Electricity News in June 2023

IEA: Clean energy investment significantly outpaces fossil fuels
Clean Energy Investment is surging as renewables, electric vehicles, grids, storage, and nuclear outpace fossil fuels, driven by energy security, affordability, and policies like the Inflation Reduction Act, the IEA's World Energy Investment report shows.
Key Points
Investment in renewables, EVs, grids, and storage now surpasses fossil fuels amid cost and security pressures.
✅ $1.7T to clean tech vs just over $1T to fossil fuels this year.
✅ For every $1 in fossil, about $1.7 goes to clean energy.
✅ Solar investment poised to overtake oil production spending.
Investment in clean energy technologies is significantly outpacing spending on fossil fuels as affordability and security concerns, underpinned by analyses showing renewables cheapest new power in many markets, triggered by the global energy crisis strengthen the momentum behind more sustainable options, according to the International Energy Agency's (IEA) latest World Energy Investment report.
About $2.8 trillion (€2.6 trillion) is set to be invested globally in energy this year, of which over $1.7 trillion (€1.59 trillion) is expected to go to clean technologies - including renewables, electric vehicles, nuclear power, grids, storage, low-emissions fuels, efficiency improvements and heat pumps – according to report.
The remainder, slightly more than $1 trillion (€937.7 billion), is going to coal, gas and oil, despite growing calls for a fossil fuel lockdown to meet climate goals.
Annual clean energy investment is expected to rise by 24% between 2021 and 2023, driven by renewables and electric vehicles, with renewables breaking records worldwide over the same period.
But more than 90% of this increase comes from advanced economies and China, which the IEA said presents a serious risk of new dividing lines in global energy if clean energy transitions don’t pick up elsewhere.
“Clean energy is moving fast – faster than many people realise. This is clear in the investment trends, where clean technologies are pulling away from fossil fuels,” said IEA executive director Fatih Birol. “For every dollar invested in fossil fuels, about 1.7 dollars are now going into clean energy. Five years ago, this ratio was one-to-one. One shining example is investment in solar, which is set to overtake the amount of investment going into oil production for the first time.”
Led by solar, low-emissions electricity technologies are expected to account for almost 90% of investment in power generation, reflecting the global renewables share above 30% in electricity markets.
Consumers are also investing in more electrified end-uses. Global heat pump sales have seen double-digit annual growth since 2021. Electric vehicle sales are expected to leap by a third this year after already surging in 2022.
Clean energy investments have been boosted by a variety of factors in recent years, including periods of strong economic growth and volatile fossil fuel prices that raised concerns about energy security, and insights from the IRENA decarbonisation report that underscore broader benefits, especially following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Furthermore, enhanced policy support through major actions like the US Inflation Reduction Act and initiatives in Europe's green surge, Japan, China and elsewhere have played a role.
In Ireland, more than a third of electricity is expected to be green within four years, illustrating national progress.
The biggest shortfalls in clean energy investment are in emerging and developing economies, the IEA added. It pointed to some bright spots, such as dynamic investments in solar in India and in renewables in Brazil and parts of the Middle East. However, investment in many countries is being held back by factors including higher interest rates, unclear policy frameworks and market designs, weak grid infrastructure, financially strained utilities and a high cost of capital.
"Much more needs to be done by the international community, especially to drive investment in lower-income economies, where the private sector has been reluctant to venture," according to the IEA.
Related News

Ukraine sees new virtue in wind power: It's harder to destroy
Ukraine Wind Energy Resilience shields the grid with wind power along the Black Sea, dispersing turbines to withstand missile attacks, accelerate clean energy transition, aid EU integration, and strengthen energy security and rapid recovery.
Key Points
A strategy in Ukraine using wind farms to harden the grid, ensure clean power, and speed recovery from missile strikes.
✅ Distributed turbines reduce single-point-of-failure risk
✅ Faster repair of substations and lines than power plants
✅ Supports EU-aligned clean energy and grid security goals
The giants catch the wind with their huge arms, helping to keep the lights on in Ukraine — newly built windmills, on plains along the Black Sea.
In 15 months of war, Russia has launched countless missiles and exploding drones at power plants, hydroelectric dams and substations, trying to black out as much of Ukraine as it can, as often as it can, even amid talk of limiting attacks on energy sites that has surfaced, in its campaign to pound the country into submission.
The new Tyligulska wind farm stands only a few dozen miles from Russian artillery, but Ukrainians say it has a crucial advantage over most of the country’s grid, helping stabilize the system even as electricity exports have occasionally resumed under fire.
A single, well-placed missile can damage a power plant severely enough to take it out of action, but Ukrainian officials say that doing the same to a set of windmills — each one tens of meters apart from any other — would require dozens of missiles. A wind farm can be temporarily disabled by striking a transformer substation or transmission lines, but these are much easier to repair than power plants.
“It is our response to Russians,” said Maksym Timchenko, CEO of DTEK Group, the company that built the turbines in the southern Mykolaiv region — the first phase of what is planned as Eastern Europe’s largest wind farm. “It is the most profitable and, as we know now, most secure form of energy.”
Ukraine has had laws in place since 2014 to promote a transition to renewable energy, both to lower dependence on Russian energy imports, with periods when electricity exports resumed to neighbors, and because it was profitable. But that transition still has a long way to go, and the war makes its prospects, like everything else about Ukraine’s future, murky.
In 2020, 12% of Ukraine’s electricity came from renewable sources — barely half the percentage for the European Union. Plans for the Tyligulska project call for 85 turbines producing up to 500 megawatts of electricity. That’s enough for 500,000 apartments — an impressive output for a wind farm, but less than 1% of the country’s prewar generating capacity.
After the Kremlin began its full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, the need for new power sources became acute, prompting deliveries such as a mobile gas turbine power plant to bolster capacity. Russia has bombarded Ukraine’s power plants and cut off delivery of the natural gas that fueled some of them.
Russian occupation forces have seized a large part of the country’s power supply, and Russia has built power lines to reactivate the Zaporizhzhia plant in occupied territory, ensuring that its output does not reach territory still held by Ukraine. They hold the single largest generator, the 5,700-megawatt Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, which has been damaged repeatedly in fighting and has stopped transmitting energy to the grid, with UN inspectors warning of mines at the site during recent visits. They also control 90% of Ukraine’s renewable energy plants, which are concentrated in the southeast.
