Electricity News in March 2017
Renewable Energy Study Released
Renewable Energy Subsidies drive market outcomes in a duopoly model, comparing mixed, output, and fixed input support under social welfare objectives, accounting for production costs, negative externalities, and impacts on electricity prices and outputs.
Key Points
Government incentives that lower renewable power costs via mixed, output, or fixed input support to enhance social welfare.
✅ Mixed subsidies maximize welfare but can raise electricity prices.
✅ Higher costs or externalities cut optimal output under output subsidies.
✅ Optimal prices and outputs hinge on externality level and costs.
Data detailed on Energy - Renewable Energy have been presented, including analyses related to falling wholesale electricity prices in some markets. According to news originating from Guangdong, People's Republic of China, by VerticalNews correspondents, amid China's push to boost wind and solar, research stated, "On the basis of the government subsidies for renewable energy electricity, this study builds a two-stage duopoly model in an industry with a renewable electricity enterprise and a conventional electricity enterprise in the market. Under the assumption of the generalised social welfare maximisation authority, this study discusses the effects of three types of government subsidies, business fixed input subsidy, output subsidy and mixed subsidy."
Our news journalists obtained a quote from the research from the University of Jinan, "First, the mixed subsidy policy is the best one under generalised social welfare. However, when the cost of renewable energy production or the energy negative coefficient is low, this subsidy policy generates a high electricity price, even though solar can be cheaper than grid electricity in China under certain conditions. Second, when the output subsidy is used, the optimal price and optimal output of renewable energy will decrease with the increase of production cost and the negative externality coefficient of renewable energy enterprises."
According to the news editors, the research concluded, noting market phenomena such as negative electricity prices during surplus conditions: "Finally, both the optimal price and optimal outputs depend on the level of negative externality and the cost of renewable energy production."
For more information on this research see: Influence of optimal government subsidies for renewable energy enterprises. IET Renewable Power Generation
Related News
OPG Reports 2016 Financial Results
OPG 2016 Financial Results underscore Ontario Power Generation's net income growth, driven by nuclear fleet output, hydroelectric capacity, and contracted generation, with Darlington refurbishment progress supporting clean energy, reliability, and stable customer rates.
Key Points
OPG earned $436M in 2016, led by nuclear output and contracted generation; Darlington and hydro projects advanced.
✅ Net income $436M, up from $402M in 2015
✅ Higher output from Darlington and Pickering nuclear units
✅ Contracted generation demand rose at Lennox and Atikokan
Ontario Power Generation Inc. (OPG) today reported net income attributable to the Shareholder of $436 million for 2016, compared to $402 million in 2015. The increase was primarily the result of higher generation from the nuclear fleet and higher earnings from the Contracted Generation Portfolio segment, as Ontario advanced plans for the Pickering B refurbishment to support future supply. The higher nuclear production reflected more days when the Darlington nuclear units were producing electricity in 2016, compared to 2015.
"I'm pleased with OPG's 2016 financial results," said OPG President and CEO
Jeff Lyash. "The continued strong financial performance of OPG benefits the Province and electricity consumers. It is essential that we manage our operations effectively, including Pickering life extensions, for the benefit of Ontarians."
"Both the Darlington and Pickering generating stations, which safely continue operating alongside our renewable power fleet of hydroelectric generating stations, produce clean, reliable power with virtually no smog or greenhouse gas emissions. The refurbishment of the Darlington station will provide another 30 years of operations at one of Ontario's most important public assets," said Lyash. "The $12.8 billion that we are investing in the refurbishment will provide important economic stimulus in Ontario, creating jobs and providing opportunities for more than 60 companies from over 25 communities across the province. At the same time, OPG continues to produce about half the electricity used in Ontario with the power priced 40 per cent lower than other generators, which helps moderate customer bills."
Higher electricity demand for stations in the Contracted Generation Portfolio segment in 2016, namely the Lennox Generating Station (GS) and the Atikokan GS, also contributed to the increase in earnings.
"We have achieved significant progress in a number of projects during the year, including the refurbishment work at the Sir Adam Beck Pump Hydroelectric Generating Station's 300-hectare reservoir, and the construction of the Peter Sutherland Sr. Hydroelectric Generating Station in northeastern Ontario. The construction of the Peter Sutherland Sr. station is our third partnership with an Indigenous community." said Lyash. "We're pleased that construction is progressing ahead of schedule and within budget. The 28 megawatt generating station is currently being commissioned and is expected to be in service this spring. This project is another example of OPG's strong partnerships with Ontario's Indigenous communities, yielding renewable power and lasting economic benefits for communities."
Related News
Comparative evaluation of different offshore wind turbine installation vessels for Korean west-south wind farm
Korean Offshore Wind Turbine Installation Vessels analyzed for WTIV, jack-up barge, and floating crane options, evaluating logistics, installation costs, transit duration, and marine conditions at the southwest offshore wind farm test and demo sites.
