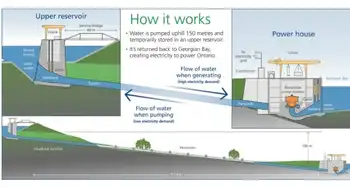
Ontario to Provide New and Expanded Energy-Efficiency Programs
CSA Z463 Electrical Maintenance -
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
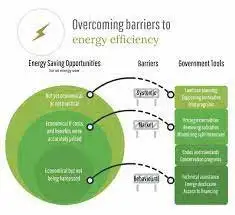
Ontario CDM Programs expand energy efficiency, demand response, and DER incentives via IESO's Save on Energy, cutting peak demand, lowering bills, and supporting electrification, retrofits, and LED lighting to meet Ontario's growing electricity needs.
Key Points
Ontario CDM Programs are IESO incentives that cut peak demand and energy use via demand response, retrofits and DERs.
✅ Delivered by IESO's Save on Energy to reduce peak demand
✅ Incentives for demand response, retrofits, LEDs, and DER solutions
✅ Help homes, businesses, and greenhouses lower bills and emissions
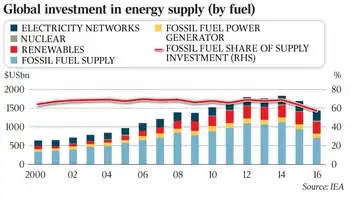
Ontario will be making available four new and expanded energy-efficiency programs, also known as Conservation and Demand Management (CDM) programs, to ensure a reliable, affordable, and clean electricity system, including ultra-low overnight pricing options to power the province, drive electrification and support strong economic growth. As there will be a need for additional electricity capacity in Ontario beginning in 2025, and continuing through the decade, CDM programs are among the fastest and most cost-effective ways of meeting electricity system needs.
Conservation and Demand Management
The Ontario government launched the 2021-2024 CDM Framework on January 1, 2021. The framework focuses on cost-effectively meeting the needs of Ontario’s electricity system, including by focusing on the achievement of provincial peak demand reductions and initiatives such as extended off-peak electricity rates, as well as on targeted approaches to address regional and/or local electricity system needs.
CDM programs are delivered by the Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO), which implemented staff lockdown measures during COVID-19, through the Save on Energy brand. These programs address electricity system needs and help consumers reduce their electricity consumption to lower their bills. CDM programs and incentives are available for homeowners, small businesses, large businesses, and contractors, and First Nations communities.
New and Expanded Programs
The four new and expanded CDM programs will include:
A new Residential Demand Response Program for homes with existing central air conditioning and smart thermostats to help deliver peak demand reductions. Households who meet the criteria could voluntarily enroll in this program and, alongside protections like disconnection moratoriums for residential customers, be paid an incentive in return for the IESO being able to reduce their cooling load on a select number of summer afternoons to reduce peak demand. There are an estimated 600,000 smart thermostats installed in Ontario.
Targeted support for greenhouses in Southwest Ontario, including incentives to install LED lighting, non-lighting measures or behind-the-meter distributed energy resources (DER), such as combined solar generation and battery storage.
Enhancements to the Save On Energy Retrofit Program for business, municipalities, institutional and industrial consumers to include custom energy-efficiency projects. Examples of potential projects could include chiller and other HVAC upgrades for a local arena, building automation and air handling systems for a hospital, or building envelope upgrades for a local business.
Enhancements to the Local Initiatives Program to reduce barriers to participation and to add flexibility for incentives for DER solutions.
It is the government’s intention that the new and expanded CDM programs will be available to eligible electricity customers beginning in Spring 2023.
The IESO estimates that the new program offers will deliver total provincial peak electricity demand savings of 285 megawatts (MW) and annual energy savings of 1.1 terawatt hours (TWh) by 2025, reflecting pandemic-era electricity usage shifts across Ontario. Savings will persist beyond 2025 with a total reduction in system costs by approximately $650 million over the lifetime of the measures, and will support economic recovery, as seen with electricity relief during COVID-19 measures, decarbonization and energy cost management for homes and businesses.
These enhancements will have a particular impact in Southwest Ontario, with regional peak demand savings of 225 MW, helping to alleviate electricity system constraints in the region and foster economic development, supported by stable electricity pricing for industrial and commercial companies in Ontario.
The overall savings from this CDM programming will result in an estimated three million tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions reductions over the lifetime of the energy-efficiency measures to help achieve Ontario’s climate targets and protect the environment for the future.
The IESO will be updating the CDM Framework Program Plan, which provides a detailed breakdown of program budgets and energy savings and peak demand targets expected to be achieved.