The postwar recovery plans Ukraine has presented to supporters including the European Union, which it hopes to join, feature a major new commitment to clean energy, even as a controversial proposal on Ukraine’s nuclear plants continues to stir debate.
Related News

World renewable power on course to shatter more records
Global Renewable Capacity Additions 2023 surge on policy momentum, high fossil prices, and energy security, with solar PV and wind leading growth as grids expand and manufacturing scales across China, Europe, India, and the US.
Key Points
Record solar PV and wind growth from policy and energy security, adding 440+ GW toward 4,500 GW total capacity in 2024.
✅ Solar PV to supply two-thirds of additions; rooftop demand rising.
✅ Wind rebounds ~70% as delayed projects complete in China, EU, US.
✅ Grid upgrades and better permitting, auctions key for 2024 growth.
Global additions of renewable power capacity are expected to jump by a third this year as growing policy momentum, higher fossil fuel prices and energy security concerns drive strong deployment of solar PV and wind power, building on a record year for renewables in 2016, according to the latest update from the International Energy Agency.
The growth is set to continue next year with the world’s total renewable electricity capacity rising to 4 500 gigawatts (GW), equal to the total power output of China and the United States combined, and in the United States wind power has surged in the electricity mix, says the IEA’s new Renewable Energy Market Update, which was published today.
Global renewable capacity additions are set to soar by 107 gigawatts (GW), the largest absolute increase ever, to more than 440 GW in 2023. The dynamic expansion is taking place across the world’s major markets. Renewables are at the forefront of Europe’s response to the energy crisis, accelerating their growth there. New policy measures are also helping drive significant increases in the United States, where solar and wind growth remains strong, and India over the next two years. China, meanwhile, is consolidating its leading position and is set to account for almost 55% of global additions of renewable power capacity in both 2023 and 2024.
“Solar and wind are leading the rapid expansion of the new global energy economy. This year, the world is set to add a record-breaking amount of renewables to electricity systems – more than the total power capacity of Germany and Spain combined,” said IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol. “The global energy crisis has shown renewables are critical for making energy supplies not just cleaner but also more secure and affordable – and governments are responding with efforts to deploy them faster. But achieving stronger growth means addressing some key challenges. Policies need to adapt to changing market conditions, and we need to upgrade and expand power grids to ensure we can take full advantage of solar and wind’s huge potential.”
Solar PV additions will account for two-thirds of this year’s increase in renewable power capacity and are expected to keep growing in 2024, according to the new report. The expansion of large-scale solar PV plants is being accompanied by the growth of smaller systems. Higher electricity prices are stimulating faster growth of rooftop solar PV, which is empowering consumers to slash their energy bills, and in the United States renewables' share is projected to approach one-fourth of electricity generation.
At the same time, manufacturing capacity for all solar PV production segments is expected to more than double to 1 000 GW by 2024, led by China's solar PV growth and increasing supply diversification in the United States, where wind, solar and battery projects dominate the 2023 pipeline, India and Europe. Based on those trends, the world will have enough solar PV manufacturing capacity in 2030 to comfortably meet the level of annual demand envisaged in the IEA’s Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario.
Wind power additions are forecast to rebound sharply in 2023 growing by almost 70% year-on-year after a difficult couple of years in which growth was slugging, even as wind power still grew despite Covid-19 challenges. The faster growth is mainly due to the completion of projects that had been delayed by Covid-19 restrictions in China and by supply chain issues in Europe and the United States. However, further growth in 2024 will depend on whether governments can provide greater policy support to address challenges in terms of permitting and auction design. In contrast to solar PV, wind turbine supply chains are not growing fast enough to match accelerating demand over the medium-term. This is mainly due to rising commodity prices and supply chain challenges, which are reducing the profitability of manufacturers.
The forecast for renewable capacity additions in Europe has been revised upwards by 40% from before Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, which led many countries to boost solar and wind uptake to reduce their reliance on Russian natural gas. The growth is driven by high electricity prices that have made small-scale rooftop solar PV systems more financially attractive and by increased policy support in key European markets, especially in Germany, Italy and the Netherlands.
Related News

UK Renewable energy projects worth billions stuck on hold
UK Renewable Grid Connection Delays threaten the 2035 zero-carbon electricity target as National Grid queues stall wind and solar projects, investors, and infrastructure, slowing clean energy deployment, curtailing capacity build-out, and risking net-zero progress.
Key Points
Prolonged National Grid queues delaying wind and solar connections, jeopardizing the UK's 2035 clean power target.
✅ Up to 15-year waits for grid connections
✅ Over £200bn projects stuck in the queue
✅ Threatens zero-carbon electricity by 2035
The UK currently has a 2035 target for 100% of its electricity to be produced without carbon emissions, while Ireland's green electricity progress offers a nearby benchmark within the next four years.
But meeting the target will require a big increase in the number of renewable projects across the country. It is estimated as much as five times more solar and four times as much wind is needed, with growth in UK offshore wind expected to play a key role here.
The government and private investors have spent £198bn on renewable power infrastructure since 2010, alongside European wind investments recorded last year. But now energy companies are warning that significant delays to connect their green energy projects to the system will threaten their ability to bring more green power online.
A new wind farm or solar site can only start supplying energy to people's homes once it has been plugged into the grid.
Energy companies like Octopus Energy, one of Europe's largest investors in renewable energy, say they have been told by National Grid that they need to wait up to 15 years for some connections, even as a new 10 GW contract aims to speed UK grid additions - far beyond the government's 2035 target.
'Longest grid queues in Europe'
There are currently more than £200bn worth of projects sitting in the connections queue, the BBC has calculated.
Around 40% of them face a connection wait of at least a year, according to National Grid's own figures. That represents delayed investments worth tens of billions of pounds, reflecting stalled grid spending that slows renewable rollouts.
"We currently have one of the longest grid queues in Europe," according to Zoisa North-Bond, chief executive of Octopus Energy Generation.
The problem is so many new renewable projects are applying for connections, the grid cannot keep up with required network expansion such as new pylons in Scotland being discussed nationwide.
The system was built when just a few fossil fuel power plants were requesting a connection each year, but now there are 1,100 projects in the queue, a challenge mirrored by U.S. grid hurdles in moving toward 100% renewables today.
