What Is Alternating Current
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
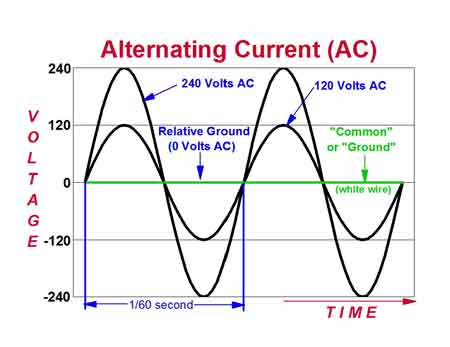
Alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical flow where the direction of current reverses periodically. Used in most homes and industries, AC is efficient for long-distance transmission and powers devices like motors, lights, and appliances through oscillating voltage.
What is Alternating Current?
Alternating current is a fundamental aspect of electrical systems that have shaped our world in countless ways. Its ability to be easily generated, converted to different voltages, and transmitted over long distances has made it the preferred choice for power transmission and distribution. Additionally, the many advantages of AC, such as compatibility with various devices and safety features, have made it indispensable in our daily lives.
✅ Powers homes, businesses, and industrial equipment through reliable energy transmission.
✅ Changes direction periodically, unlike DC, which flows one way.
✅ Enables long-distance energy delivery with reduced power loss.
To answer the question: What is alternating current? We need to first understand the role of a conductor, which is essential in AC systems, as conductors carry the oscillating electrical energy throughout circuits.
| Aspect | Description | Related Concept |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electric current that periodically reverses direction, forming a sine wave. | What is Alternating Current |
| AC vs. DC | AC changes direction; DC flows in one direction only. | Difference Between AC and DC |
| Waveform | Typically sinusoidal, but can also be square or triangular. | Impedance |
| Frequency | Number of cycles per second (50 Hz or 60 Hz depending on the region). | Unit of Electrical Resistance |
| Voltage Transformation | Easily adjusted using transformers for long-distance transmission. | Transformer Grounding |
| Measurement Tools | Multimeters and voltmeters measure AC voltage and current. | What is a Multimeter, What is a Voltmeter |
| Key Components | Conductors, capacitors, resistors, and inductors are essential to AC systems. | What is a Capacitor, What is a Conductor |
| Generation Principle | Based on electromagnetic induction through rotating magnetic fields. | Electromagnetic Induction |
| Common Applications | Powering homes, industrial machines, and electrical grids. | Electricity Grid |
| Inventor | Nikola Tesla pioneered practical AC power systems and the induction motor. | History of Electricity |
Understanding AC and DC
In the world of electricity, there are two primary forms of electric current: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Understanding the distinctions between these two types of currents and their applications in daily life is essential to appreciate the advances in electrical engineering and the technology that surrounds us. A multimeter is commonly used to measure AC voltage and current in residential and industrial electrical systems.
AC vs. DC: Basic Differences
AC and DC are two distinct methods by which electric charge is transferred through a circuit. AC involves the flow of charge that periodically reverses direction, creating a waveform typically resembling a sine wave. On the other hand, DC refers to the flow of charge in a single, constant direction. The differences in their nature, functionality, and applications create a contrasting landscape in the electrical power sector. Devices like the voltmeter are specifically designed to measure AC or DC voltage, helping technicians verify circuit functionality and safety.
Why AC Is Preferred for Power Transmission
One key reason why AC is preferred over DC is its ability to easily convert to and from high voltages, making electric power transmission across long distances more efficient. Additionally, transformers can increase or decrease AC voltage, resulting in minimal power loss during long-distance transmission. In contrast, DC power cannot be altered as conveniently, making it less suitable for power transmission over extended distances.
How Alternating Current Works
The working principle of AC is centred around the changing magnetic field created by the flow of electric current. As the current changes direction, the magnetic field also alternates, inducing a voltage in the nearby conductors. This property of AC is fundamental to the operation of AC generators and transformers.
-
AC operation is based on electromagnetic induction
-
Rreversal creates alternating magnetic fields
-
Voltage is induced in nearby conductors
The Role of Nikola Tesla in AC Development
The invention of AC can be attributed to multiple individuals, but the Serbian-American inventor, Nikola Tesla, is often credited with pioneering AC systems. Tesla's work on AC power transmission and his development of the induction motor helped establish AC as the dominant form of electricity.
Frequency: 50 Hz vs. 60 Hz
In frequency, the terms 50-cycle and 60-cycle AC refer to the number of times the current changes direction in one second. The frequency of AC power varies globally, with 50 Hz being the standard in many parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, while 60 Hz is the norm in North America.
-
50 Hz is standard in Europe, Asia, and Africa
-
60 Hz is common in North America
-
Frequency affects compatibility and performance of electrical devices
This difference in frequency can affect the operation of certain appliances and devices, making it essential to use the appropriate frequency for the intended purpose.
Advantages of Alternating Current
The advantages of AC over DC extend beyond efficient power transmission. AC is easier to generate and is widely used for electric power generation, making it more accessible and cost-effective. Moreover, AC systems are safer as they can be easily switched off when required, reducing the risk of electrical accidents. AC is versatile and can power various devices, from small household appliances to large industrial machines.
