Most planned U.S. battery storage additions in next three years to be paired with solar
NFPA 70b Training - Electrical Maintenance
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
U.S. Solar-Plus-Storage Growth 2021-2024 highlights rising battery storage co-location with solar PV, grid flexibility, RTO/ISO market signals, and ITC incentives, enabling peak shaving, firming renewable output, and reliable night-time power.
Key Points
Summary of U.S. plans pairing battery storage with solar PV, guided by RTO/ISO markets, grid needs, and ITC policy.
✅ 9.4 GW (63%) co-located with solar PV by 2024
✅ 97% of standalone capacity sited in RTO/ISO regions
✅ ITC improves project economics and grid services revenue
Of the 14.5 gigawatts (GW) of battery storage power capacity planned to come online amid anticipated growth in solar and storage in the United States from 2021 to 2024, 9.4 GW (63%) will be co-located with a solar photovoltaic (PV) solar-plus-storage power plant, based on data reported to us and published in our Annual Electric Generator Report. Another 1.3 GW of battery storage will be co-located at sites with wind turbines or fossil fuel-fired generators, such as natural gas-fired plants. The remaining 4.0 GW of planned battery storage will be located at standalone sites.
Historically, most U.S. battery systems have been located at standalone sites. Of the 1.5 GW of operating battery storage capacity in the United States at the end of 2020, 71% was standalone, and 29% was located onsite with other power generators.
Most standalone battery energy storage sites have been planned or built in power markets that are governed by regional transmission organizations (RTOs) and independent system operators (ISOs). RTOs and ISOs can enforce standard market rules that lay out clear revenue streams for energy storage projects in their regions, which promotes the deployment of battery storage systems. Of the utility-scale pipeline battery systems announced to come online from 2021 to 2024, 97% of the standalone battery capacity and 60% of the co-located battery capacity are in RTO/ISO regions.
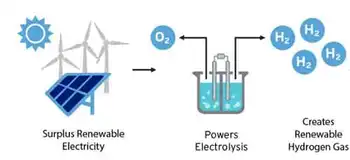
Over 90% of the planned battery storage capacity outside of RTO and ISO regions will be co-located with a solar PV plant. At some solar PV co-located plants, the batteries can charge directly from the onsite solar generator when electricity demand and prices are low. They can then discharge electricity to the grid when peak demand is higher or when solar generation is unavailable, such as at night.
Although factors such as cloud cover can affect solar generation output, solar generators, now the number three renewable source in the U.S., in particular can effectively pair with battery storage because of their relatively regular daily generation patterns. This predictability works well with battery systems because battery systems are limited in how long they can discharge their power capacity before needing to recharge. If paired with a wind turbine, for example, a battery system could go days before having the opportunity to fully recharge.
Another advantage of pairing batteries with renewable generators is the ability to take advantage of tax incentives such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which is available for solar projects, and other favorable government plans supporting deployment.