Key Points
Ships and barges that transport and install offshore wind turbines in Korea, optimized for cost, schedule, and site conditions.
✅ Compares WTIV, jack-up barge, and floating crane options
✅ Evaluates costs, transit duration, and weather downtime
✅ Aligns vessel choice with southwest Korean site conditions
New Findings from Pusan National University in the Area of Farming Described (Comparative evaluation of different offshore wind turbine installation vessels, building on U.K. wind lessons, for Korean west-south wind farm)
By a News Reporter-Staff News Editor at Energy Weekly News -- Current study results on Farming have been published. According to news reporting originating from Busan, South Korea, where a Yellow Sea floating solar project is planned, by VerticalNews correspondents, research stated, "The purpose of this study is to evaluate various means of wind power turbines installation in the Korean west south wind farm (Test bed 100 MW, Demonstrate site 400 MW). We presented the marine environment of the southwest offshore wind farm in order to decide the appropriate installation vessel to be used in this site."
Our news editors obtained a quote from the research from Pusan National University, "The various vessels would be WTIV (Wind turbine installation vessel), jack-up barge, or floating crane... etc. We analyzed the installation cost of offshore wind turbine and the transportation duration for each vessel, noting parallels with U.S. offshore wind trends."
According to the news editors, the research concluded: "The analysis results showed the most suitable installation means for offshore wind turbine in the Korean west south wind farm, and align with World Bank wind programs supporting emerging markets."
For more information on this research see: Comparative evaluation of different offshore wind turbine installation vessels for Korean west-south wind farm and related DOE wind projects that underscore ongoing investment. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 2017;9(1):45-54. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering can be contacted at: Soc Naval Architects Korea, Sci & Technol Bldg, Rm 508, 635-4, Yeoksam-Dong, Gangnam-Gu, Seoul, 135-703, South Korea.
Related News
India's on-grid solar power development. Historical transitions, present status and future driving forces
India On-Grid Solar Power is accelerating under supportive policies, ambitious targets, and grid integration efforts, boosting installed capacity, cutting emissions, and attracting investment across states through auctions, incentives, and reforms in the electricity sector.
Key Points
Utility-scale PV connected to India's grid, advanced by policy targets, competitive auctions, and state support.
✅ Rapid capacity growth via auctions and incentives
✅ Grid integration, curtailment, and storage are key challenges
✅ Continued policy support critical to meet 2030 targets
Researchers' Work from University of Melbourne Focuses on Renewable Energy South Australia's renewables boom offering a regional example (India's on-grid solar power development: Historical transitions, present status and future driving forces)
Current study results on Energy - Renewable Energy have been published. According to news reporting originating from Melbourne, Australia, by VerticalNews correspondents, research stated, "India with a fast growing demand for electricity and increasing consideration to emissions reduction is investing strongly in renewable electricity generation. Among renewables, the Central and State Governments have set aspirational targets for on-grid solar electricity as renewables surpass coal in India and legislated several supporting policies to realise these targets."
Our news editors obtained a quote from the research from the University of Melbourne, "As a result of the favourable political environment, the development of on-grid solar, in terms of the rate of growth in installed capacity, has been increasing in the recent years, with parallels such as China's rapid solar PV growth in 2016, and it is expected to continue in the future. This paper aims to investigate the impact of historical transitions of India's electricity sector on the ongoing development of on-grid solar electricity and to explore the prospect of solar sector development in the future. First of all, we investigate how the historical transformation of governmental intervention's approach intertwined with the gradual shift of the source of generation has paved the way for the current achievements in on-grid solar electricity. Second, we envision the future challenges and opportunities for the development of solar sector by looking ahead and discussing the continuity of government's support and the prospective competitions between different sources, including an India coal generation surge within the market."
According to the news editors, the research concluded: "We conclude the paper with some required steps, aligning with global electricity network goals, to be taken in order to secure the achievement of the targets in solar electricity in the future."
Related News
Digital Transformation of Commercial Buildings
Intelligent Buildings Trends 2017 spotlight IoT, analytics, energy management, and building automation, showing how data integration and software services optimize operations, cut costs, and support corporate sustainability and reliability goals.
Key Points
Intelligent Buildings Trends 2017 highlight IoT analytics and BAS that improve efficiency and sustainability.
✅ IT-OT convergence drives smarter facilities management
✅ Data analytics deliver actionable insights and optimization
✅ Energy management cuts costs and meets sustainability goals
A new white paper from Navigant Research highlights the top 10 trends for the intelligent buildings market in 2017, and adjacent grid edge trends that shape the ecosystem, including the major market issues driving investment in intelligent building solutions, as well as the business case and opportunities associated with various intelligent building solution areas.
