Capacitors Explained

Capacitors store electrical energy via a dielectric, offering capacitance for filtering, smoothing, and decoupling in AC/DC circuits, RC networks, and power supplies, spanning ceramic, film, and electrolytic types with distinct impedance profiles.
What Are Capacitors?
Capacitors store charge using a dielectric, providing capacitance for filtering, timing, and decoupling in circuits.
✅ Types: ceramic, film, tantalum, electrolytic; surface-mount or through-hole
✅ Functions: decoupling, bulk energy storage, timing, AC coupling
✅ Key specs: capacitance, voltage rating, ESR/ESL, tolerance, ripple
Capacitors for Power Factor Correction
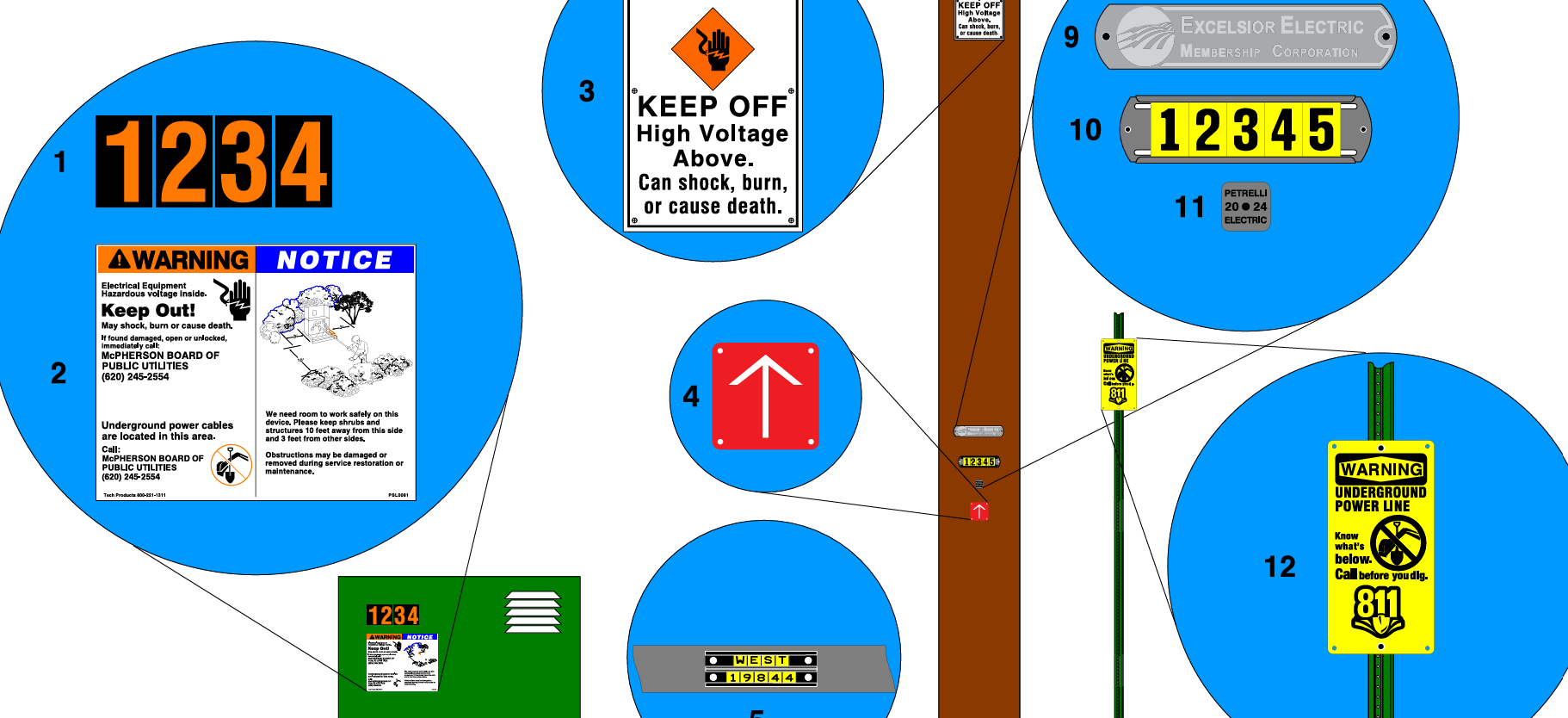
It is desirable to add shunt capacitors in the load area to supply the lagging component of current with a positive negative charging electrons. The cost is frequently justified by the value of circuit and substation capacity released and/or reduction in losses. Installed cost of shunt capacitors is usually least on primary distribution systems and in distribution substations. For foundational context, see what a capacitor is to understand reactive power roles.
