Thevenin's Theorem
By William Conklin, Associate Editor
Thevenin’s Theorem simplifies complex linear circuits into a single voltage source and series resistance, making circuit analysis easier for engineers. It helps calculate current, load behavior, and equivalent resistance in practical electrical systems.
What is Thevenin’s Theorem?
Thevenin’s Theorem is a method in circuit analysis that reduces any linear electrical network to an equivalent circuit with a voltage source (Vth) in series with a resistance (Rth).
✅ Simplifies circuit analysis for engineers and students
✅ Calculates load current and voltage with accuracy
✅ Models equivalent resistance for real-world applications
Thevenin’s Theorem allows any linear, two-terminal circuit to be represented by a single voltage source in series with a resistance.
-
Reduces complex circuits to a simple equivalent consisting of a voltage source and a resistor
-
Makes analyzing load response and network behavior straightforward, saving time and effort
-
Widely used for calculating current, voltage, or power across loads in electrical networks
To fully grasp why Thevenin’s Theorem matters, it helps to revisit the principles of basic electricity, where voltage, current, and resistance form the foundation of all circuit analysis.
Understanding Thevenin’s Theorem
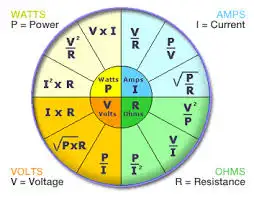
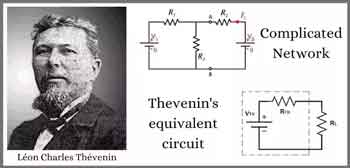
Thevenin’s Theorem is a cornerstone of basic electrical engineering and circuit analysis. First introduced by French engineer Léon Charles Thévenin in the late 19th century, the theorem allows engineers and students alike to simplify a complex electrical network to a single voltage source (known as the Thevenin voltage, Vth) in series with a single resistor (known as the Thevenin resistance, Rth). This is particularly useful when analyzing how a circuit will behave when connected to different loads. Concepts such as Ohm’s Law and electrical resistance work in conjunction with Thevenin’s method, ensuring accurate load and network calculations.
Thevenin’s Theorem states that any linear electrical network can be simplified to an equivalent circuit consisting of a single voltage source in series with a resistance. By removing the load resistance, engineers can calculate the equivalent circuit voltage at the terminals, which represents how the circuit will behave when reconnected. This approach replaces multiple components and ideal voltage sources with one simplified model, making circuit analysis more efficient while preserving accuracy in predicting load behavior.
How Thevenin’s Theorem Works
According to Thevenin’s Theorem, no matter how complicated a linear circuit may be, with multiple sources and resistors, it can be replaced by an equivalent Thevenin circuit. This greatly simplifies the process when you’re only interested in the voltage, current, or power delivered to a specific part of the circuit. The steps typically followed when using Thevenin’s Theorem are:
-
Identify the portion of the circuit for which you want to find the Thevenin equivalent (usually across two terminals where a load is or will be connected).
-
Remove the load resistor and determine the open-circuit voltage across the terminals. This voltage is the Thevenin voltage (Vth).
-
Calculate the Thevenin resistance (Rth) by deactivating all independent voltage sources (replace them with short circuits) and current sources (replace them with open circuits), then determining the resistance viewed from the terminals.
-
Redraw the circuit as a single voltage source Vth in series with resistance Rth, with the load resistor reconnected.
Why Use Thevenin’s Theorem?
There are several reasons why Thevenin’s Theorem is so widely used in both academic and practical electrical engineering:
-
Simplification – Instead of solving a complex network repeatedly each time the load changes, engineers can just reconnect different loads to the Thevenin equivalent, saving time and reducing the potential for error.
-
Insight – By reducing a circuit to its essential characteristics, it’s easier to understand how changes will affect load voltage, current, or power.
-
Foundation for Further Analysis – Thevenin’s Theorem forms the basis for other network analysis techniques, such as Norton's Theorem, and is fundamental to understanding more advanced topics like maximum power transfer.
Example Application
Imagine a scenario where you need to analyze a circuit with multiple resistors and voltage sources connected in series, with a load resistor at the end. Without Thevenin’s Theorem, calculating the voltage across or current through the load each time you change its resistance would require solving complicated sets of equations. Thevenin’s Theorem allows you to do all the hard work once, finding Vth and Rth, and then quickly see how the load responds to different values.
Illustrative Case: A power supply circuit needs to be tested for its response to varying loads. Instead of recalculating the entire network for each load, the Thevenin equivalent makes these calculations swift and efficient. A deeper look at capacitance and inductance shows how energy storage elements influence circuit behavior when simplified through equivalent models.
Limitations and Conditions
While powerful, Thevenin’s Theorem has limitations:
-
It only applies to linear circuits, those with resistors, sources, and linear dependent sources.
-
It cannot directly simplify circuits containing nonlinear elements such as diodes or transistors in their nonlinear regions.
-
The theorem is most useful for “two-terminal” or “port” analysis; it doesn’t help as much with multiple output terminals simultaneously, though extensions exist.
Connections to Broader Electrical Concepts
Thevenin’s Theorem is closely related to other concepts, such as Norton’s Theorem, which prescribes an equivalent current source and parallel resistance. Both theorems are widely applied in real-world scenarios, including power distribution, signal analysis, and the design of electronic circuits. For example, it's relevant when considering how hydro rates impact load distribution in utility networks.
Thevenin’s Theorem is more than just a trick for simplifying homework—it is a core analytical tool that forms the backbone of practical circuit analysis. Whether you are a student learning circuit theory or an engineer designing power systems, understanding and applying Thevenin’s Theorem is essential. Understanding current flow and the role of a conductor of electricity provides practical insight into why reducing networks to simple equivalents makes engineering analysis more efficient.
Related Articles