The promise of revenue growth, improvements in operational efficiency, and meeting corporate sustainability goals are the fundamental drivers that have encouraged the development of the intelligent buildings marketplace. This momentum continues to grow as intelligent building technology becomes more sophisticated and as shifting customer demands, the deployment of EU smart meters and related customer analytics, climate change mitigation goals, power reliability concerns, and budget constraints increase interest.
“The unyielding pressure to be connected is beginning to transform expectations for how commercial buildings are operated,” says Casey Talon, principal research analyst at Navigant Research. “As a result, 2017 is poised to tip the scales for investment in intelligent building technologies and a smarter electricity infrastructure across markets.”
According to the white paper, the rapid deployment of cost-effective data acquisition devices and the integration of IT with traditional building automation and controls, and the digital grid are changing the industry of facilities management. With an evolving menu of software analytics and energy management services that leverage data to provide actionable insights for efficiency and optimization, intelligent buildings are becoming dynamic systems to manage energy consumption for efficiency and non-energy business improvements.
The white paper, 10 Trends for Intelligent Buildings in 2017 and Beyond, presents the top 10 trends for the intelligent buildings market in 2017 based on recent Navigant Research syndicated research report findings and ongoing technology investigations. It focuses on evolutions in technology, delivery models, and customer demand that are building the thrust for the digital transformation of commercial buildings. The paper presents the major market issues driving investment in intelligent building solutions, as well as the business case and opportunities associated with various intelligent building solution areas and related utility domains such as substation integration that intersect with building operations. An Executive Summary of the report is available for free download on the Navigant Research website.
Related News
Coal unit retirements addressed by Montana lawmakers
Colstrip plant closure legislation addresses coal power transitions at the 2,100 MW site, guiding decommissioning, tax revenue replacement, worker retraining, low-interest loans, and environmental cleanup as Talen Energy and Puget Sound Energy exit older units.
Key Points
Montana bills to manage Colstrip closures with decommissioning, cleanup, tax offsets, and worker retraining through 2022.
✅ SB 338 mandates decommissioning and transition plans
✅ Low-interest loans aim to keep Talen's unit running to 2022
✅ Measures address tax revenue loss and worker retraining
The 2,100 MW Colstrip power plant faces challenges familiar to coal-burners throughout the United States — competition from cheap natural gas and renewables combined with the increased costs of environmental upgrades and looming plant closures across the sector.
Last year, Puget Sound and Talen announced, following moves like the Idaho Power settlement in the region, they would close the two oldest units at the plant that date back to the 1970s.
In Talen's case, that closure could come in about a year, stoking concerns among state lawmakers about the impact of lost tax revenue and jobs in the region. In response, a group of legislators this weekend unveiled the first in three bills aimed at keeping the old Colstrip units open until 2022, similar to decisions like Hydro One's coal plant plan for the foreseeable future.
The bill, would direct the power companies to design plans to deal with the costs of the unit shutdowns, reportedly including those associated with the physical unit as well as the loss of tax revenues, real estate values and the cost of worker retraining programs, issues that echo Three Mile Island debates in the nuclear sector.
Subsequent measures are expected to target environmental cleanup plans and provide low-interest loans to keep the unit owned by Talen Energy open until 2022, even as jurisdictions like Alberta's coal phase-out move ahead of schedule. The loans would reportedly amount to $10 million a year from the state's $1 billion coal tax fund.
SB 338, which would direct the decommissioning plans, is set for a Thursday hearing. The other bills have not yet been introduced.
Related News
Projected electricity generation mix is sensitive to policies, natural gas prices
AEO2017 electricity fuel mix shows how natural gas prices, Clean Power Plan policy, and technology costs shift U.S. generation across coal, gas, renewables, wind, solar, and nuclear through varied scenarios and capacity additions.
Key Points
It summarizes how gas prices and the Clean Power Plan shift U.S. power from coal toward gas, renewables, and nuclear.
✅ Gas price scenarios drive coal, gas, and renewables dispatch
✅ Clean Power Plan alters retirements, capacity additions
✅ Low price case favors gas; high price lifts coal, renewables, nuclear
The mix of fuels used to generate electricity in the United States has changed in response to differences in the expected cost of fuels and electricity-generating technology costs and their deployment. These factors, together with policies affecting emissions from power generation and shifts in electricity demand, will determine the generation fuel mix of the future.
Multiple cases in EIA’s Annual Energy Outlook 2017 (AEO2017) show how projected electricity generation is affected by fuel prices, especially natural gas prices, and the Clean Power Plan, a final Environmental Protection Agency rule issued in 2015 whose enforcement was stayed by the U.S. Supreme Court in February 2016 pending the resolution of legal challenges, while broader global trends such as renewables overtaking coal by 2025 provide context.
