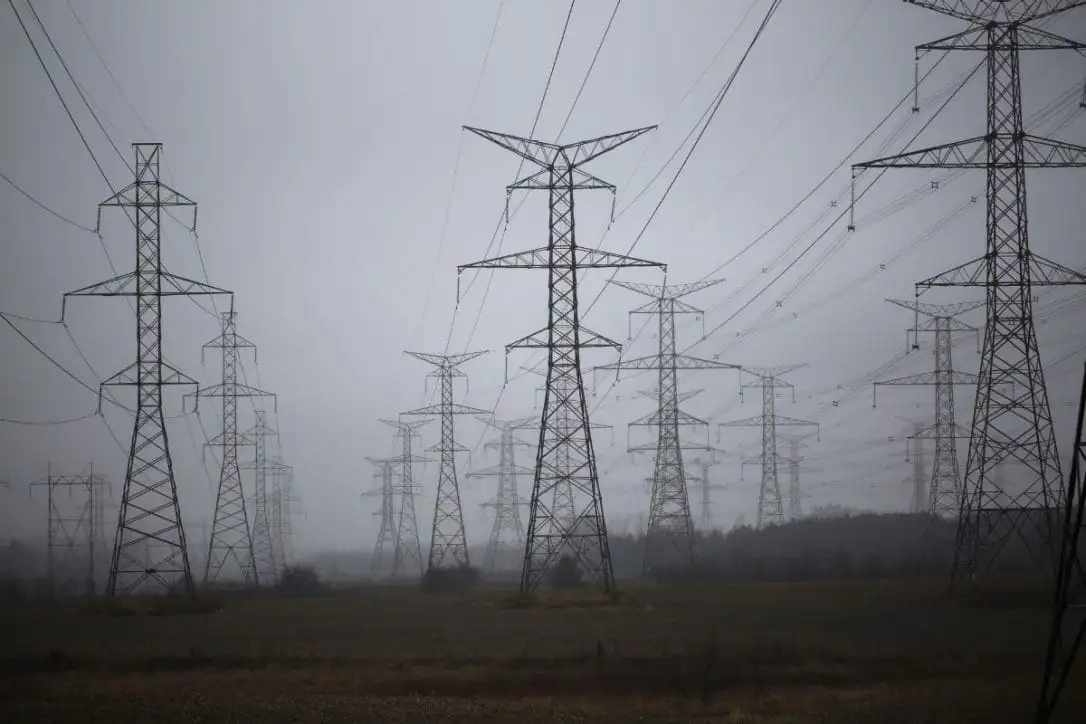
Mississippi power plant costs cross $7.5B

NFPA 70b Training - Electrical Maintenance
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Kemper County power plant costs and delays highlight lignite coal gasification, syngas production, carbon capture targets, and looming rate plans as Mississippi Power navigates Public Service Commission oversight and shareholder-ratepayer risk.
Key Points
Costs exceed $7.5B with repeated delays; rate impacts loom as syngas, lignite, and carbon capture systems mature.
✅ Estimate tops $7.5B; customers could fund about $4.3B
✅ Carbon capture target: 65% CO2 via syngas from lignite
✅ Rate plans pending before the Public Service Commission
A Mississippi utility on Monday delayed making proposals for how its customers should pay for an ever-more-expensive power plant, even as the estimated cost of the facility crossed $7.5 billion.
The Kemper County power plant will be tasked with mining lignite coal a few hundred yards away from the plant. That coal is moved through a process that will convert it to syngas. The syngas is then used to drive the energy output of the plant, and the resulting electricity is then moved into the grid, where transmission projects influence regional reliability and capacity.
Thomas Fanning, CEO of parent Southern Co., told shareholders in May that Mississippi Power would file rate plans for its Kemper County power plant this month. But still unable to operate the plant steadily enough to declare it finished, Mississippi Power punted, instead asking to hold rates level for 11 months to pay off costs that have already been approved by regulators.
Mississippi Power says it now hopes to reach commercial operation in June. The plant is more than three years behind schedule, with 10 delays announced in the past 18 months. It was originally supposed to cost $2.9 billion.
The company also said monday that it will have to replace troublesome parts of the facility much sooner than expected, including units that cool the synthetic gas produced from soft lignite coal by two gasifier units, plus ash handling systems in the gasifiers.
Kemper is designed to take synthetic gas, pipe it through a chemical plant to remove carbon dioxide and other chemicals, and then burn the gas in turbines to generate electricity. It’s designed to capture 65 percent of carbon dioxide from the coal, releasing only as much of the climate-warming gas as a typical natural gas plant. It’s a key effort nationally to maintain coal as a viable fuel source, even as coal unit retirements proceed in other states.
Mississippi Power raised its estimate of Kemper’s cost by $209.4 million, with shareholders absorbing $185.9 million, while ratepayers could be asked to pay $23.5 million. Overall, customers could be asked to pay $4.3 billion. Southern shareholders have agreed to absorb $3.1 billion, which has risen by $500 million since November.
The elected three-member Public Service Commission in 2015 allowed the company to raise rates on its 188,000 customers by $126 million a year. That paid for $840 million in Kemper work, which began generating electricity in 2014 using piped-in natural gas. Some items covered by that 15 percent rate increase will be paid off in coming months, but Mississippi Power now proposes to repay costs from regulatory proceedings earlier than originally projected.
In testimony filed with the Public Service Commission, Mississippi Power Chief Financial Officer Moses Fagin said that keeping rates level would reduce whiplash to customers when rates rise later to pay for Kemper, would pay off accumulated costs more quickly and would help the company wean itself off financial support from Southern Co. while maintaining credit ratings and positioning for a possible bond rating upgrade over time.
“Cash flow is important to the company in maintaining its current ratings and beginning to rebuild its credit strength on a more independent basis apart from the extraordinary parental support that has been required in recent years to maintain financial integrity,” Fagin testified.
Spokesman Jeff Shepard said Mississippi Power is still drawing up two rate plans — one requiring a sharp, immediate rate increase, and a “rate mitigation plan” that might cushion increases amid declining returns in coal markets. He said the company isn’t sure when it will file them. Fagin suggested the Public Service Commission set a new deadline of March 2, 2018.