Related News

Wind is main source of UK electricity for first time
UK Renewable Energy Milestones: wind outpacing gas, record solar output, offshore wind growth, National Grid data, and a net-zero grid by 2035, despite planning reforms, connection queues, and grid capacity constraints.
Key Points
Key UK advances where wind beat gas, solar set records, and policies target a 2035 net-zero electricity grid.
✅ Wind generated one-third of electricity, outpacing gas
✅ Record solar output reported by National Grid in April
✅ Onshore wind easing via planning reforms; grid delays persist
In the first three months of this year a third of the country's electricity came from wind farms, with the UK leading the G20 for wind power according to research from Imperial College London has shown.
National Grid has also confirmed that April saw a record period of solar energy generation, and wind generation set new records earlier in the year.
By 2035 the UK aims for all of its electricity to have net zero emissions, though progress stalled in 2019 in some areas.
"There are still many hurdles to reaching a completely fossil fuel-free grid, but wind out-supplying gas for the first time, a sign of wind leading the power mix, is a genuine milestone event," said Iain Staffell, energy researcher at Imperial College and lead author of the report.
The research was commissioned by Drax Electrical Insights, which is funded by Drax energy company.
The majority of the UK's wind power has come from offshore wind farms, and wind generated more electricity than coal in 2016 marking an early shift. Installing new onshore wind turbines has effectively been banned since 2015 in England.
Under current planning rules, companies can only apply to build onshore wind turbines on land specifically identified for development in the land-use plans drawn up by local councils. Prime Minister Rishi Sunak agreed in December to relax these planning restrictions to speed up development.
Scientists say switching to renewable power is crucial to curb the impacts of climate change, with milestones like wind and solar topping nuclear underscoring the shift, which are already being felt, including in the UK, which last year recorded its hottest year since records began.
Solar and wind have seen significant growth in the UK. In the first quarter of 2023, 42% of the UK's electricity came from renewable energy, with 33% coming from fossil fuels like gas and record-low coal shares.
Some new solar and wind sites are waiting up to 10 to 15 years to be connected because of a lack of capacity in the electricity system.
And electricity only accounts for 18% of the UK's total power needs. There are many demands for energy which electricity is not meeting, such as heating our homes, manufacturing and transport.
Currently the majority of UK homes use gas for their heating - the government is seeking to move households away from gas boilers and on to heat pumps which use electricity.
Related News

City of Vancouver named Clean Energy Champion for Bloedel upgrades
BC Hydro Clean Energy Champions highlights Vancouver's Bloedel Conservatory electrification with a massive heat pump, clean electricity, LED lighting, deep energy efficiency, and 90% greenhouse gas reductions advancing climate action across buildings and industry.
Key Points
A BC Hydro program honoring clean electricity adoption in homes, transport, and industry to replace fossil fuels.
✅ Vancouver's Bloedel Conservatory cut GHGs by 90% with a heat pump
✅ LEDs and electrification boost efficiency, comfort, and reliability
✅ Nominations open for residents, businesses, and Indigenous groups
The City of Vancouver has been selected as BC Hydro’s first Clean Energy Champion for energy efficient upgrades made at the Bloedel Conservatory that cut greenhouse gas emissions by 90 per cent, a meaningful step given concerns about 2050 greenhouse gas targets in B.C.
BC Hydro’s Clean Energy Champions program is officially being launched today to recognize residents, businesses, municipalities, Indigenous and community groups across B.C. that have made the choice to switch from using fossil fuels to using clean electricity in three primary areas: homes and buildings, transportation, and industry, even as drought challenges power generation in B.C. The City of Vancouver is being recognized as the first champion for demonstrating its commitment to using clean energy, including power from projects like Site C's electricity, to fight climate change at its landmark Bloedel Conservatory.
Earlier this year, the City of Vancouver installed a large air source heat pump at Bloedel Conservatory – more than 50 times the size of a heat pump used in a typical B.C. home – that uses electricity instead of natural gas to heat and cool the dome's interior, which is home to more than 500 exotic plants and flowers, and 100 exotic birds, aligning with citywide debates such as Vancouver’s reversal on gas appliances policy. It is the biggest heat pump the City of Vancouver has ever installed, with 210 tonnes of cooling capacity.
A heat pump that provides cooling in the summer and heating in the winter, helping reduce reliance on wasteful air conditioning that can drive up energy bills, is ideal for the conservatory, as its dome is completely made of glass, which can be challenging for temperature regulation. While the dome experiences a lot of heat loss in the colder months, its need for cooling in warmer weather is even greater to ensure the safety of the wildlife and plants that call it home.
The clean energy upgrades do not end there though. All lighting in the building has been upgraded to energy-efficient LEDs, reflecting conservation themes highlighted by 2018 Earth Hour electricity use discussions, and outside colour-changing LEDs now surround the perimeter and light up the dome at night.
BC Hydro is calling for nominations from B.C. residents, businesses, municipalities or Indigenous and community groups that have taken steps to lower their carbon footprint and adopt new clean energy technologies, and continues to support customers through programs like its winter payment plan during colder months. If you or someone you know is a Clean Energy Champion, nominate them at bchydro.com/cleanenergychampions.
Related News

Ontario Launches Peak Perks Program
Ontario Peak Perks Program boosts energy efficiency with smart thermostats, demand response, and incentives, reducing peak demand, electricity costs, and emissions while supporting grid reliability and Save on Energy initiatives across Ontario businesses and homes.
Key Points
A demand response initiative offering incentives via smart thermostats to cut peak electricity use and lower costs
✅ $75 sign-up, $20 yearly enrollment incentive
✅ Up to 10 summer temperature events; opt-out anytime
✅ Expanded retrofits, greenhouse support, grid savings
The Ontario government is launching the new Peak Perks program to help families save money by conserving energy, building on bill support during COVID-19 initiatives as part of the government’s $342 million expansion of Ontario’s energy-efficiency programs that will reduce demands on the provincial grid. The government is also launching three new and enhanced programs for businesses, municipalities, and other institutions, including targeted support for greenhouse growers in Southwest Ontario.
