functional testing in December. Teollisuuden Voima Oyj—owner and operator of the site—expects the unit to produce its first power by the end of this year, with commercial operation now slated to begin in May 2019.
Although work on Taishan 1 began years after Olkiluoto 3 and Flamanville 3, it is the furthest along of the EPR units. Reports surfaced on January 2 that China General Nuclear (CGN) had completed hot functional testing on Taishan 1, and that the company expects the unit to be the first EPR to startup. CGN said Taishan 1 would begin commercial operation later this year, with Taishan 2 following in 2019.
Hualong One Steam Generators Installed
Another Chinese project reached a notable milestone on January 8. China National Nuclear Corp. announced the third of three steam generators had been installed at the Hualong One demonstration project, which is being constructed as Unit 5 at the Fuqing nuclear power plant.
The Hualong One pressurized water reactor unit, also known as the HPR 1000, is a domestically developed design, part of China’s nuclear program, based on a French predecessor. It has a 1,090 MW capacity. The steam generators reportedly weigh 365 metric tons and stand more than 21 meters tall. The first steam generator was installed at Fuqing 5 on November 10, with the second placed on Christmas Eve.
Barakah Switchyard Energized
In the United Arab Emirates, more progress has been made on the four South Korean–designed APR-1400 units under construction at the Barakah nuclear power plant. On January 4, Emirates Nuclear Energy Corp. (ENEC) announced that the switchyard for Units 3 and 4 had been energized and connected to the power grid, a crucial step in Abu Dhabi toward completion. Unit 2’s main power transformer, excitation transformer, and auxiliary power transformer were also energized in preparation for hot functional testing on that unit.
“These milestones are a result of our extensive collaboration with our Prime Contractor and Joint Venture partner, the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO),” ENEC CEO Mohamed Al Hammadi said in a press release. “Working together and benefitting from the experience gained when conducting the same work on Unit 1, the teams continue to make significant progress while continuing to implement the highest international standards of safety, security and quality.”
In 2017, ENEC and KEPCO achieved several construction milestones including installation and concrete pouring for the reactor containment building liner dome section on Unit 3, and installation of the reactor containment liner plate rings, reactor vessel, steam generators, and condenser on Unit 4.
Construction began on the four units (Figure 1) in July 2012, May 2013, September 2014, and September 2015, respectively. Unit 1 is currently undergoing commissioning and testing activities while awaiting regulatory review and receipt of the unit’s operating license from the Federal Authority for Nuclear Regulation, before achieving 100% power in a later phase. According to ENEC, Unit 2 is 90% complete, Unit 3 is 79% complete, and Unit 4 is 60% complete.
VVER Units Power Up
On December 29, Russia’s latest reactor to commence operation—Rostov 4 near the city of Volgodonsk—reached criticality, as other projects like Leningrad II-1 advance across the fleet, and was operated at its minimum controlled reactor power (MCRP). Criticality is a term used in the nuclear industry to indicate that each fission event in the reactor is releasing a sufficient number of neutrons to sustain an ongoing series of reactions, which means the neutron population is constant and the chain reaction is stable.
“The transfer to the MCRP allows [specialists] to carry out all necessary physical experiments in the critical condition of [the] reactor unit (RU) to prove its design criteria,” Aleksey Deriy, vice president of Russian projects for ASE Engineering Co., said in a press release. “Upon the results of the experiments the specialists will decide on the RU powerup.”
Rostov 4 is a VVER-1000 reactor with a capacity of 1,000 MW. The site is home to three other VVER units: Unit 1 began commercial operation in 2001, Unit 2 in 2010, and Unit 3 in 2015.
Related News

Israeli ministries order further reduction in coal use
Israel Coal Reduction accelerates the energy transition, cutting coal use in electricity production by 30% as IEC shifts to natural gas, retires Hadera units, and targets a 2030 phase-out to lower emissions.
Key Points
Plan to cut coal power by 30%, retire IEC units, and end coal by 2030, shifting electricity generation to natural gas.
✅ 30% immediate cut in coal use for electricity by IEC
✅ Hadera units scheduled for retirement and gas replacement by 2022
✅ Complete phase-out of coal and gasoil in power by 2030
Israel's Energy and Water and Environmental Protection Ministers have ordered an immediate 30% reduction in coal use for electricity production by state utility Israel Electric Corporation as the country increases its dependence on domestic natural gas.
IEC, which operates four coal power plants with a total capacity of 4,850 MW and imports thermal coal from Australia, Colombia, Russia and South Africa, has been planning, as part of the decision to reduce coal use, to shut one of its coal plants during autumn 2018, when demand is lowest.
Israel has already decided to shut the four units of the oldest coal power plant at Hadera by 2022, echoing Britain's coal-free week milestones, and replace the capacity with gas plants.
"By 2030 Israel will completely stop the use of coal and gasoil in electricity production," minister Yuval Steinmetz said.
