Dynamic Electricity Explained
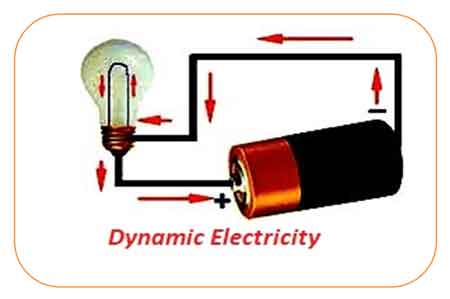
Dynamic electricity is the continuous flow of electric charge—electric current—through a conductor, typically driven by a voltage source. Think of it like water flowing in a pipe, where electrons move uniformly to carry energy.
What is Dynamic Electricity?
Dynamic electricity refers to the continuous movement of electric charges, commonly known as electric current.
-
Describes the flow of electrons or electric charge through a conductor
-
Facilitates energy transfer, enabling devices and machines to operate
-
Used in powering household appliances, industrial processes, lighting, and electronics
It is the continuous flow of electric charges through a conductor, commonly referred to as electric current. Think of it like water flowing through a pipe: voltage acts as water pressure, current as the flow of water, and resistance as the size of the pipe. This motion of electrons is what powers devices, lights homes, and drives entire industries.
Unlike static electricity, which involves charges at rest, dynamic electricity is defined by the constant movement of charge carriers, making it the foundation of modern electrical systems. To understand how voltage, current, and resistance interact in circuits, see our detailed guide on Ohm’s Law.
It depends on the movement of charges through conductive materials. Learn more about the difference between conductors and electrical insulators.
Dynamic electricity is closely tied to the concept of electrical energy, which is produced when an energy source creates movement between charges. A negative charge is naturally drawn toward a positively charged region, and objects with opposite charges will attract one another. This interaction between positive and negative charges is the foundation of current flow. Every type of electrical system, from simple batteries to complex power grids, relies on this basic principle to generate and transfer usable energy.
How It Works (Voltage, Current, Ohm’s Law)
Dynamic electricity occurs when a voltage difference is applied across a conductor, such as copper or aluminum wire. This creates an energy imbalance that causes electrons to flow from one end to the other.
-
Electrons drift slowly, but the electrical effect travels nearly at the speed of light, allowing instant energy transfer.
-
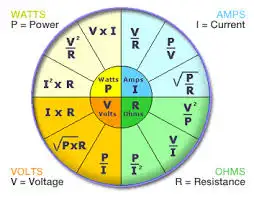
The flow of current is governed by Ohm’s Law: V = IR, where voltage (V) equals current (I) times resistance (R).
-
Moving charges generate magnetic fields and produce heat, demonstrating the role of resistance in circuits and enabling the operation of motors, electromagnets, and heating devices.
-
Current is measured in amperes (A), typically using an ammeter or other measurement instruments.
Electric current is measured in amperes, a unit explained in our introduction to electrical current.
The safe handling of flowing charges requires proper electrical grounding techniques to prevent hazards.
Analogy: Imagine marbles in a tube. Push one marble in, and the entire line shifts almost instantly. Similarly, electron movement is slow, but the effect propagates quickly through the entire circuit.
AC vs DC Explained
| Type of Current | Description | Common Uses | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Current (DC) | Electrons flow in a single, steady direction | Batteries, electronics, solar panels, EVs | Stable output, essential for digital devices and storage systems |
| Alternating Current (AC) | Electron flow reverses direction periodically | Power grids, appliances, and industrial systems | Efficient long-distance transmission, adaptable to transformers |
- Why AC? Its ability to change voltage levels makes it ideal for transmitting energy over long distances with minimal energy loss.
-
Why DC? Critical for low-voltage devices, renewable integration, and battery storage, where stable current is required.
For a deeper look at how alternating current functions in grids, see our overview of alternating current.
Direct current plays a vital role in storage and electronics. Explore its applications on our page on direct current.
Everyday Applications
Dynamic electricity drives nearly every aspect of modern life:
-
Homes: power lighting, appliances, heating, and electronics.
-
Industry: runs motors, automation systems, and manufacturing equipment.
-
Transportation: essential for electric vehicles, rail systems, and aviation technologies.
-
Renewable energy: harnessed by solar panels, wind turbines, and hydroelectric systems, which is then transmitted via power grids over long distances through reliable power transmission systems.
-
Energy storage: stored in batteries to support grid reliability and electric mobility.
-
Communication systems: support telecom networks, internet infrastructure, and data centers.
In renewable energy systems, dynamic electricity is produced and stored for later use. Learn how it relates to energy storage.
The flow of current must be managed carefully in fault conditions. For details, see our guide on fault current calculation.
Safety and Control
Because moving charges create heat, sparks, and electromagnetic fields, electrical circuits are designed with protective devices:
-
Circuit breakers and fuses prevent overheating and fire risks.
-
Insulation and grounding ensure safe handling of conductors.
-
Control systems regulate current flow for efficiency and reliability.
Circuit safety relies on protective systems. Explore our page on electrical protection for more details.
Static vs Dynamic Electricity
Understanding the difference is key:
-
Static
-
Charges accumulate on surfaces.
-
It can cause small shocks or sparks.
-
Temporary and uncontrolled.
-
-
Dynamic
-
Charges move continuously through conductors.
-
Power devices and grids.
-
Reliable and controllable.
-
Future Challenges and Developments
The demand for dynamic electricity is expanding as society transitions to net-zero energy systems. Key developments include:
-
Smart grids to balance supply and demand.
-
Advanced energy storage to integrate renewable sources.
-
Global electrification in emerging economies, driving higher usage worldwide.
It will continue to shape technology, transportation, and sustainability goals in the decades ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between static and dynamic electricity?
Static involves charges at rest, while dynamic is defined by moving charges, producing electric current used to power systems.
Why is it important in daily life?
It powers homes, industries, transport, communication, and renewable energy systems, making it the foundation of modern civilization.
How is it measured?
It is measured in amperes (A), using tools like ammeters to detect the flow of current in a circuit.
Related Articles