Without the Clean Power Plan, there is less incentive to switch from carbon-intensive coal to less carbon-intensive natural gas or carbon-free fuels such as wind and solar. In the scenario where the Clean Power Plan is not implemented, coal again becomes the leading source of electricity generation by 2019, consistent with a subsequent uptick in coal-fired generation later in the decade, and retains that position through 2032, longer than in the Reference case, which includes the Clean Power Plan. Electricity generation from renewable sources remains below coal-fired electricity generation through 2040. Fewer coal plants are retired, and as a result, natural gas and renewable capacity additions are lower compared with the Reference case.
In addition to environmental regulations, the price of natural gas is an important factor in decisions about the operation, retirement, and expansion of electricity generation capacity. Of the cases included in the AEO2017, natural gas prices are lowest in the High Oil and Gas Resource and Technology case. In this case, prices remain close to their current levels through 2040, as lower extraction costs and higher resource availability result in more natural gas production. Conversely, the Low Oil and Gas Resource and Technology case assumes the opposite, and by 2040, natural gas prices return to the relatively high levels of the mid-2000s.
With more optimistic assumptions for natural gas supply that result in lower natural gas prices, the High Oil and Gas Resource and Technology case has more natural gas-fired electricity, displacing both coal-fired and renewable generation, even as wind and solar reached 10% of U.S. electricity in early 2018 nationwide. Compared with the Reference case, more coal plants retire or switch to natural gas and less renewable capacity is built.
Conversely, higher natural gas prices in the Low Oil and Gas Resource and Technology case result in more electricity generation from both coal-fired and renewable plants, and coal-fired generation exceeds natural gas-fired generation through 2040. Because of higher coal-fired generation and lower natural gas-fired generation, more zero-carbon generation is required to comply with the Clean Power Plan, which is included in the Reference case that is the starting point for both Oil and Gas Resource and Technology cases. Renewables gain market share, and EIA expected solar and wind to be larger U.S. generation sources in summer 2022, surpassing natural gas in 2022 and surpassing coal in 2028. The Low Oil and Gas Resource and Technology case is the only scenario in AEO2017 that results in new nuclear capacity beyond what is currently under construction.
Related News
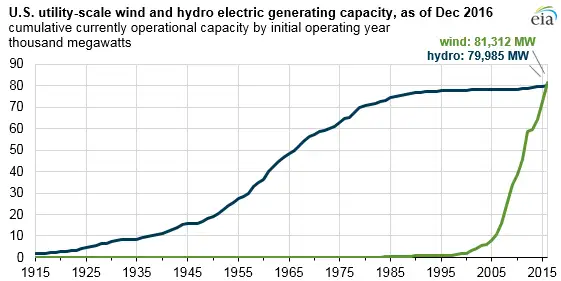
U.S. wind generating capacity surpasses hydro capacity at the end of 2016
US Wind and Hydropower Capacity surpassed milestones as wind overtook hydro in installed MW, yet hydro generation leads on higher capacity factors, seasonal hydrology, and West Coast precipitation, with ERCOT and SPP setting peaks.
Key Points
It refers to installed MW and seasonal generation shaped by capacity factors, hydrology, and regional grid dynamics.
✅ Wind capacity surpassed hydro, but hydro still leads in generation.
✅ Capacity factors and hydrology drive seasonal output variability.
✅ ERCOT and SPP recorded high wind shares and peak outputs.
Installed wind electric generating capacity in the United States surpassed conventional hydroelectric generating capacity, long the nation’s largest source of renewable electricity, after 8,727 megawatts (MW) of new wind capacity came online in 2016 amid wind power surges in the U.S. electricity mix. However, given the hydro fleet’s higher average capacity factors and the above-normal precipitation on the West Coast so far this year, hydro generation will likely once again exceed wind generation in 2017.
Wind and hydro generation both follow strong seasonal patterns. Hydro generation typically reaches its seasonal peak in the spring and early summer, especially in the Pacific Northwest and California where about half of U.S. hydropower is produced. Across most of the country, wind generation typically peaks in the spring and has become the most-used renewable source nationally with a smaller peak in late fall and early winter. The Pacific Northwest and California have a slightly different seasonal pattern for wind resources, with generally only one peak in the early summer.
In the Southwest Power Pool (SPP) electric system, which extends from northern Texas to North Dakota and Montana, wind power recently supplied more than half of the system’s generation mix for a brief period, as renewables surpassed coal nationally in 2022, reaching 52.1% (11,419 MW) in the early hours of February 12, 2017—a first for any of the seven U.S. regional transmission organization (RTO) electric systems that together serve two-thirds of the country’s electricity consumption.
The Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) system which covers most of Texas continues to set records for the highest level of wind generation on any U.S. electric system as renewables became the second-most prevalent U.S. electricity source in 2020, highlighting broader shifts. ERCOT’s most recent record of 16,022 MW occurred on the morning of December 25, 2016, and accounted for slightly more than 47% of the generation mix at the time
Compared with other electricity generating sources such as nuclear, geothermal, and combined-cycle natural gas, hydro and wind have lower average capacity factors (i.e., generation output as a percentage of total generating capacity). Both sources are sensitive to fluctuations in weather conditions such as droughts, heavy precipitation, and changes in regional wind patterns. Given the hydro fleet's historically higher capacity factors compared with wind and the expected strong hydrological conditions on the West Coast this year, such as the recent heavy rainfall in California and the Pacific Northwest, hydro generation in 2017 will likely still be higher than wind generation even with anticipated continuing additions of new wind capacity throughout the year.