Coal consumption peaked in 2012 at 14 million mt and has declined steadily, aligning with global trends where renewables poised to eclipse coal in power generation, with the coming on line of Israel's huge Tamar offshore gas field in 2013.
In 2015 coal accounted for more than 50% of electricity production, even as German renewables outpaced coal in generation across that market. Coal's share would decline to less than 30% under the latest decision.
Israel's coal consumption in 2016 totaled 8.7 million mt, as India rationed coal supplies amid surging demand, and was due to decline to 8 million mt last year.
Three years ago, the ministers ordered a 15% reduction in coal use, while Germany's coal generation share remained significant, and the following year a further 5% cut was added.
Related News
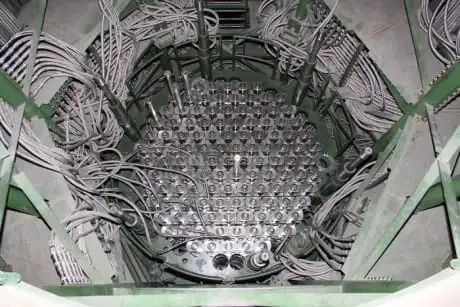
Leningrad II-1 reactor assembled
Leningrad II VVER-1200 Reactor Vessel assembly completed in Sosnovy Bor, with Rosenergoatom preparing for first criticality, hydraulic tests, and physical startup checks of neutron physics, control systems, and passive heat removal safety.
Key Points
Core vessel for Leningrad II Unit 1, completed, sealed, and prepared for hydraulic tests ahead of first criticality.
✅ Hydraulic tests to verify circuit integrity and equipment density
✅ Physical tests to refine neutron-physics of initial fuel loading
✅ Passive heat removal system testing completed; fuel loading began
Rosenergoatom has completed the assembly of the reactor vessel for unit 1 of the Leningrad Phase II nuclear power plant, which is in Sosnovy Bor in western Russia, even as it develops power lines to reactivate the Zaporizhzhia plant in a separate project. The nuclear power plant operator subsidiary of state nuclear corporation Rosatom said yesterday the VVER-1200 is now being prepared for first criticality this month.
Alexander Belyaev, chief engineer of Leningrad NPP, said in the company statement, noting industry-wide nuclear project milestones this year: "The reactor is fully assembled, sealed and ready for hydraulic tests of the first and second circuits, during which we will once again check the equipment of the reactor installation, and finally confirm its density. After that, it will be possible to start the reactor at the minimum controlled power level."
Belyaev said this preparatory phase "envisages a whole series of physical tests that will make it possible to refine the neutron-physical characteristics of the first fuel loading of the nuclear reactor, as well as prove the reliability of the entire control and safety system (in line with the US NRC's final safety evaluation for the NuScale SMR) of the reactor installation".
The existing Leningrad plant site has four operating RMBK-1000 units, while Leningrad II will have four VVER-1200 units, as projects like the Georgia nuclear expansion continue to take shape globally. Testing of the passive heat removal system of unit 1 of Leningrad II was completed in late August and fuel loading began in December, while a new U.S. reactor startup underscored the broader resurgence.
Related News

India Proposes 70 Percent Duty on China, Malaysia Solar Imports
India Solar Safeguard Duty could impose a 70% tariff on Chinese and Malaysian solar cells and modules, citing serious injury, protecting domestic manufacturing, affecting imports, prices, tenders, and the 2017 record-low tariff trajectory.
Key Points
A proposed 70% provisional tariff on Chinese and Malaysian solar cells and modules to protect India's domestic industry.
✅ 70% provisional duty for 200 days on cells and modules
✅ Aims to prevent serious injury and job losses
✅ Likely to raise tariffs and slow tendered solar projects
India, the largest importer of Chinese solar equipment, proposed a 70 per cent "safeguard duty" on cells and modules shipped from China, where solar is cheaper than grid electricity in many cities, and Malaysia, citing “threat of serious injury” to the domestic industry.
Acting on an application by five local cell and module makers, the Directorate General of Safeguards, Customs and Central Excise made the proposal in a document dated Jan. 5. It recommended the levy remain in effect for 200 days, as Germany saw a solar power boost amid broader energy concerns.
“Existing critical circumstances justify the immediate imposition of a provisional safeguard duty in order to save the domestic industry from further serious injury, which would be difficult to repair,” the Finance Ministry said in the document, also citing the potential for job losses.
Globally, external shocks such as the coronavirus pandemic have stalled a third of new U.S. utility solar this year, according to one report.
India’s annual manufacturing capacity for solar cells is only around 3 GW, compared with the average requirement of 20 GW for its on-grid solar power sector, according to a government note last month. The rest has to be purchased on the international market, it said. The South Asian nation was the largest solar-cell and module importer from China last year, buying a third of that nation’s $8 billion of shipments from January through September, according to research by Bloomberg New Energy Finance.