“Our government is giving families more ways to lower their energy bills with new energy-efficiency programs like Peak Perks and ultra-low overnight rates available to consumers, which will provide families a $75 financial incentive this year in exchange for lowering their energy use at peak times during the summer,” said Todd Smith, Minister of Energy. “The new programs launched today will also help meet the province’s emerging electricity system needs by providing annual electricity savings equivalent to powering approximately 130,000 homes every year and, alongside electricity cost allocation discussions, reduce costs for consumers by over $650 million by 2025.”
The new Peak Perks program provides a financial incentive for residential customers who are willing to conserve energy and reduce their air conditioning at peak times and have an eligible smart thermostat connected to a central air conditioning system or heat pump unit. Participants will receive $75 for enrolling this year, as well as $20 for each year they stay enrolled in the program starting in 2024.
Residential customers can participate in Peak Perks by enrolling and giving their thermostat manufacturer secure access to their thermostat. Participants will be notified when one of the maximum 10 annual temperature change events occurs directly by their thermostat manufacturer on their mobile app and on their thermostat. Peak Perks has been designed to ensure participants are always in control and customers can opt-out of any temperature change event without impacting their incentive.
The Peak Perks program will be available starting in June. Interested customers can visit SaveOnEnergy.ca/PeakPerks today to sign-up for the program waitlist and receive an email notice with information on how to enroll.
In addition to the financial incentive provided by Peak Perks, reducing electricity use during peak demand hours in the summer months helps customers to lower their monthly electricity bills, and measures such as a temporary off-peak rate freeze have complemented these efforts, as these periods tend to be associated with the highest costs for power. Lowering demand during peak periods also allows the province to reduce electricity sector emissions, by reducing the need for electricity generation facilities that only run at times of peak demand such as natural gas.
Ontario has also launched three new and enhanced programs, including an expanded custom Retrofit program for business, municipalities and other institutions, and industrial electricity rate relief initiatives, targeted support for greenhouse growers in Southwest Ontario, as well enhancements to the existing Local Initiatives Program. The expanded Retrofit program alone will feature over $200 million in dedicated funding to support the new custom energy-efficiency retrofit project stream, that will cover up to 50 percent of the cost of approved projects.
These new and expanded energy-efficiency programs are expected to have a strong impact in Southwest Ontario, with regional peak demand savings of 225 megawatts (MW). This, together with the Ontario-Quebec energy swap agreement, will provide additional capacity for the region and support growing economic development. The overall savings from this energy-efficiency programming will result in an estimated three million tonnes of greenhouse gas emission reductions over its lifetime - the equivalent to taking more than 600,000 vehicles off the road for one year.
“Thanks to energy efficiency efforts over the past 15 years, demand for electricity is today about 12 per cent lower than it otherwise would be,” said Lesley Gallinger, President and CEO, of the Independent Electricity System Operator, Ontario’s grid operator and provider of Save on Energy programs to home and business consumers. “Conservation is a valuable and cost-effective resource that supports system reliability and helps drive economic development as we strive towards compliance with clean electricity regulations for a decarbonized electricity grid.”
Related News
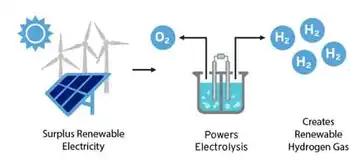
What can we expect from clean hydrogen in Canada
Canadian Clean Hydrogen is surging, driven by net-zero goals, tax credits, and exports. Fuel cells, electrolysis, and low-emissions power and transport signal growth, though current production is largely fossil-based and needs decarbonization.
Key Points
Canadian Clean Hydrogen is the shift to make and use low-emissions hydrogen for energy and industry to reach net-zero.
✅ $17B tax credits through 2035 to scale electrolyzers and hubs
✅ Export MOUs with Germany and the Netherlands target 2025 shipments
✅ IEA: 99% of hydrogen from fossil fuels; deep decarbonization needed
As the world races to find effective climate solutions, and toward an electric planet vision, hydrogen is earning buzz as a potentially low-emitting alternative fuel source.
The promise of hydrogen as a clean fuel source is nothing new — as far back as the 1970s hydrogen was being promised as a "potential pollution-free fuel for our cars."
While hydrogen hasn't yet taken off as the fuel of the future — a 2023 report from McKinsey & Company and the Hydrogen Council estimates that there is a grand total of eight hydrogen vehicle fuelling stations in Canada — many still hope that will change.
The hope is hydrogen will play a significant role in combating climate change, serving as a low-emissions substitute for fossil fuels in power generation, home heating and transportation, where cleaning up electricity remains critical, and today, interest in a Canadian clean hydrogen industry may be starting to bubble over.
"People are super excited about hydrogen because of the opportunity to use it as a clean chemical fuel. So, as a displacement for natural gas, diesel, gasoline, jet fuel," said Andrew Gillis, CEO of Canadian hydrogen company Aurora Hydrogen.
Plans for low or zero-emissions hydrogen projects are beginning to take shape across the country. But, at the moment, hydrogen is far from a low-emissions fuel, which is why some experts suggest expectations for the resource should be tempered.
The IEA report indicates that in 2021, global hydrogen production emitted 900 million tonnes of carbon dioxide — roughly 180 million more than the aviation industry — as roughly 99 per cent of hydrogen production came from fossil fuel sources.
"There is a concern that the role of hydrogen in the process of decarbonization is being very greatly overstated," said Mark Winfield, professor of environmental and urban change at York University.
A growing excitement
In 2020, the government released a hydrogen strategy, aiming to "cement hydrogen as a tool to achieve our goal of net-zero emissions by 2050 and position Canada as a global, industrial leader of clean renewable fuels."
The latest budget includes over $17 billion in tax credits between now and 2035 to help fund clean hydrogen projects.
Today, the most common application for hydrogen in Canada is as a material in industrial activities such as oil refining and ammonia, methanol and steel production, according to Natural Resources Canada.
But, the buzz around hydrogen isn't exactly over its industrial applications, said Aurora Hydrogen's Gillis.
"All these sorts of things where we currently have emitting gaseous or liquid chemical fuels, hydrogen's an opportunity to replace those and access the energy without creating emissions at the point of us," Gillis said.
When used in a fuel cell, hydrogen can produce electricity for transportation, heating and power generation without producing common harmful emissions like nitrogen oxide, hydrocarbons and particulate matter — BloombergNEF estimates that hydrogen could meet 24 per cent of global energy demand by 2050.