For electricity reliability planning purposes, hydro and wind capacity are reduced (or derated) when estimating their expected contributions to meet projected peak-period electricity demand. Hydro capacity is generally derated to a much lesser degree than wind capacity. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation’s(NERC’s) latest summer reliability assessment shows the difference between the nameplate capacity and the expected on-peak capacity for variable renewable sources (wind, solar, and hydro) in each region, and recent U.S. solar growth underscores changing contributions across markets. In both SPP and the PJM Interconnection electric system, which covers a highly populated area of Mid-Atlantic, Southern, and Midwestern states, hydro provides more expected on-peak capacity than wind even though there is about twice as much installed wind capacity as hydro capacity in both regions.
Related News
Warm weather leads to first recorded natural gas storage injection in February
First February Natural Gas Injection reflects warm weather, low heating degree days, EIA storage build in the Lower 48, South Central salt and nonsalt sites, Bcf surplus, softer demand, steady production, and electricity generation
Key Points
An EIA-reported late-winter storage build from warm weather, fewer heating degree days, and South Central injections.
✅ Week ending Feb 24 saw a net 7 Bcf injection in the Lower 48
✅ Warm Northeast and Midwest cut heating demand and withdrawals
✅ South Central salt and nonsalt facilities led storage builds
Warmer than normal weather throughout much of the United States resulted in the first recorded net natural gas injection during a week in February since weekly storage data has been collected. For the week ending February 24, the amount of natural gas in storage in the Lower 48 states increased 7 billion cubic feet (Bcf). While some weeks during March in previous years had recorded injections, net injections of natural gas into storage do not typically occur until at least April.
Weekly changes in natural gas storage reflect changes in natural gas consumption, production, and, to a lesser extent, trade. Natural gas consumption is particularly sensitive to fluctuations in weather, and polar deep freezes can sharply increase heating demand and grid stress. Not only is natural gas consumed directly by furnaces and boilers in homes and businesses for heating, but natural gas is also used to generate electricity, which then fuels electric heat pumps and radiant heaters.
Temperatures throughout much of the United States have been higher than normal for many weeks this winter heating degrees days are a standard index of heating needs that are calculated based on deviations relative to a base temperature of 65 degrees Fahrenheit, and higher numbers of heating degree days reflect colder weather. For the week ending February 25, there were only 98 population-weighted heating degree days for the United States as a whole—a level more typical of mid-April weather, which often softens electricity and natural gas prices during winter. Based on normal weather data for 1971–2000, heating degree days would normally be near 172 for the week ending February 25. Temperatures were especially warm in the Northeast and Midwest, where natural gas heating is common.
The net injection of 7 Bcf during the week ending February 24, 2017, was extremely rare in a market where electricity prices have occasionally surged alongside weather-driven demand. Based on data from 2010–16, weekly changes during the month of February ranged from a net withdrawal of 48 Bcf to a net withdrawal of 243 Bcf. Previously, the earliest net injection of the calendar year occurred during the week ending March 16, 2012.
In the week ending February 24, natural gas injections in the South Central region offset unseasonably low withdrawals in other regions, as the broader energy crisis continues to influence electricity and gas markets. In EIA’s weekly report the amount of natural gas stored in South Central nonsalt facilities increased by 16 Bcf and in South Central salt facilities by 5 Bcf. After that injection, natural gas storage levels totaled 2,363 Bcf, or about 300 Bcf more than the previous five-year average for that week (2012–16). EIA’s latest short term forcast expects natural gas storage levels to fall to 2,121 Bcf by the end of March, or about 335 Bcf higher than the previous five-year average.
Related News
New White Paper from IEC assesses the worldwide need for Global Energy Interconnection
Global Energy Interconnection enables cross-border grids to share renewables, enhance reliability, and cut emissions through IEC standards, smart transmission, and policy coordination, advancing sustainable energy access, decarbonization, and climate resilience worldwide.
Key Points
A worldwide grid concept to share renewables, boost dependability, and expand clean energy access.
✅ Harmonizes international standards for ultra-high-voltage transmission
✅ Enhances grid dependability and cross-border renewable integration
✅ Requires global policy, market, and stakeholder coordination
Energy is central to nearly every major challenge and opportunity the world faces. However, one fifth of the world population still lacks access to energy and 3 billion people rely on wood, coal or animal waste for cooking and heating. Today, sustainable energy and grid climate risks are big global concerns.