The ministry’s document said China’s solar exports to India constituted 1.52 percent of its total global exports during 2012, a figure that surged to almost 22 percent in 2016.
“India’s solar story is built on Chinese panels, and the duty, if implemented, would mean the end of record low solar tariffs that we saw in 2017,” said Vandana Gombar, a BNEF analyst in New Delhi, even as India's solar growth slows in recent assessments.
The government’s proposal came after five domestic manufacturers — Adani Enterprises Ltd.-backed Mundra Solar PV Ltd., Indosolar Ltd., Jupiter Solar Power Ltd., Websol Energy Systems Ltd. and Helios Photo Voltaic Ltd. — filed an application on Dec. 5 seeking a duty on imports of solar cells “whether or not assembled in modules or panels.”
Related News

Tesla’s lead battery expert hired by Uber to help power its ‘flying car’ service
Uber Elevate eVTOL Batteries enable electric air taxis with advanced energy storage, lithium-ion cell quality, safety engineering, and zero-emissions performance for urban air mobility, ride-hailing aviation, and scalable battery pack development.
Key Points
Battery systems for Uber's electric air taxis, maximizing energy density, safety, and cycle life for urban air mobility.
✅ Ex-Tesla battery leader guides pack design and cell quality
✅ All-electric eVTOL targets zero-emissions urban air mobility
✅ Focus on safety, energy density, fast charge, and lifecycle
Celina Mikolajczak, a senior manager for battery pack development at Tesla, has been hired by Uber to help the ride-hail company’s “flying car” project get off the ground. It’s an important hire because it signals that Uber plans to get more involved in the engineering aspects of this outlandish-sounding project.
For six years, Mikolajczak served as senior manager and technical lead for battery technology, cell quality, and materials analysis. She worked with Tesla’s suppliers, tested the car company’s lithium-ion batteries for long-term use as the age of electric cars accelerates, oversaw quality assurance, and conducted “failure analysis” to drive battery cell production and design improvements. In other words, Mikolajczak was in charge of making sure the most crucial component in Tesla’s entire assembly line was top of the line.
Now she works for Uber — and not just for Uber, but for Uber Elevate, the absurdly ambitious air taxi service that hinges on the successful development of electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) vehicles. There are practically zero electric planes in service today, and definitely none being used in a commercial ride-hail service. The hurdles to getting this type of service off the ground are enormous.
Her title at Uber is director of engineering and energy storage systems, and today marks her first week on the job. She joins Mark Moore, the former chief technologist for on-demand mobility at NASA’s Langley Research Center, who joined Uber almost a year ago to help lend a professional appearance to Elevate. Both serve under Jeff Holden, Uber’s head of product, who oversees the air taxi project.
Uber first introduced its plan to bring ride-sharing to the skies in a white paper last year. At the time, Uber said it wasn’t going to build its own eVTOL aircraft, but stood ready to “contribute to the nascent but growing VTOL ecosystem and to start to play whatever role is most helpful to accelerate this industry’s development.”
Instead, Uber said it would be partnering with a handful of aircraft manufacturers, real estate firms, and government regulators to better its chances of developing a fully functional, on-demand flying taxi service. It held a day-long conference on the project in Dallas in April, and plans to convene another one later this year in Los Angeles. In 2020, Uber says its aerial service will take off in three cities: LA, Dallas-Fort Worth, and Dubai.
UBER’S TAKING A MORE PROMINENT ROLE
Now, Uber’s taking a more prominent role in the design and manufacturing of its fleet of air taxis, which signals a stronger commitment to making this a reality — and also more of a responsibility if things eventually go south, as setbacks like Eviation's collapse underscore.
Perhaps most ambitiously, Uber says the aircraft it plans to use (but, importantly, do not exist yet) will run on pure battery-electric power, and not any hybrid of gasoline and electricity. Most of the companies exploring eVTOL admit that battery’s today aren’t light enough or powerful enough to sustain flights longer than just a few minutes, but many believe that battery technology will eventually catch up, with Elon Musk suggesting a three-year timeline for cheaper, more powerful cells.
Uber believes that in order to sustain a massive-scale new form of transportation, it will need to commit to an all-electric, zero-operational emissions approach from the start, even as potential constraints threaten the EV boom overall. And since the technology isn’t where it needs to be yet, the ride-hail company is taking a more prominent role in the development of the battery pack for its air taxi vehicles. Mikolajczak certainly has her work cut out for her.
Related News

UK must be ready for rise of electric vehicles, says ABB chief
UK EV Charging Infrastructure is accelerating as ABB and Formula E spotlight fast charging, smart grids, and public stations, preparing Britain for mass electric vehicle adoption with expanded capacity, reliable connectors, and nationwide coverage.