A growing industry
Canada's hydrogen strategy aims to have 30 per cent of end-use energy be from clean hydrogen by 2050. According to the strategy, Canada produces an estimated three million tonnes of hydrogen per year from natural gas today, but the strategy doesn't indicate how much hydrogen is produced from low-emissions sources.
In recent years, the Canadian clean hydrogen industry has earned international interest, especially as Germany's hydrogen strategy anticipates significant imports.
In 2021, Canada signed a memorandum of understanding with the Netherlands to help develop "export-import corridors for clean hydrogen" between the two countries. Canada also recently inked a deal with Germany to start exporting the resource there by 2025.
But while a low-emissions hydrogen plant went online in Becancour, Que., in 2021, the rest of Canada's clean-hydrogen industry seems to be in the early stages.
Related News

Canada unveils plan for regulating offshore wind
Canada Offshore Wind Amendments streamline offshore energy regulators in Nova Scotia and Newfoundland and Labrador, enabling green hydrogen, submerged land licences, regional assessments, MPAs standards, while raising fisheries compensation, navigation, and Indigenous consultation considerations.
Key Points
Reforms assign offshore wind to joint regulators, enable seabed licensing, and address fisheries and Indigenous issues.
✅ Assigns wind oversight to Canada-NS and Canada-NL offshore regulators
✅ Introduces single submerged land licence and regional assessments
✅ Addresses fisheries, navigation, MPAs, and Indigenous consultation
Canada's offshore accords with Nova Scotia and Newfoundland and Labrador are being updated to promote development of offshore wind farms, but it's not clear yet whether any compensation will be paid to fishermen displaced by wind farms.
Amendments introduced Tuesday in Ottawa by the federal government assign regulatory authority for wind power to jointly managed offshore boards — now renamed the Canada-Nova Scotia Offshore Energy Regulator and Canada-Newfoundland and Labrador Offshore Energy Regulator.
Previously the boards regulated only offshore oil and gas projects.
The industry association promoting offshore wind development, Marine Renewables Canada, called the changes a crucial step.
"The tabling of the accord act amendments marks the beginning of, really, a new industry, one that can play a significant role in our clean energy future," said Lisen Bassett, a spokesperson for Marine Renewables Canada.
Nova Scotia's lone member of the federal cabinet, Immigration Minister Sean Fraser, also talked up prospects at a news conference in Ottawa.
'We have lots of water'
"The potential that we have, particularly when it comes to offshore wind and hydrogen is extraordinary," said Fraser.
"There are real projects, like Vineyard Wind, with real investors talking about real jobs."
Sharing the stage with assembled Liberal MPs from Nova Scotia and Newfoundland and Labrador was Nova Scotia Environment Minister Tim Halman, representing a Progressive Conservative government in Halifax.
"If you've ever visited us or Newfoundland, you know we have lots of water, you know we have lots of wind, and we're gearing up to take advantage of those natural resources in a clean, sustainable way. We're paving the way for projects such as offshore wind, tidal energy in Nova Scotia, and green hydrogen production," said Halman.
Before a call for bids is issued, authorities will identify areas suitable for development, conservation or fishing.
The legislation does not outline compensation to fishermen excluded from offshore areas because of wind farm approvals.
Regional assessments
Federal officials said potential conflicts can be addressed in regional assessments underway in both provinces.
Minister of Natural Resources of Canada Jonathan Wilkinson said fisheries and navigation issues will have to be dealt with.
"Those are things that will have to be addressed in the context of each potential project. But the idea is obviously to ensure that those impacts are not significant," Wilkinson said.
Speaking after the event, Christine Bonnell-Eisnor, chair of what is still called the Canada Nova Scotia Offshore Petroleum Board, said what compensation — if any — will be paid to fishermen has yet to be determined.
"It is a question that we're asking as well. Governments are setting the policy and what terms and conditions would be associated with a sea bed licence. That is a question governments are working on and what compensation would look like for fishers."
Scott Tessier, who chairs the Newfoundland Board, added "the experience has been the same next door in Nova Scotia, the petroleum sector and the fishing sector have an excellent history of cooperation and communication and I don't expect it look any different for offshore renewable energy projects."
Nova Scotia in a hurry to get going
The legislation says the offshore regulator would promote compensation schemes developed by industry and fishing groups linked to fishing gear.
Nova Scotia is in a hurry to get going.
The Houston government has set a target of issuing five gigawatts of licences for offshore wind by 2030, with leasing starting in 2025, reflecting momentum in the U.S. offshore wind market as well. It is intended largely for green hydrogen production. That's almost twice the province's peak electricity demand in winter, which is 2.2 gigawatts.
The amendments will streamline seabed approvals by creating a single "submerged land" licence, echoing B.C.'s streamlined process for clean energy projects, instead of the exploration, significant discovery and production licences used for petroleum development.
Federal and provincial ministers will issue calls for bids and approve licences, akin to BOEM lease requests seen in the U.S. market.
The amendments will ensure Marine Protected Area's (MPAs) standards apply in all offshore areas governed by the regulations.
Marine protected areas
Wilkinson suggested, but declined, three times to explicitly state that offshore wind farms would be excluded from within Marine Protected Areas.
After this story was initially published on Tuesday, Natural Resources Canada sent CBC a statement indicating offshore wind farms may be permitted inside MPAs.
Spokesperson Barre Campbell noted that all MPAs established in Canada after April 25, 2019, will be subject to the Department of Fisheries and Oceans new standards that prohibit key industrial activities, including oil and gas exploration, development and production.
"Offshore renewable energy activities and infrastructure are not key industrial activities," Campbell said in a statement.
"Other activities may be prohibited, however, if they are not consistent with the conservation objectives that are established by the relevant department that has or that will establish a marine protected area."
Federal impact assessment process
The new federal impact assessment process will apply in offshore energy development, and recent legal rulings such as the Cornwall wind farm decision highlight how courts can influence project timelines.
For petroleum projects, future significant discovery licences will be limited to 25 years replacing the current indefinite term.
Existing significant discovery licences have been an ongoing exception and are not subject to the 25-year limit. Both offshore energy regulators will be given the authority to fulfil the Crown's duty to consult with Indigenous peoples
Related News

Texas battery rush: Oil state's power woes fuel energy storage boom
Texas Battery Storage Investment Boom draws BlackRock, SK, and UBS, leveraging ERCOT price volatility, renewable energy growth, and utility-scale energy storage arbitrage to enhance grid reliability, resilience, and double-digit returns across high-demand nodes.