The interconnection of grids as seen in Texas grid connection efforts would open up an unprecedented opportunity to globally share the resources of the whole planet, bringing clean energy to everybody, everywhere in the world.
Global Energy Interconnection
Global energy interconnection (GEI) is technically highly complex, with enablers like HVDC technology in play. It will require a level of dependability never seen before. International Standards inherently contain solutions that will help pre-address this complexity and they will play a crucial role in mastering dependability upfront.
This White Paper aims to assess the worldwide needs, benefits, policies and preconditions for GEI. It examines the readiness of potential markets and identifies technical and business trends such as the digital grid as well as hurdles. The White Paper analyzes and compares several global transmission scenarios and evaluates their impact on energy supply, the environment, technologies, and policies, as well as standards development.
Last but not least, this White Paper will provide recommendations on how standardization for such a large system of systems will need to be conducted and which stakeholders have to be involved.
Dr. Hu Hao, Senior Project Manager, International Cooperation Department, State Grid Corporation of China, states “To achieve the ambitious concept of global energy interconnection (GEI) or large scale, regional, intercontinental interconnection, requires political vision and a worldwide collaborative effort. Drawing up GEI concepts at an early stage by a consensus based process and through close cooperation between researchers, industry, regulators and standardization bodies is one of the central requirements for success of the implementation of the concept.”
This White Paper was developed by the IEC Market Strategy Board with major contributions from the International Energy Agency and State Grid Corporation of China, aligning with initiatives to build a smarter electricity infrastructure globally.
Related News

Four-Year U.S. Wind Forecast Sees Quarter-Million Jobs
American Wind Power Expansion drives 248,000 jobs, $85B economic activity, 35 GW capacity growth, boosting manufacturing, rural communities, and tax revenues, supported by the PTC and record renewable energy deployment through 2020.
Key Points
American Wind Power Expansion adds 35 GW by 2020, fueling 248,000 jobs and $85B in U.S. economic activity.
✅ 35 GW new capacity from 2017-2020 across rural America
✅ Projected 248,000 jobs; 33k in factories, 114k in O&M
✅ Generates $8B taxes; $85B total economic activity
The expansion of American wind power, as recent grid data show across the U.S., is poised to drive 248,000 jobs and $85 billion dollars in economic activity over the next four years, according to the American Wind Energy Association (AWEA), citing a new report from Navigant Consulting.
These and other economic benefits will result from the addition of 35 GW of new wind power capacity through the end of 2020, even as the timeline to reach 1 GW of U.S. offshore wind remains uncertain for grid connection, which also mark’s the end of President Donald Trump’s term in office, AWEA says.
AWEA has released an accompanying white paper. “Wind brings jobs and economic development to all 50 states,” to highlight the economic benefits wind already delivers to the U.S. economy today. For the first time ever, the U.S. wind industry supports more than 100,000 jobs; in fact, there are 102,500 workers in all 50 states.
“Growing wind energy revitalizes America’s rural areas and Rust Belt manufacturing centers,” comments Tom Kiernan, CEO of AWEA. “With over 100,000 jobs today, the industry is just getting started. This new analysis projects the industry could drive nearly a quarter-million jobs by 2020 – with $85 billion in economic activity over the next four years alone.”
AWEA says American wind industry jobs grew nearly 17% during 2016, and Navigant expects this growth to continue: Through 2020, the consultant expects a total of 248,000 wind-related American jobs, including induced jobs. By that time, there would be 33,000 Americans working in factories supplying the wind industry; 114,000 Americans building, operating and maintaining wind turbines; and an additional 102,000 workers in jobs supported by the industry.
The 102,500 wind industry jobs previously documented by AWEA include Americans working only for wind companies or in their supply chain in 2016 (not jobs in supporting industries). And unlike previous AWEA figures reporting the amount of private investment in new turbines each year, the Navigant study incorporates additional economic activity from operating and maintaining wind turbines, payments to landowners, and taxes paid by the wind industry, AWEA points out.
Rural areas that sorely need investment will be the largest beneficiaries of this growth, as illustrated by new Midwestern wind projects that attract capital, considering 99% of wind projects are located in rural areas today, the association says.
Wind power development funds states and local communities through sales, income and property taxes, and Navigant calculates that the new wind activity will pay over $8 billion in taxes over the next four years – on top of the tax revenues from existing wind projects. These tax revenues help local communities fix roads, build schools and improve emergency services, notes AWEA.
As pointed out in a recent AWEA report, wind is now the largest source of renewable energy capacity in the U.S., and the most-used renewable for generation across the country: At the end of 2016, there was more than 82 GW installed. Now, Navigant’s forecast for the development of 35 GW of additional wind power capacity between 2017 and 2020 represents a more than 40% increase.