Key Points
The UK network of charge points, grid capacity, and services enabling secure, scalable electric vehicle adoption.
✅ ABB urges rapid rollout of fast chargers and smart grid upgrades
✅ National Grid forecasts up to 9m EVs by 2030 in the UK
✅ Government GBP 400m investment targets reliable nationwide coverage
The UK should speed up preparations for the rise of electric vehicles, according to the chief executive of ABB, the world’s largest supplier of fast-charging points.
Speaking as the Switzerland-based engineering firm became the first official sponsor of the electric street racing series Formula E, Ulrich Spiesshofer predicted a flood of consumer take-up of plug-in cars, noting how EV inquiries surged in the UK during a recent fuel supply crisis.
And he added his voice to warnings that Britain must move faster to make sure owners of electric vehicles are not stymied by a shortage of charging bays or cost concerns among consumers.
“E-mobility is unstoppable, it’s just a question of how fast and how deep it will be deployed,” he said. “The UK has a big population that really wants to contribute to a greener, more sustainable world. But there’s always a question of whether it’s quick enough. In the next couple of years, it’s in the interest of everybody to make sure the infrastructure is coming up.”
How green are electric cars?
He said this would include adding to the UK’s network of electric charging points, as well as ensuring enough energy capacity so that the grid can cope with rising demand.
There are 14,344 charging connectors in the UK, according to ZapMap, which charts the scale of the UK’s network.
Those charging points served around 132,000 plug-in vehicles at the end of 2017, but the National Grid has predicted that the number of electric cars could surge to 9m by 2030.
“In the next couple of years, it’s in the interest of everybody to make sure the infrastructure is coming up,” said Spiesshofer.
He welcomed the government’s budget pledge to spend £400m on improving the UK’s charging point network but warned that the power grid also needed to be ready to meet the increased demand, which many argue is manageable with proper management approaches.
Electric cars have been forecast to add about 18 gigawatts of power demand to the grid, the equivalent of six Hinkley Point C nuclear power stations.
Spiesshofer said he hoped ABB’s sponsorship of Formula E, which will last until 2025, would help spur interest in electric cars and lead to technological breakthroughs, even as the US EV boom tests charging capacity elsewhere.
Related News

New Rules for a Future Puerto Rico Microgrid Landscape
Puerto Rico Microgrid Regulations outline renewable energy, CHP, and storage standards, enabling islanded systems, PREPA interconnection, excess energy sales, and IRP alignment to boost resilience, distributed resources, and community power across the recovering grid.
Key Points
Rules defining microgrids, requiring 75 percent renewables or CHP, and setting interconnection and PREPA fee frameworks.
✅ 75 percent renewables or CHP; hybrids allowed
✅ Registration, engineer inspection, and annual generation reports
✅ PREPA interconnection fees; excess energy sales permitted
The Puerto Rico Energy Commission unveiled 29 pages of proposed regulations last week for future microgrid installations on the island.
The regulations, which are now open for 30 days of public comment, synthesized pages of responses received after a November 10 call for recommendations. Commission chair José Román Morales said it’s the most interest the not-yet four-year-old commission has received during a public rulemaking process.
The goal was to sketch a clearer outline for a tricky-to-define concept -- the term "microgrid" can refer to many types of generation islanded from the central grid -- as climate pressures on the U.S. grid mount and more developers eye installations on the recovering island.
“There’s not a standard definition of what a microgrid is, not even on the mainland,” said Román Morales.
According to the commission's regulation, “a microgrid shall consist, at a minimum, of generation assets, loads and distribution infrastructure. Microgrids shall include sufficient generation, storage assets and advanced distribution technologies, including advanced inverters, to serve load under normal operating and usage conditions.”
All microgrids must be renewable (with at least 75 percent of power from clean energy), combined heat and power (CHP) or hybrid CHP-and-renewable systems. The regulation applies to microgrids controlled and owned by individuals, customer cooperatives, nonprofit and for-profit companies, and cities, but not those owned by the Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority (PREPA). Owners must submit a registration application for approval, including a certification of inspection from a licensed electric engineer, and an annual fuel, generation and sales report that details generation and fuel source, as well as any change in the number of customers served.
Microgrids, like the SDG&E microgrid in Ramona in California, can interconnect with the PREPA system, but if a microgrid will use PREPA infrastructure, owners will incur a monthly fee. That amounts to $25 per customer up to a cap of $250 per month for small cooperative microgrids. The cost for larger systems is calculated using a separate, more complex equation. Operators can also sell excess energy back to PREPA.
Big goals for the island's future grid
In total, 53 groups and companies, including Sunnova, AES, the Puerto Rico Solar Energy Industries Association (PR-SEIA), the Advanced Energy Management Alliance (AEMA), and the New York Smart Grid Consortium, submitted their thoughts about microgrids or, in many cases, broader goals for the island’s future energy system. It was a quick turnaround: The Puerto Rico Energy Commission offered a window of just 10 days to submit advice, although the commission continued to accept comments after the deadline.