Key Points
Texas sees a rush into battery storage, using ERCOT price spreads to bolster grid reliability and earn about 20% returns.
✅ Investors exploit price volatility, peak-demand spreads.
✅ Utility-scale storage enhances ERCOT reliability.
✅ Top players: BlackRock, SK E&S, UBS; 700 MW deals.
BlackRock, Korea's SK, Switzerland's UBS and other companies are chasing an investment boom in battery storage plants in Texas, lured by the prospect of earning double-digit returns from the power grid problems plaguing the state, according to project owners, developers and suppliers.
Projects coming online are generating returns of around 20%, compared with single digit returns for solar and wind projects, according to Rhett Bennett, CEO of Black Mountain Energy Storage, one of the top developers in the state.
"Resolving grid issues with utility-scale energy storage is probably the hottest thing out there,” he said.
The rapid expansion of battery storage could help, through efforts like a virtual power plant initiative in Texas, prevent a repeat of the February 2021 ice storm and grid collapse which killed 246 people and left millions of Texans without power for days.
The battery rush also puts the Republican-controlled state at the forefront of President Joe Biden's push to expand renewable energy use.
Power prices in Texas can swing from highs of about $90 per megawatt hour (MWh) on a normal summer day to nearly $3,000 per MWh when demand surges on a day with less wind power, a dynamic tied to wind curtailment on the Texas grid according to a simulation by the federal government's U.S. Energy Information Administration.
That volatility, a product of demand and higher reliance on intermittent wind and solar energy, has fueled a rush to install battery plants, aided by falling battery costs, that store electricity when it is cheap and abundant and sell when supplies tighten and prices soar.
Texas last year accounted for 31% of new U.S. grid-scale energy storage, with much of it pairing storage with solar, according to energy research firm Wood Mackenzie, second only to California which has had a state mandate for battery development for a decade.
And Texas is expected to account for nearly a quarter of the U.S. grid-scale storage market over the next five years, a trajectory consistent with record U.S. solar-plus-storage growth noted by analysts, according to Wood Mackenzie projections shared with Reuters.
Developers and energy traders said locations offering the highest returns -- in strapped areas of the grid -- will become increasingly scarce as more storage comes online and, as diversifying resources for better projects suggests, electricity prices stabilize.
Texas lawmakers this week voted to provide new subsidies for natural gas power plants in a bid to shore up reliability. But the legislation also contains provisions that industry groups said could encourage investment in battery storage by supporting 'unlayering' peak demand approaches.
Amid the battery rush, BlackRock acquired developer Jupiter Power from private equity firm EnCap Investments late last year. Korea's SK E&S acquired Key Capture Energy from Vision Ridge Partners in 2021 and UBS bought five Texas projects from Black Mountain last year for a combined 700 megawatts (MW) of energy storage. None of the sales' prices were disclosed.
SK E&S said its acquisition of Key Capture was part of a strategy to invest in U.S. grid resiliency.
"SK E&S views energy storage solutions in Texas and across the U.S. as a core technology that supports a new energy infrastructure system to ensure American homes and businesses have affordable power," the company said in a statement.
Related News

U.S. residential electricity bills increased 5% in 2022, after adjusting for inflation
U.S. Residential Electricity Bills rose on stronger demand, inflation, and fuel costs, with higher retail prices, kWh consumption, and extreme weather driving 2022 spikes; forecasts point to stable summer usage and slight price increases.
Key Points
They are average household power costs shaped by prices, kWh use, weather, and upstream fuel costs.
✅ 2022 bills up 13% nominal, 5% real vs. 2021
✅ Retail price rose 11%; consumption up 2% to 907 kWh
✅ Fuel costs to plants up 34%, pressuring rates
In nominal terms, the average monthly electricity bill for residential customers in the United States increased 13% from 2021 to 2022, rising from $121 a month to $137 a month. After adjusting for inflation—which reached 8% in 2022, a 40-year high—electricity bills increased 5%. Last year had the largest annual increase in average residential electricity spending since we began calculating it in 1984. The increase was driven by a combination of more extreme temperatures, which increased U.S. consumption of electricity for both heating and cooling, and higher fuel costs for power plants, which drove up retail electricity prices nationwide.
Residential electricity customers’ monthly electricity bills are based on the amount of electricity consumed and the retail electricity price. Average U.S. monthly electricity consumption per residential customer increased from 886 kilowatthours (kWh) in 2021 to 907 kWh in 2022, even as U.S. electricity sales have declined over the past seven years. Both a colder winter and a hotter summer contributed to the 2% increase in average monthly electricity consumption per residential customer in 2022 because customers used more space heating during the winter and more air conditioning during the summer, with some states, such as Pennsylvania, facing sharp winter rate increases.
Although we don’t directly collect retail electricity prices, we do collect revenues from electricity providers that allow us to determine prices by dividing by consumption, and industry reports show major utilities spending more on electricity delivery than on power production. In 2022, the average U.S. residential retail electricity price was 15.12 cents/kWh, an 11% increase from 13.66 cents/kWh in 2021. After adjusting for inflation, U.S. residential electricity prices went up by 2.5%.
Higher fuel costs for power plants drove the increase in residential retail electricity prices. The cost of fossil fuels—including natural gas prices, coal, and petroleum—delivered to U.S. power plants increased 34%, from $3.82 per million British thermal units (MMBtu) in 2021 to $5.13/MMBtu in 2022. The higher fuel costs were passed along to residential customers and contributed to higher retail electricity prices, and Germany power prices nearly doubled over a year in a related trend.
In the first three months of 2023, the average U.S. residential monthly electricity bill was $133, or 5% higher than for the same time last year, according to data from our Electric Power Monthly. The increase was driven by a 13% increase in the average U.S. residential retail electricity price, which was partly offset by a 7% decrease in average monthly electricity consumption per residential customer, and industry outlooks also see U.S. power demand sliding 1% on milder weather. This summer, we expect that typical household electricity bills will be similar to last year’s, with customers paying about 2% more on average. The slight increase in electricity costs forecast for this summer stems from higher retail electricity prices but similar consumption levels as last summer.