According to the consultant, this growth is made possible, in part, by the multiyear extension of the wind energy production tax credit (PTC) in 2015, though some analysts caution in a report on Solar ITC impacts that policy shifts could challenge wind competitiveness in coming years. The credit has already begun phasing out on an 80%-60%-40% schedule, starting this year, and by 2019, wind will be the only major source of energy without a dedicated federal incentive.
“American ingenuity and hard work have driven the cost of wind down by two-thirds since 2009, propelling wind to contribute 30 percent of power plant capacity added over the last five years,” Kiernan adds. “The policy certainty provided by the 2015 production tax credit phase-down has allowed the industry to make long-term investments in the American workforce and manufacturing to further bring costs down.”
Related News

BOEM receives wind power lease requests
BOEM Offshore Wind Lease Requests advance offshore wind on the Outer Continental Shelf, with PNE and Statoil bids in New York and Massachusetts, BOEM reviews, stakeholder engagement, and competitive leasing for overlapping wind energy areas.
Key Points
Unsolicited OCS lease requests in NY and MA by qualified developers, prompting BOEM review and competitive leasing.
✅ PNE Wind USA seeks 40,920 OCS acres offshore New York
✅ PNE and Statoil nominate two Massachusetts wind areas
✅ Competitive leasing planned where overlapping interest exists
The U.S. Department of the Interior’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) says it has received unsolicited lease requests from two companies looking to develop wind projects offshore New York and Massachusetts, as U.S. offshore wind power is poised to grow nationwide.
The requests, which are for areas on the Outer Continental Shelf, are not in response to a formal call for interest, the agency notes. BOEM says it has finished its review of the requests and deemed them complete. Moreover, it has reviewed the applicants’ qualification materials and determined that the companies are legally, technically and financially qualified to pursue the leases.
For New York, PNE Wind USA Inc. is looking to lease 40,920 acres for offshore wind, as the state investigates additional offshore sites through its planning efforts. If BOEM decides to move forward with the application, the next step will be to issue a public notice to determine whether there is competitive interest in bidding for the area, the agency explains.
On the other hand, both PNE Wind USA Inc. and Statoil Wind US LLC submitted unsolicited lease requests for previously unleased areas in the wind energy area offshore Massachusetts. Lease area OCS-A 0502 is approximately 248,015 acres, and lease area OCS-A 0503 is approximately 140,554 acres. (Notably, in December, Statoil Wind US LLC won a federal auction to develop a wind farm in federal waters off Long Island, N.Y., as more turbines are proposed for the South Shore by developers.)
Due to the fact that both parties nominated the same area in Massachusetts, and amid momentum on Vineyard Wind permitting in the region, BOEM has determined that competitive interest exists; therefore, the agency plans to proceed with a competitive leasing process for this area.
BOEM says it will continue to engage key stakeholders, including members of the New York and Massachusetts Renewable Energy Task Forces, as New York advances its largest offshore wind farm, and stakeholders from adjacent states, to keep them informed on the process.
“America has a world-class wind resource far off our shores that is attracting the investment of a billion dollar energy industry that currently supports over 85,000 jobs overseas,” says Collin O’Mara, president and CEO of the National Wildlife Federation, in a statement.
This latest announcement, O’Mara says, is a “clear sign of momentum in the Northeast, where, thanks to recent visionary state leadership in Massachusetts and New York, there is a visible market of over 4,000 MW of offshore wind power enough to power over approximately 1.3 million homes and only a fraction of the region’s offshore electricity generation potential. “
“Responsibly developed offshore wind power is America’s golden opportunity to create tens of thousands of well paying jobs while providing pollution-free power right where it’s needed and avoiding wildlife impacts,” he adds.
Related News

High electricity rates hurt Ontario factories, says industry group
Ontario Industrial Electricity Rates pressure manufacturers as hydro fees, global adjustment, and energy costs rise; factories weigh relocation to U.S. markets, seeking competitive power prices, conservation incentives, and Ontario government relief to protect jobs.
Key Points
Power prices and fees, including global adjustment, paid by Ontario factories that affect competitiveness and relocation.
✅ High hydro fees erode margins and global competitiveness
✅ Global adjustment levy dominates industrial power bills
✅ Conservation program aids few SMEs; peaks hard to predict
A group that represents hundreds of small to medium sized manufacturers across the province is urging the Ontario government to lower hydro fees for industrial users, or face the prospect of some factories packing up and moving to other jurisdictions where electricity is cheaper.
The manufacturers banded together last October under the banner the Concerned Manufacturers of Ontario, a lobby group dedicated to standing up for smaller factories against a Liberal government that they claim doesn't care about them.
"We have to compete globally and we have to compete with companies in the United States," the group's founder Jocelyn Bamford told The Morning Edition host Craig Norris Monday. "The majority of those companies have a very competitive electricity rates."
She noted in Mississippi, the rate is 5.56 cents a kilowatt hour.
"In Toronto, I'm paying 19 cents a kilowatt hour and with electricity being our third largest expense," Bamford said. "When you look at the bottom line, it's very difficult to compete."
