Types of Resistors
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
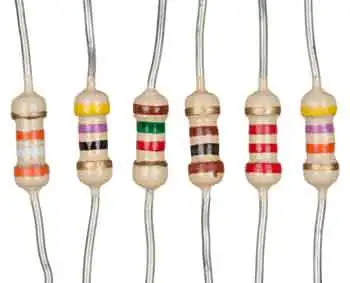
Types of resistors are essential in electronics, as they control current, reduce voltage, and ensure circuit stability. From fixed and variable resistors to specialized forms like thermistors and photoresistors, each type plays a critical role in electrical engineering.
What are the Various Types of Resistors?
Types of resistors describe categories of electronic components designed to limit current and manage voltage in circuits."
✅ Fixed resistors ensure stable resistance values
✅ Variable resistors adjust resistance as needed
✅ Specialized resistors respond to heat or light
There are two main types of resistors: fixed and variable. Fixed resistors maintain a constant value, while variable resistors can be adjusted to suit changing requirements. Within these groups are many designs crafted from various materials, each selected for its precision, stability, and suitability in specific applications. When studying how different resistor types perform, it helps to review Ohm’s Law Formula, which explains the mathematical relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
In addition to resistors, other passive components, such as capacitors, are equally important for controlling current flow and stabilizing electrical circuits.
Common Types of Resistors
| Type | Key Feature | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Film | Low cost, general use | Everyday electronics |
| Metal Film | High accuracy, low noise | Precision circuits |
| Metal Oxide | Surge resistant | Power supplies |
| Wire-Wound | High power handling | Industrial applications |
| Surface-Mount (SMD) | Compact, space-saving | Modern circuit boards |
| Potentiometer | Adjustable resistance | Volume/tuning controls |
| Thermistor | Temperature-sensitive | Sensors, protection devices |
Fixed Types of Resistors
Carbon Film Resistors
Carbon film resistors are inexpensive, reliable, and widely used in general-purpose electronics. By applying a thin carbon layer to a ceramic base, they provide a stable resistance for everyday circuits. While not as precise as modern designs, they remain popular where high accuracy isn’t required.
Carbon Composition Resistors
Once the standard in consumer electronics, carbon composition resistors are now less common, but they still serve in circuits that need high pulse load capacity. They offer durability in the face of sudden surges, although their long-term stability and accuracy are lower than those of newer types.
Metal Film Resistors
Metal film resistors, made by depositing a nickel-chromium alloy onto a ceramic substrate, are prized for their precision. With excellent stability, low noise, and tight tolerances, they are widely chosen for high-frequency and sensitive applications. However, they cannot dissipate as much power as wire-wound resistors and are vulnerable to strong surges.
Metal Oxide Resistors
Using oxides like tin or ruthenium on ceramic, metal oxide resistors are known for their robustness. They combine good tolerance with the ability to withstand high voltages, making them ideal where surge protection is essential. While not as accurate as metal film resistors, they offer higher reliability in demanding conditions.
Wire-Wound Resistors
Built from coiled metal wire wrapped around a ceramic or fibreglass core, wire-wound resistors excel in high-power applications. Their ability to handle large currents and high temperatures makes them indispensable in heavy-duty circuits. Their main drawback is bulk, and at high frequencies, their inductance can interfere with performance.
Metal Strip (Foil) Resistors
Metal strip or foil resistors deliver the highest accuracy and stability, with tolerances as fine as 0.005%. Their precision makes them the component of choice in measurement instruments and high-end electronics. Their primary downsides are cost and limited power dissipation, which restrict their use in everyday applications.
Thick and Thin Film Resistors
Produced by different deposition techniques, thick and thin film resistors serve specialized roles. Thick film designs are durable and suited to power electronics and automotive systems, while thin film types offer high accuracy and stability in precision or high-frequency circuits.
Surface-Mount Resistors (SMDs)
Surface-mount resistors are compact components soldered directly onto printed circuit boards. They make modern electronics smaller and more efficient, and although tiny, they cover a wide range of resistance values to support everything from consumer devices to industrial controls.
Variable Types of Resistors
Engineers often use practical examples to compare the unit of electrical resistance with how resistors function in series and parallel arrangements.
Potentiometers
Potentiometers are adjustable resistors that allow manual control over current or voltage. They are common in volume dials, tuning controls, and adjustable circuits where user input is required.
Light-Dependent Resistors (LDRs)
LDRs change resistance with varying light levels, making them useful in light sensors, alarms, and automatic lighting systems.
Thermistors
Thermistors alter resistance with temperature. Positive temperature coefficient (PTC) types increase resistance as they heat, protecting circuits from over-current, while negative temperature coefficient (NTC) types reduce resistance with rising temperature, making them useful for sensing and regulation.
When considering the various types of resistors, they may be simple components, but their diversity makes them essential to every circuit. Whether precision, power handling, or responsiveness to environmental changes is needed, there is a resistor designed for the task. Selecting the right one ensures accuracy, stability, and safety in electronic design.
Related Articles





_1497174704.webp)

_1497173102.webp)