Related News

EPA: New pollution limits proposed for US coal, gas power plants reflect "urgency" of climate crisis
EPA Power Plant Emissions Rule proposes strict greenhouse gas limits for coal and gas units, leveraging carbon capture (CCS) under the Clean Air Act to cut CO2 and accelerate decarbonization of the U.S. grid.
Key Points
A proposed EPA rule setting CO2 limits for coal and gas plants, using CCS to cut power-sector greenhouse gases.
✅ Applies to existing and new coal and large gas units
✅ Targets near-zero CO2 by 2038 via CCS or retirement
✅ Cites grid, health, and climate benefits; faces legal challenges
The Biden administration has proposed new limits on greenhouse gas emissions from coal- and gas-fired power plants, its most ambitious effort yet to roll back planet-warming pollution from the nation’s second-largest contributor to climate change.
A rule announced by the Environmental Protection Agency could force power plants to capture smokestack emissions using a technology that has long been promised but is not used widely in the United States, and arrives amid changes stemming from the NEPA rewrite that affect project reviews.
“This administration is committed to meeting the urgency of the climate crisis and taking the necessary actions required,″ said EPA Administrator Michael Regan.
The plan would not only “improve air quality nationwide, but it will bring substantial health benefits to communities all across the country, especially our front-line communities ... that have unjustly borne the burden of pollution for decades,” Regan said in a speech at the University of Maryland.
President Joe Biden, whose climate agenda includes a clean electricity standard as a key pillar, called the plan “a major step forward in the climate crisis and protecting public health.”
If finalized, the proposed regulation would mark the first time the federal government has restricted carbon dioxide emissions from existing power plants, following a Trump-era replacement of Obama’s power plant overhaul, which generate about 25% of U.S. greenhouse gas pollution, second only to the transportation sector. The rule also would apply to future electric plants and would avoid up to 617 million metric tons of carbon dioxide through 2042, equivalent to annual emissions of 137 million passenger vehicles, the EPA said.
Almost all coal plants — along with large, frequently used gas-fired plants — would have to cut or capture nearly all their carbon dioxide emissions by 2038, the EPA said, a timeline that echoed concerns raised during proposed electricity pricing changes in the prior administration. Plants that cannot meet the new standards would be forced to retire.
The plan is likely to be challenged by industry groups and Republican-leaning states, much like litigation over the Affordable Clean Energy rule unfolded in recent years. They have accused the Democratic administration of overreach on environmental regulations and warn of a pending reliability crisis for the electric grid. The power plant rule is one of at least a half-dozen EPA rules limiting power plant emissions and wastewater treatment rules.
“It’s truly an onslaught” of government regulation “designed to shut down the coal fleet prematurely,″ said Rich Nolan, president and CEO of the National Mining Association.
Regan denied that the power plant rule was aimed at shutting down the coal sector, but acknowledged — even after the end to the 'war on coal' rhetoric — “We will see some coal retirements.”
Related News

Energy-insecure households in the U.S. pay 27% more for electricity than others
Community Solar for Low-Income Homes expands energy equity by delivering renewable energy access, predictable bill savings, and tax credit benefits to renters and energy-insecure households, accelerating distributed generation and storage adoption nationwide.
Key Points
A program model enabling renters and LMI households to subscribe to off-site solar and save on utility bills.
✅ Earn bill credits from shared solar generation.
✅ Expands access for renters and LMI subscribers.
✅ Often paired with storage and IRA tax credit adders.
On a square-foot basis, the issue of inequality is made worse by higher costs for energy usage in the nation. Efforts like community solar programs such as Maryland community solar are underway to boost low-income participation in the cost benefits of renewable energy.
The Energy Information Administration (EIA) shows that households that are considered energy insecure, or those that have the inability to adequately meet basic household energy costs, are paying more for electricity than their wealthier counterparts.
On average in the United States in 2020, households were billed about $1.04 per square foot for all energy sources. For homes that did not report energy insecurity, that average was $0.98 per square foot, while homes with energy insecurity issues paid an average of $1.24 per square foot for energy. This means that U.S. residents that need the most support on their energy bills are stuck with costs 27% higher than their neighbors on square-foot-basis.
EIA said energy-insecure households have reduced or forgone basic necessities to pay energy bills, kept their houses at unsafe temperatures because of energy cost concerns, or been unable to repair heating or cooling equipment because of cost.
In 2020, households with income less than $10,000 a year were billed an average of $1.31 per square foot for energy, while households making $100,000 or more were billed an average of $0.96 per square foot, said EIA. Renters paid considerably more ($1.28 per square foot) than owners ($0.98 per square foot). There were also considerable differences between regions, with New England solar growth sparking grid upgrade debates, ethnic groups and races, and insulation levels, as seen below.
The energy transition toward renewables like solar has offered price stability, amid record solar and storage growth nationwide, but thus far energy-insecure communities have relatively been left behind. A recent Berkeley Lab report, Residential Solar-Adopter Income and Demographic Trends, indicates that even though the rate of solar adoption among low-income residents is increasing (from 5% in 2010 to 11% in 2021), that segment of energy consumers remains under-represented among solar adopters, relative to its share of the population.
Community solar efforts
As such, the United States is targeting communities most impacted by energy costs that have not benefitted from the transition, highlighting “Energy Communities” that are eligible for an additional 10% tax credit through funds made possible by the Inflation Reduction Act.
Additionally, a push for community solar development is taking place nationwide to extend access to affordable solar energy to renters and other residents that aren’t able to leverage finances to invest in predictable, low-cost residential solar systems. The Biden Administration set a goal this year to sign up 5 million community solar households, achieving $1 billion in bill savings by 2025. The community solar model only represents about 8% of the total distributed solar capacity in the nation. This target would entail a jump from 3 GW installed capacity to 20 GW by the target year. The Department of Energy estimates community solar subscribers save an average of 20% on their bills.
California this year passed AB 2316, the Community Renewable Energy Act takes aim at four acute problems in the state’s power market: reliability amid rising outage risks, rates, climate and equity. The law creates a community renewable energy program, including community solar-plus-storage, supported by cheaper batteries, to overcome access barriers for nearly half of Californians who rent or have low incomes. Community solar typically involves customers subscribing to an off-site solar facility, receiving a utility bill credit for the power it generates.