“PREC wanted the input as fast as possible because of the urgency,” said AES CEO Chris Shelton.
AES’ plan includes a network of “mini-grids” that could range in size from several megawatts to one large enough to service the entire city of San Juan.
“The idea is, you connect those to each other with transmission so they can have a co-optimized portfolio effect and lower the overall cost,” said Shelton. “But they would be largely autonomous in a situation where the tie-lines between them were broken.”
According to estimates provided in AES’ filing, utility-scale solar installations over 50 megawatts on the island could cost between $40 and $50 per megawatt-hour. Those prices make solar located near load centers an economic alternative to the island’s fossil-fuel generating plants. The utility’s analysis showed that a 10,000-megawatt solar system could replace 12,000 gigawatt-hours of fossil generation, with 25 gigawatt-hours of battery storage leveling out load throughout the day. Puerto Rico’s peak load is 3,000 megawatts.
In other filings, PR-SEIA urged a restructuring of FEMA funds so they’re available for microgrid development. GridWise Alliance wrote that plans should consider cybersecurity, and AEMA recommended the commission develop an integrated resource plan (IRP) that includes distributed energy resources, microgrids and non-wires alternatives.
An air of optimism, though 1.5 million are still without power
After the commission completes the microgrid rulemaking, a new IRP is next on the commission’s to-do list. PREPA must file that plan in July, and regulators are working furiously to make sure it incorporates the recent flood of rebuilding recommendations from the energy industry.
Though the commission has the final say when it comes to approval of the plan, PREPA will lead the IRP process. The utility’s newly formed Transformation Advisory Council (TAC), a group of 11 energy experts, will contribute.
With that group, along with New York’s Resiliency Working Group, lessons from California's grid transition, the Energy Commission, the utility itself, and the dozens of other clean energy experts and entrepreneurs who want to offer their two cents, the energy planning process has a lot of moving parts. But according to Julia Hamm, CEO of the Smart Electric Power Alliance and a member of both the Energy Resiliency Working Group and the TAC, those working to establish standards for Puerto Rico’s future are hitting their stride.
“Certainly over the past three months, it has been a bit of a challenge to ensure that everybody has been coordinating efforts. Just over the past couple of weeks, we’ve seen some good progress on that front. We’re starting to see a lot more communication,” she said, adding that an air of optimism has settled on the process. “The key stakeholders all have a very common vision for Puerto Rico when it comes to the power sector.”
Nisha Desai, a PREPA board member who is liaising with the TAC, affirmed that collaborators are on the same page. “Everyone is violently in agreement that the future of Puerto Rico involves renewables, microgrids and distributed generation,” she said.
The TAC will hold its first in-person meeting in mid-January, and has already consulted with the utility on its formal fiscal plan submission, due January 10.
Though many taking part in the process feel the once-harried recovery is beginning to adopt a more organized approach, Desai acknowledges that “there are a lot of people in Puerto Rico who feel forgotten.”
Puerto Rico’s current generation sits at just 72.6 percent, in a nation facing longer, more frequent outages due to extreme weather. The government recently offered its first estimate that about half the island, 1.5 million residents, remains without power.
In late December and into January, 1,500 more crewmembers from 18 utilities in states as far flung as Minnesota, Missouri and Arizona will land on the island to aid further restoration through mutual aid agreements.
“The system is getting up to speed, getting to 100 percent, but there’s still some instability,” said Román Morales. “Right now it’s a matter of time.”
Related News

Massachusetts stirs controversy with solar demand charge, TOU pricing cut
Massachusetts Solar Net Metering faces new demand charges and elimination of residential time-of-use rates under an MDPU order, as Eversource cites grid cost fairness while clean energy advocates warn of impacts on distributed solar growth.
Key Points
Policy letting solar customers net out usage with exports; MDPU now adds demand charges and ends TOU rates.
✅ New residential solar demand charges start Dec 31, 2018.
✅ Optional residential TOU rates eliminated by MDPU order.
✅ Eversource cites grid cost fairness; advocates warn slower solar.
A recent Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities' rate case order changes the way solar net metering works and eliminates optional residential time-of-use rates, stirring controversy between clean energy advocates and utility Eversource and potential consumer backlash over rate design.
"There is a lot of room to talk about what net-energy metering should look like, but a demand charge is an unfair way to charge customers," Mark LeBel, staff attorney at non-profit clean energy advocacy organization Acadia Center, said in a Tuesday phone call. Acadia Center is an intervenor in the rate case and opposed the changes.
The Friday MDPU order implements demand charges for new residential solar projects starting on December 31, 2018. Such charges are based on the highest peak hourly consumption over the course of a month, regardless of what time the power is consumed.