Key benefits of AC:
-
Easily transformed to higher or lower voltages
-
Safer switching and control in circuits
-
Powers a wide range of residential and industrial devices
How AC Is Generated and Transmitted
The generation and transmission of AC are crucial components of the electrical power infrastructure. AC is generated through various means, such as hydroelectric, thermal, and nuclear power plants, which use generators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Transmission components:
-
Transformers: Adjust voltage levels
-
Transmission towers: Carry high-voltage lines
-
Substations: Regulate voltage for safe end-use
Once generated, AC is transmitted through power lines that consist of transformers, transmission towers, and substations, which adjust the voltage levels for efficient distribution and usage.
The Role of AC in Daily Life
AC plays a vital role in our daily lives, as it powers most of the appliances and devices we rely on, including lights, computers, and household appliances. In addition, its compatibility with transformers, ease of generation, and ability to transmit power over long distances make it a cornerstone of modern electrical systems.
Frequency has a notable impact on AC usage. In addition to determining the compatibility of devices with a region's power supply, the frequency of AC power affects the speed and performance of electrical motors. A change in frequency may result in the motor operating at a different speed or, in some cases, causing it to malfunction.
Transformers are essential devices in AC systems, as they adjust voltage levels to meet the requirements of various applications. They function by utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field in the primary coil induces a voltage in the secondary coil. By adjusting the number of turns in the coils, transformers can efficiently increase or decrease the voltage of AC power, depending on the specific application's needs.
The differences between AC and DC are crucial in understanding the diverse landscape of electrical power. The invention of AC by Nikola Tesla and other inventors has revolutionized the way electricity is generated, transmitted, and utilized. With an appreciation for the characteristics and applications of AC, we can gain a deeper understanding of the technology and infrastructure that powers our world.
How Does Alternating Current Work?
AC works by periodically reversing the direction of the electric charge flow within a circuit. In contrast to DC, which flows in a constant direction, AC oscillates back and forth. This oscillation is typically represented as a waveform, often in the shape of a sine wave. Let's dive deeper into how AC works.
AC is characterized by a waveform that typically takes the shape of a sine wave, allowing for smooth and continuous changes in voltage over time. This makes it ideal for long-distance transmission across the power grid, where electricity generated by a generator must travel efficiently to homes and businesses. The frequency of this current—measured in cycles per second or hertz (Hz)—determines how rapidly the voltage changes direction, impacting device performance and grid efficiency. As current flows through a conductor, it can be stepped up or down using a transformer, enabling voltage levels to be optimized for safe and effective delivery.
Generation: AC is generated using a rotating magnetic field to induce an electric current in a conductor. This is done using devices such as generators and alternators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. In these devices, a coil of wire rotates within a magnetic field, or a magnet rotates around a stationary coil. This rotation causes the magnetic field to interact with the conductor, inducing a voltage and, consequently, an electric current that changes direction periodically.
Waveform: The alternating nature of AC is depicted by a waveform, which shows the voltage or current as a function of time. The most common waveform for AC is the sine wave, which can also take other forms, such as square or triangular waves. The waveform's shape determines the characteristics of the AC and how it interacts with various electrical components.
Frequency: One important parameter of AC is its frequency, which indicates the number of complete cycles the current undergoes per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz). Common frequencies include 50 Hz and 60 Hz, but other frequencies can also be used depending on the application. The frequency of the AC power supply affects the performance and compatibility of devices and equipment connected to it.
Voltage and current relationship: In an AC circuit, the voltage and current can be in phase (i.e., they reach their peak values simultaneously) or out of phase (i.e., they reach their peak values at different times). The phase relationship between voltage and current in an AC circuit can significantly impact power delivery and system efficiency. A voltage sag can disrupt sensitive equipment, making voltage regulation a key part of power quality analysis.
Transformers: A key advantage of AC is that its voltage can be easily changed using transformers. Transformers operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field in the primary coil induces a voltage in the secondary coil. By adjusting the number of turns in the coils, the transformer can step up or down the AC voltage as needed. This ability to adjust voltage levels makes AC an efficient choice for long-distance power transmission.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the formula to calculate alternating current?
To calculate the value of AC at any given time, you need to know the current's amplitude (maximum value) and the angular frequency. The general formula for calculating instantaneous current in an AC circuit is:
i(t) = I_max * sin(ωt + φ)
Where:
-
i(t) is the instantaneous current at time t
-
I_max is the amplitude or peak current
-
ω (omega) is the angular frequency, calculated as 2πf (where f is the frequency in hertz)
-
t is the time at which you want to calculate the current
-
φ (phi) is the phase angle, which accounts for any phase shift between the voltage and the current waveforms
Remember that this formula assumes a sinusoidal waveform, the most common form of AC. If the waveform is not sinusoidal, the formula will be different and depend on the specific shape of the waveform.
Another important value for AC circuits is the root-mean-square (RMS) current, which measures the effective value of the current. The RMS current is useful for calculating power in AC circuits and can be compared to the steady current value in DC circuits. The formula to calculate RMS current from the peak current is as follows:
I_RMS = I_max / √2
Where:
-
I_RMS is the root-mean-square current
-
I_max is the amplitude or peak current
-
√2 is the square root of 2, approximately 1.414
-
Using these formulas, you can calculate the instantaneous current value for an alternating current waveform and determine the effective or RMS current value.
To understand how voltage affects electrical circuits, it's essential to examine how voltage drop can lead to energy loss, particularly over long distances.
Related Articles