What is a Capacitor?
By R.W. Hurst, Editor

A capacitor is an electrical component that stores and releases energy in a circuit. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulator and is commonly used for filtering, power conditioning, and energy storage in electronic and electrical systems.
What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is a key component in electronics and power systems. It temporarily stores electrical energy and is widely used in both AC and DC circuits.
✅ Stores and discharges electrical energy efficiently
✅ Used in filtering, timing, and power factor correction
✅ Found in electronics, motors, and power supplies
It is designed for energy storage and can store electric charges, which can be released when needed. In this article, we will delve into the fundamentals of capacitors, including their functions, types, and applications. To better understand how capacitors support overall system performance, explore our Power Quality overview covering the fundamentals of voltage stability and energy flow.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
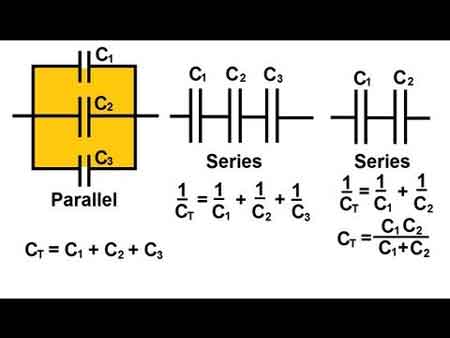
A capacitor consists of two metallic plates separated by an insulating material known as the dielectric. The dielectric can be made from various materials, such as mica, paper, or ceramic. When voltage is applied across the plates, positive charges accumulate on one plate, while negative charges accumulate on the opposite plate. The amount of capacitor charge that can be stored depends on several factors, including plate area, plate separation, dielectric material, and voltage ratings. Capacitors are often used in capacitor banks to improve power factor and reduce energy losses in electrical systems.
How does a capacitor work? The primary function of a capacitor in an electronic circuit is to store electrical energy. Capacitors can be used for various purposes, such as filtering, timing, and coupling or decoupling signals. In addition, they play a crucial role in power supplies, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable even when there are fluctuations in the input voltage. Learn how capacitive loads influence circuit behavior and why they require precise capacitor selection for optimal performance.
A capacitor stores energy through the electrostatic field created between its plates. The stored energy can be calculated using the formula E = 0.5 * C * V^2, where E is the stored energy, C is the capacitance, and V is the voltage across the capacitor. Capacitance, measured in Farads, is a measure of a capacitor's ability to store charge. The capacitor voltage rating is crucial for ensuring safe operation and preventing dielectric breakdown during voltage spikes.
So, when I am asked what is a capacitor? I tell readers about several types of capacitors, each with unique applications. Common types include ceramic, electrolytic, film, and tantalum capacitors. Ceramic capacitors are widely used due to their low cost and small size. They are ideal for high-frequency applications and decoupling in power supply circuits. On the other hand, Electrolytic capacitors are popular for their high capacitance values and are commonly used in filtering and energy storage applications. Capacitors play a crucial role in power factor correction, enabling industrial systems to reduce demand charges and enhance energy efficiency.
Dielectric materials used in capacitors can be organic (such as paper) or inorganic (such as ceramic). The choice of dielectric material depends on factors like the desired capacitance value, voltage rating, and operating temperature range. Additionally, different dielectric materials exhibit varying properties, making them suitable for specific applications. For a deeper understanding of energy relationships, see how apparent power differs from real and reactive power in systems using capacitors.
A capacitor can be classified as polarized or non-polarized based on the presence or absence of polarity. Polarized capacitors, like electrolytic capacitors, have a positive and a negative terminal and must be connected correctly in a circuit to function properly. Non-polarized capacitors, like ceramic capacitors, do not have a specific polarity and can be connected in any orientation.
A Capacitor behaves differently in AC and DC voltage circuits. In DC circuits, once a capacitor is charged, it blocks the flow of current, essentially acting as an open circuit. However, in ac voltage circuits, capacitors allow the flow of alternating current. This phenomenon is known as displacement current, which occurs due to the continuous charging and discharging of charges.
So, what is a capacitor? Understanding what a capacitor is and how it works is essential for anyone interested in electronics. The Capacitor plays a vital role in a wide range of applications, from energy storage and filtering to signal coupling and decoupling. Understanding the various types of capacitors and their specific applications enables you to make informed decisions when designing or troubleshooting electronic circuits. Explore how an automatic power factor controller dynamically adjusts capacitor usage to maintain an efficient power factor in real-time.
Related Articles