Eversource contends the demand charge will more fairly distribute the costs of maintaining the local power grid, echoing minimum charge proposals aimed at low-usage customers. Net metering is often criticized for not evenly distributing those costs, which are effectively subsidized by non-net-metered customers.
"What the demand charge will do is eliminate, to the extent possible, the unfair cross subsidization by non-net-metered customers that currently exists with rates that only have kilowatt-hour charges and no kilowatt demand, Mike Durand, Eversource spokesman, said in a Tuesday email.
"For net metered facilities that use little kilowatt-hours, a demand charge is a way to charge them for their fair share of the cost of the significant maintenance and upgrade work we do on the local grid every day," Durand said. "Currently, their neighbors are paying more than their share of those costs."
It will not affect existing facilities, Durand said, only those installed after December 31, 2018.
Solar advocates are not enthusiastic about the change and see it slowing the growth of solar power, particularly residential rooftop solar, in the state.
"This is a terrible outcome for the future of solar in Massachusetts," Nathan Phelps, program manager of distributed generation and regulatory policy at solar power advocacy group Vote Solar, said in a Tuesday phone call.
"It's very inconsistent with DPU precedent and numerous pieces of legislation passed in the last 10 years," Phelps said. "The commonwealth has passed several pieces of legislation that are supportive of renewable energy and solar power. I don't know what the DPU was thinking."
TIME-OF-USE PRICING ELIMINATED
It does not matter when during the month peak demand occurs -- which could be during the week in the evening -- customers will be charged the same as they would on a hot summer day, LeBel said. Because an individual customer's peak usage does not necessarily correspond to peak demand across the utility's system, consumers are not being provided incentives to reduce energy usage in a way that could benefit the power system, Acadia Center said in a Tuesday statement.
However, Eversource maintains that residential customer distribution peaks based on customer load profiles do not align with basic service peak periods, which are based on Independent System Operator New England's peaks that reflect market-based pricing, even as a Connecticut market overhaul advances in the region, according to the MDPU order.
"The residential Time of Use rates we're eliminating are obsolete, having been designed decades ago when we were responsible for both the generation and the delivery of electricity," Eversource's Durand said.
"We are no longer in the generation business, having divested of our generation assets in Massachusetts in compliance with the law that restructured of our industry back in the late 1990s. Time Varying pricing is best used with generation rates, where the price for electricity changes based on time of day and electricity demand and can significantly alter electric bills for households," he said.
Additionally, only 0.02% of residential customers take service on Eversource's TOU rates and it would be difficult for residential customers to avoid peak period rates because they do not have the ability to shift or reduce load, according to the order.
"The Department allowed the Companies' proposal to eliminate their optional residential TOU rates in order to consolidate and align their residential rates and tariffs to better achieve the rate structure goal of simplicity," the MDPU said in the order.
Related News

Coal CEO blasts federal agency's decision on power grid
FERC Rejects Trump Coal Plan, denying subsidies for coal-fired and nuclear plants as energy policy shifts toward natural gas and renewables, citing no grid reliability threat and warning about electricity prices and market impacts.
Key Points
FERC unanimously rejected subsidies for coal and nuclear plants, finding no grid reliability risk from retirements.
✅ Unanimous FERC vote rejects coal and nuclear compensation
✅ Cites no threat to grid reliability from plant retirements
✅ Opponents warned subsidies would distort power markets and prices
A decision by an independent energy agency to reject the Trump administration’s electricity pricing plan to bolster the coal industry could lead to more closures of coal-fired power plants and the loss of thousands of jobs, a top coal executive said Tuesday.
Robert Murray, CEO of Ohio-based Murray Energy Corp., called the action by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission “a bureaucratic cop-out” that will raise the cost of electricity and jeopardize the reliability and security of the nation’s electric grid.
“While FERC commissioners sit on their hands and refuse to take the action directed by Energy Secretary Rick Perry and President Donald Trump, the decommissioning of more coal-fired and nuclear plants could result, further jeopardizing the reliability, resiliency and security of America’s electric power grids,” Murray said. “It will also raise the cost of electricity for all Americans.”
The five-member energy commission voted unanimously Monday to reject Trump’s plan to reward nuclear and coal-fired power plants for adding reliability to the nation’s power grid. The plan would have made the plants eligible for billions of dollars in government subsidies and help reverse a tide of bankruptcies and loss of market share suffered by the once-dominant coal industry as utilities' shift to natural gas and renewable energy continues.
The Republican-controlled commission said there’s no evidence that any past or planned retirements of coal-fired power plants pose a threat to reliability of the nation’s electric grid.
Murray disputed that and said the recent cold snap that hit the East Coast showed coal’s value, as power users in the Southeast were asked to cut back on electricity usage because of a shortage of natural gas. “If it were not for the electricity generated by our nation’s coal-fired and nuclear power plants, we would be experiencing massive brownouts risk and blackouts in this country,” he said.