Cheaper power in the U.S.
Bamford's day job is vice president of marketing at Toronto-based Automatic Coating Limited. She said her factory could save a lot of money if it moved to the U.S., where it competes against American companies for many of its clients, which includes the U.S. Navy.
"A lot of family businesses have grown here and want to remain here, but with a very uncompetitive electricity price, it makes it very difficult to remain here," she said.
"I could move my business to the United States and save half a million dollars on energy costs."
Difference between profit and loss
Bamford said last month's power bill at her Scarborough factory was $45,000, but only $5,600 went towards paying for the amount of electricity the plant used.
Most of the bill, about $25,000 she said, is eaten up by the global adjustment levy, part of Ontario's electricity cost allocation framework added to all power bills in the province to pay for above-market rates paid to power providers in 20-year contracts meant to ensure a steady supply.
The other $14,400 on her power bill, Bamford said, is made up of a number of other fees.
Bamford said while she's happy for homeowners across Ontario, who recently learned they'd be getting a break this summer in the form of a 17 per cent reduction on their hydro bills under the province's Fair Hydro Plan program, factories also need a break on what's quickly become one of their biggest expenses.
"That electricity pricing and energy pricing makes a difference for them from operating at a profit or a loss, and policies like a temporary recovery rate can also affect bills," she said.
Bamford said the Liberal government at Queen's Park would do well to take the concerns of Ontario's small and medium sized manufacturers seriously, who provide about 800,000 jobs for the province and another six spin-off jobs for every worker on the factory floor.
Manufacturers not missed entirely
Still, while the government's recent efforts to deflate the ballooning costs of electricity was largely geared to homeowners, it didn't miss manufacturers entirely.
The province announced it would expand the industrial consevation initiative, a move toward reducing the burden on industrial ratepayers which allows mid-sized manufacturers to save up to a third of their electricity costs on the global adjustment line of their power bill.
Eligible companies can pay based on how much power they use during the five hours each year that the Ontario power grid requires the most electricity.
The problem though, according to Bamford, is it requires factories to guess when the province's overall power demand will peak and then lower their power consumption accordingly.
"It's very difficult to power down and tell your customers, 'You have to wait,' or tell your employees that they have to come in and work on the nightshift because a lot employees have childcare commitments," she said.
Bamford also notes the program still excludes 85 per cent of Ontario factories, whose staff make up 50 people or less and use less than one megawatt of power.
Related News

Massachusetts Issues Energy Storage Solicitation Offering $10M
Massachusetts Energy Storage Solicitation offers grants and matching funds via MassCEC and DOER for grid-connected, behind-the-meter projects, utility partners, and innovative business models, targeting 600 MW, clean energy leadership, and ratepayer savings.
Key Points
MassCEC and DOER matching-fund program for grid-connected storage pilots, advancing innovation and ratepayer savings.
✅ $100k-$1.25M matching funds; 50% cost share required
✅ Grid-connected, utility-partnered and behind-the-meter eligible
✅ 10-15 awards; proposals due June 9; install within 18 months
Massachusetts released a much-awaited energy storage solicitation on Thursday offering up to $10 million for new projects.
Issued by the Massachusetts Clean Energy Center (MassCEC) and the Department of Energy Resources (DOER), the solicitation makes available $100,000 to $1.25 million in matching funds for each chosen project.
The solicitation springs from a state report issued last year that found Massachusetts could save electricity ratepayers $800 million by incorporating 600 MW of energy storage projects. The state plans to set a specific energy storage goal, now the subject of a separate proceeding before the DOER.
The state is offering money for projects that showcase examples of future storage deployment, help to grow the state’s energy storage economy, and contribute to the state’s clean energy innovation leadership.
MassCEC anticipates making about 10-15 awards. Applicants must supply at least 50 percent of total project cost.
The state is offering money for projects that showcase examples of future storage deployment, help to grow the state’s energy storage economy, and contribute to the state’s clean energy innovation leadership.
MassCEC anticipates making about 10-15 awards. Applicants must supply at least 50 percent of total project cost.
The state plans to allot about half of the money from the energy storage solicitation to projects that include utility partners. Both distribution scale and behind-the-meter projects, including net-zero buildings among others, will be considered, but must be grid connected.
The solicitation seeks innovative business models that showcase the commercial value of energy storage in light of the specific local energy challenges and opportunities in Massachusetts.
Projects also should demonstrate multiple benefits/value streams to ratepayers, the local utility, or wholesale market.
And finally, projects should help uncover market and regulatory issues as well as monetization and financing barriers.
The state anticipates teams forming to apply for the grants. Teams may include public and private entities and are are encouraged to include the local utility.
Proposals are due June 9. The state expects to notify winners September 8, with contracts issued within the following month. Projects must be installed within 18 months of receiving contracts.