“Community renewable energy is a proven powerful tool to help close California’s clean energy gap, bringing much needed relief to millions struggling with high housing costs and utility debt,” said Alexis Sutterman, energy equity program manager at the California Environmental Justice Alliance.
The program has energy equity baked into its structure, working to make sure Californians of all income levels participate in the benefits of the energy transition. Not only does it open solar access to renters, the law ensures that at least 51% of subscribers are low-income customers, which is expected to make projects eligible for a 10% tax credit adder under the IRA.
“The money’s on the table now,” said Jeff Cramer, president and chief executive of the Coalition for Community Solar Access. “While there are groups pushing for solar access for all, and states with strong legislation, there are other pockets of interest in surprising places in the United States. For example, Louisiana has no policy for community solar or support for low-income residents going solar but the city of New Orleans has its own utility commission with a community solar program. In Nebraska, forward-looking co-operatives have created community solar projects.
Community solar markets are active in 22 states, with more expected to come online in the future as states pursue 100% clean energy targets across the country. However, the market is expected to require strong community outreach efforts to foster trust and gain subscribers.
“There is a distrust of community solar initially in LMI communities as many have been burned before by retail energy false promises,” said Eric LaMora, executive director, community solar, Nautilus Solar on a panel at the Solar Energy Industries Association Finance, Tax, and Buyers seminar. “People are suspicious but there really are no hooks with community solar.”
LMI residents are leery to provide tax records or much documents at all in order to sign up for community solar, LaMora said. “We were surprised to see less of a default rate with LMI residents. We attribute this to the fact that they see significant savings on their electric bill, making it easier to pay each month,” he said.
Related News

Scientists generate 'electricity from thin air.' Humidity could be a boundless source of energy.
Air Humidity Energy Harvesting converts thin air into clean electricity using air-gen devices with nanopores, delivering continuous renewable energy from ambient moisture, as demonstrated by UMass Amherst researchers in Advanced Materials.
Key Points
A method using nanoporous air-gen devices to harvest continuous clean electricity from ambient atmospheric moisture.
✅ Nanopores drive charge separation from ambient water molecules
✅ Works across materials: silicon, wood, bacterial films
✅ Predictable, continuous power unlike intermittent solar or wind
Sure, we all complain about the humidity on a sweltering summer day. But it turns out that same humidity could be a source of clean, pollution-free energy, aligning with efforts toward cheap, abundant electricity worldwide, a new study shows.
"Air humidity is a vast, sustainable reservoir of energy that, unlike wind and solar power resources, is continuously available," said the study, which was published recently in the journal Advanced Materials.
While humidity harvesting promises constant output, advances like a new fuel cell could help fix renewable energy storage challenges, researchers suggest.
“This is very exciting,” said Xiaomeng Liu, a graduate student at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst, and the paper’s lead author. “We are opening up a wide door for harvesting clean electricity from thin air.”
In fact, researchers say, nearly any material can be turned into a device that continuously harvests electricity from humidity in the air, a concept echoed by raindrop electricity demonstrations in other contexts.
“The air contains an enormous amount of electricity,” said Jun Yao, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst and the paper’s senior author. “Think of a cloud, which is nothing more than a mass of water droplets. Each of those droplets contains a charge, and when conditions are right, the cloud can produce a lightning bolt – but we don’t know how to reliably capture electricity from lightning.
"What we’ve done is to create a human-built, small-scale cloud that produces electricity for us predictably and continuously so that we can harvest it.”
The heart of the human-made cloud depends on what Yao and his colleagues refer to as an air-powered generator, or the "air-gen" effect, which relates to other atmospheric power concepts like night-sky electricity studies in the field.
In broader renewable systems, flexible resources such as West African hydropower can support variable wind and solar output, complementing atmospheric harvesting concepts as they mature.
The study builds on research from a study published in 2020. That year, scientists said this new technology "could have significant implications for the future of renewable energy, climate change and in the future of medicine." That study indicated that energy was able to be pulled from humidity by material that came from bacteria; related bio-inspired fuel cell design research explores better electricity generation, the new study finds that almost any material, such as silicon or wood, also could be used.
The device mentioned in the study is the size of a fingernail and thinner than a single hair. It is dotted with tiny holes known as nanopores, it was reported. "The holes have a diameter smaller than 100 nanometers, or less than a thousandth of the width of a strand of human hair."
Related News

Time running out for Ontario to formally request Pickering nuclear power station extension
Pickering Nuclear Plant Extension faces CNSC approval as Ontario Power Generation pursues license renewal before the June 30, 2023 deadline, amid a 2025 capacity crunch and grid reliability risks from decommissioning and overlapping nuclear outages.
Key Points
A plan to run Pickering past 2024 to Sept 2026, pending CNSC license renewal to address Ontario's 2025 capacity gap.
✅ CNSC approval needed for operation beyond Dec 31, 2024
✅ OPG aims to file by June 30, 2023 deadline
✅ Extension targets grid reliability through 2026
Ontario’s electricity generator has yet to file an official application to extend the life of the Pickering nuclear power plant, more than eight months after the Ford government announced a plan to continue operating Pickering for longer.
As the province faces an electricity shortfall in 2025 and beyond, the Ford government scrambled to prolong the Pickering power plant until September 2026, in order to guarantee a steady supply of power as the province experiences a rise in demand and shutdowns at other nuclear power plants.
The life extension may come down to the wire, however, as the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC), the federal regulator tasked with approving or denying the extension, tells Global News the province has yet to file key paperwork.
The information is required for the application, including materials related to the proposed Pickering B refurbishment, and the government now has a month before the deadline runs out.
“The Commission requires that Ontario Power Generation submit specific information by June 30, 2023, if it intends to operate the Pickering Nuclear Generating Station beyond December 31, 2024,” the CNSC told Global News in a statement. “The Commission Registry has not yet received an application from Ontario Power Generation.”
If Ontario doesn’t receive the green light, the power plant which currently is responsible for 14 per cent of the province’s energy grid will be decommissioned in 2025, leaving the province with a significant electricity supply gap if replacement sources are not secured.
For its part, the Ford government doesn’t seem concerned about the impending timeline, even though the station was slated to close as planned, suggesting the Crown corporation responsible for the application will get it in on time.
“OPG is on track to submit their application before the end of June and has already started to submit supporting materials as part of the regulatory process toward clean power goals,” a spokesperson for energy minister Todd Smith said.