Murray Energy is the largest privately owned coal company in the United States, with mining operations in Ohio, Illinois, Kentucky, Utah and West Virginia. Robert Murray, a Trump friend and political supporter, has been pushing hard for federal assistance for his industry. The Associated Press reported last year that Murray asked the Trump administration to issue an emergency order protecting coal-fired power plants from closing. Murray warned that failure to act could cause thousands of coal miners to be laid off and force his largest customer, Ohio-based FirstEnergy Solutions, into bankruptcy.
Perry ultimately rejected Murray’s request, but later asked energy regulators to boost coal and nuclear plants as the administration moved to replace the Clean Power Plan with a more limited approach.
The plan drew widespread opposition from business and environmental groups that frequently disagree with each other, even as some coal and business interests backed the EPA's Affordable Clean Energy rule in court.
Jack Gerard, president and CEO of the American Petroleum Institute, said Tuesday that the Trump plan was “far too narrow” in its focus on power sources that maintain a 90-day fuel supply.
API, the largest lobbying group for oil and gas industry, supports coal and other energy sources, Gerard said, “but we should not put our eggs in an individual basket defined as a 90-day fuel supply (while) unnecessarily intervening in private markets.”
Related News

Turning seawater into electricity: NB Power's untested idea for Belledune
NB Power Hydrogen-from-Seawater Project explores clean energy R&D with Joi Scientific, targeting zero-emission electricity for Belledune using Bay of Chaleur seawater, hydrogen production, and possible carbon credits within Canada's climate plan.
Key Points
An NB Power R&D initiative with Joi Scientific to produce hydrogen from seawater for zero-emission power at Belledune.
✅ Targets coal phase-out by 2030 at Belledune
✅ Evaluates costs, efficiency, and carbon credits
✅ Seawater-to-hydrogen tech via proprietary R&D
NB Power is betting $7 million on a promising but untested new way to generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases: turning seawater from the Bay of Chaleur into energy, a marine approach similar to Nova Scotia's Bay of Fundy tidal tests in recent years.
CEO Gaëtan Thomas talked last month about converting the Belledune generating station to hydrogen power by 2030, after coal is phased out, though some argue planning should be led by an independent planning body to ensure long-term oversight.
But the public utility is tight-lipped so far o
"Unfortunately, it is too early in the process to be discussing details of this research and development project," said NB Power spokesperson Marie-Andrée Bolduc.
Joi Scientific's vice-president of marketing, Vicky Harris, said in an email statement that the company is "involved in multiple research projects, in many different sectors, but, as I am sure you would understand, we are not sharing details of our proprietary research and development work at this time."
On its website, the company calls hydrogen "the universe's most abundant element and the world's cleanest source of energy."
In its collaboration with Florida-based Joi Scientific, a start-up headquartered at the Kennedy Space Centre.
What to do with Belledune?
The federal government has set 2030 as the deadline for provinces to phase out coal-powered electricity under its national climate plan, and NB Power has pursued deals to import Quebec power as part of its transition.
NB Power says other options for Belledune include burning natural gas or biomass, and small nuclear reactors have been discussed provincially as well. But those options would still generate some carbon dioxide emissions.
Green Party Leader David Coon said last month that it was "news to me" that hydrogen power could be generated affordably enough to use in a power plant.
University of New Brunswick chemical engineering professor Willy Cook says turning hydrogen into energy is simple, but it's not necessarily cost-effective because the process itself requires a lot of electricity, while Nova Scotia is pursuing more wind and solar to meet its goals.
"You can't get something for nothing," he said. "Using electricity to produce hydrogen to go back to the process to produce electricity--that in itself probably isn't economically viable."
But he said he's not familiar with Joi Scientific's technology and it's possible the company has come up with "a more efficient process."
He also said if NB Power earned carbon credits for reducing emissions, hydrogen technology might become competitive with other energy sources.
"I have faith in the NB Power engineers to come through and do that assessment properly," he said.
Related News

Stop messaging me about arc flash training
Arc Flash Training equips electricians with electrical safety best practices, CSA Z462 and NFPA 70E compliance, PPE selection, incident energy and risk assessment, lockout/tagout, and refreshed skills to cut arc blast hazards and injuries.
Key Points
Arc Flash Training covers CSA Z462/NFPA 70E, risk assessment, and PPE to reduce incident energy and prevent injuries.
✅ Meets CSA Z462/NFPA 70E electrical safety requirements
✅ Teaches PPE selection, boundaries, and labeling
✅ Retraining recommended every 3 years for compliance
"Stop messaging me about arc flash training. It's a f****** joke. I'm a certified electrician I don't need to pay someone to tell me the dangers of my job."