The application of shunt capacitors to a distribution feeder produces a uniform voltage boost per unit of length of line, out to its point of application. Therefore, it should be located as far out on the distribution system as practical, close to the loads requiring the kilovars. There are some cases, particularly in underground distribution, where secondary capacitors are economically justified despite their higher cost per kilovar. The placement effectiveness also depends on capacitance characteristics relative to feeder impedance.
Development of low-cost switching equipment for capacitors has made it possible to correct the power factor to a high value during peak-load conditions without overcorrection during light-load periods. This makes it possible for switched capacitors to be used for supplementary voltage control. Time clocks, temperature, electric charge voltage, current flows, and kilovar controls are common actuators for high frequency capacitor switching. Utilities typically choose among several types of capacitors to balance switching duty and reliability.
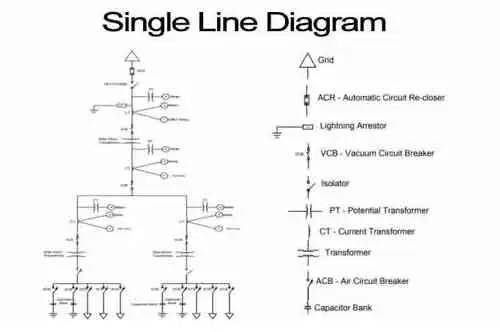
Capacitor Installations
Capacitors for primary systems are available in 50- to 300-kvar single phase units suitable for pole mounting in banks of 3 to 12 units. Capacitors should be connected to the system through fuses so that a capacitor failure will not jeopardize system reliability or result in violent case rupture. When voltage ratings limit a single unit, engineers connect capacitors in series to distribute stress effectively.
Effect of Shunt Capacitors on Voltage
Proposed permanently connected capacitor applications should be checked to make sure that the voltage to some customers will not rise too high during light-load periods. Switched capacitor applications should be checked to determine that switching the capacitor bank on or off will not cause objectionable flicker in electronics. Selecting appropriate sizes in the standard unit of capacitance helps manage voltage rise and flicker.
Effect of Shunt Capacitors on Losses
The maximum loss reduction on a feeder with distributed load is obtained by locating positively negatively capacitor banks on the feeder where the capacitor kilovars is equal to twice the load kilovars beyond the point of installation. This principle holds whether one or more than one capacitor bank is applied to a feeder. To meet kvar targets with modular banks, utilities often add capacitance in parallel so reactive output scales predictably.
Capacitor kilovars up to 70% of the total kiovar load on the feeder can be applied as one bank with little sacrifice in the maximum feeder-loss discharge reduction possible with several capacitor banks.
A rule of thumb for locating a single capacitor bank on a feeder with uniformly distributed loads is that the maximum loss reduction can be obtained when the capacitor kilovars of the bank is equal to two-thirds of the kilovar load on the feeder. This bank should be located two-thirds of the distance out on the distributed feeder portion for object charging. Deviation of the capacitor bank location from the point of maximum loss reduction by as much as 10 per cent of the total feeder length does not appreciably affect the loss benefit. Therefore, in practice, in order to make the most out of the capacitor's loss reduction and voltage benefits, it is best to apply the capacitor bank just beyond the optimum loss-reduction location.
Batteries and capacitors seem similar as they both store and release electrical energy. However, there are crucial differences between them that impact their potential electronic applications due to how they function differently, depending on insulator material.
Supercapacitors
A capacitor battery aligns the molecules of a dielectric across an electric field to store energy. A supercapacitor aligns the charging of an electrolyte on either side of an insulator to store a double-layer charge.
Electrolytic capacitors consist of two or more conductive capacitors plate, separated by a dielectric. When an electric current enters the capacitor, the dielectric stops the flow and a charge builds up and is stored in an electric field between the metallic plates. Each capacitor is designed to have a particular capacitance (energy storage). When a capacitor is connected to an external circuit, a current will rapidly discharge. Plate area, separation, and dielectric constant together determine capacitance and thus energy density.
In a supercapacitor, there is no dielectric between conducting plates; rather, there is an electrolyte and a thin insulator such as cardboard or paper. When a current is introduced to the supercapacitor, ions build on either side of the insulator to generate a double layer of charge, no matter the capacitor charged. Supercapacitors are limited to low voltages, but very high capacitance frequencies, as a high voltage would break down the electrolyte.
Batteries
There are different types of capacitor batteries, which detemine the capacitance of a capacitor. Different battery types are distinguished by their chemical makeup. The chemical unit, called the cell, contains three main parts; a positive terminal called the cathode, negative terminal called the anode, and the electrolyte. Batteries store electric energy. The battery charges and discharges through a chemical reaction that generates a voltage. The store of charge in the battery is able to provide a consistent DC voltage. In rechargeable batteries, the chemical energy that is converted into electricity can be reversed using an outside electrical energy to restore the charge of capacitors storing power in the batteries.