That's what someone wrote to me yesterday when I sent my promotion about our upcoming arc flash training course, at
https://electricityforum.com/electrical-training/arc-flash-training
It’s a real glimpse into the thinking of many electrical professionals who think they are right, right up until the day they find out they are wrong.
And it’s the kind of resistance professional electrical safety trainers face every day and an indication of a knowledge gap in safety education.
We ask our students in class: Think of a time when you had a really close call, and ‘got away with it’. And In every class, we find our that every electrician in class has had at least one of those moments. Many electricians have been shocked or burned, and most electricians at least know a story of someone who ended up in the hospital. We know five electricians that have been burned in arc flash incidents over the years.
Electrical workers with that kind of thinking and who work uninjured, are lucky, though leadership in worker safety can improve outcomes.
However, the best way to prevent thousands of arc flash accidents every year in North America is "Good Training", not "Good Luck!"
Every electrical professional needs electrical safety training, including fire alarm training for life safety systems. And every electrical worker needs retraining, every three years.
The Electricity Forum Training Institute organizes regular arc flash training courses to review changes made to CSA Z462, with options such as Vancouver arc flash training available to regional attendees.
Here is more information about our Arc Flash Training courses, and we also provide live online fire alarm training for complementary competencies.
Visit our Arc Flash Training Page
Related News

Despite delays, BC Hydro says crews responded well to 'atypical' storm
BC Hydro Ice Storm Response to Fraser Valley power outages highlights freezing rain impacts, round the clock crews, infrastructure challenges, and climate change risks across the Lower Mainland during winter weather and restoration efforts.
Key Points
A plan for freezing rain events that prioritizes safety, rapid repairs, and clear communication to restore power.
✅ Prioritizes hazards, critical loads, and public safety first
✅ Deploys crews, contractors, and equipment across affected areas
✅ Addresses climate risks without costly undergrounding expansion
Call it the straw that broke the llama's back.
The loss of power during recent Fraser Valley ice storms meant Jennifer Quick, who lives on a Mission farm, had no running water, couldn't cook with appliances and still had to tend to a daughter sick with stomach flu.
As if that wasn't enough, she had to endure the sight of her shivering llamas.
"I brought them outside at one point and when I brought them back in, they had icicles on their fur," she said, adding the animals stayed in the warmth of their barn from then on.
For three and a half days, Quick and her family were among more than 160,000 BC Hydro customers in the Fraser Valley left in the dark after ice storms whipped through the region.
BC Hydro expects to get all customers back online Tuesday, five days after the storm hit.
And with another storm possibly on the horizon, the utility is defending its response to the treacherous weather, noting that windstorm power outages can be widespread.
BC Hydro spokesperson Mora Scott said the utility has a "best in class" storm response system, similar to PG&E winter storm prep in the U.S.
"In a typical storm situation we normally have 95 per cent of our customers back up within 24 hours. Ice storms are different and obviously this was an atypical storm for us," she said.
Scott said that in this case, the utility got power back on for 75 per cent of customers within 24 hours. It took the work of 450 employees called in from around B.C., working around the clock, a mobilization echoed by Sudbury Hydro crews after a storm, she said.
The work was complicated by trees falling near crews, icy roads, low visibility and even substations so frozen over the ice had to be melted off with blowtorches.
She said that in the long term, BC Hydro has no plans to make changes to how it responds to extreme ice storms or how infrastructure is built.
"Seeing ice build up in the Lower Mainland like this is a rare event," she said. "So to build for extremes like that probably doesn't make a lot of sense."
Climate change will bring storms
But CBC meteorologist Johanna Wagstaffe said that might not always be the case as climate change continues to impact our planet.
"The less severe winter events, like light snowfall, will happen less often," she said. "But the disruptive events — like last week's storm — will actually happen more often and we are already seeing this shift happen."
Marc Eliesen, a former CEO of BC Hydro in the early 1990s, said the utility needs to keep that in mind when planning for worst-case scenarios.
"This [storm] is a condition characteristic of the weather in the east, particularly in Ontario and Quebec, where freezing rain outages in Quebec are more common, which is organized to deal with freezing rain and heavy snow on the lines," he said. "This is a new phenomenon for British Columbia."
Eliesen questions whether BC Hydro has adequate equipment and crew training to deal with ice storms if they become more frequent, pointing to Hydro One storm restoration in Ontario as a comparison.
'Always something we can learn'
Scott disagrees with some of Eliesen's points.
She said some of the crews called in to deal with the recent storm come from northern B.C. and the Interior and have plenty of experience with snow.
"There's always something we can learn in every major storm situation," she said.
The idea of putting power lines underground was raised by some CBC readers and listeners, but Scott said running underground lines is five to 10 times the cost of running lines on pole, so it is done sparingly. Besides, equipment like substations and transmission lines need to be kept aboveground.
Meanwhile, Wagstaffe said that beginning Thursday, wintry weather could return to the Lower Mainland.













